|
Rapid Diagnostic Test
A rapid diagnostic test (RDT) is a medical diagnostic test that is quick and easy to perform. RDTs are suitable for preliminary or emergency medical screening and for use in medical facilities with limited resources. They also allow point-of-care testing in primary care for things that formerly only a laboratory test could measure. They provide same-day results within two hours, typically in approximately 20 minutes. The European Union defines that a rapid test means qualitative or semi-quantitative in vitro-diagnostic medical devices, used singly or in a small series, which involve non-automated procedures and have been designed to give a fast result.2009/886/ECCommission Decision of 27 November 2009 amending Decision 2002/364/EC on common technical specifications for in vitro diagnostic medical devices/ref> Lateral flow tests are probably the most known type of rapid diagnostic tests, similar to pregnancy tests, but there exist other systems as dipsticks, vertical flow, etc. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Plasma Reagin
The rapid plasma reagin test (RPR test or RPR titer) is a type of rapid diagnostic test that looks for non-specific antibodies in the blood of the patient that may indicate an infection by syphilis or related non-venereal treponematoses. It is one of several nontreponemal tests for syphilis (along with the Wassermann test and the VDRL test). The term ''reagin'' means that this test does not look for antibodies against the bacterium itself, ''Treponema pallidum'', but rather for antibodies against substances released by cells when they are damaged by ''T. pallidum'' ( cardiolipin and lecithin). Traditionally, syphilis serologic testing has been performed using a nontreponemal test (NTT) such as the RPR or VDRL test, with positive results then confirmed using a specific treponemal test (TT) such as TPPA or FTA-ABS. This algorithm is currently endorsed by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In addition to screening for syphilis, a titer can be used to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-of-care Testing
Point-of-care testing (POCT or bedside testing) is defined as medical diagnostic testing at or near the point of care—that is, at the time and place of patient care. This contrasts with the historical pattern in which testing was wholly or mostly confined to the medical laboratory, which entailed sending off specimens away from the point of care and then waiting hours or days to learn the results, during which time care must continue without the desired information. Technology Point-of-care tests are simple medical tests that can be performed at the bedside. In many cases, the simplicity was not achievable until technology developed not only to make a test possible at all but then also to mask its complexity. For example, various kinds of urine test strips have been available for decades, but portable ultrasonography did not reach the stage of being advanced, affordable, and widespread until the 2000s and 2010s. Today, portable ultrasonography is often viewed as a "simple" te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Urease Test
Rapid urease test, also known as the CLO test (Campylobacter-like organism test), is a rapid diagnostic test for diagnosis of ''Helicobacter pylori''. The basis of the test is the ability of ''H. pylori'' to secrete the urease enzyme, which catalyzes the conversion of urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide. Process The test is performed at the time of gastroscopy. A biopsy of mucosa is taken from the antrum of the stomach, and is placed into a medium containing urea and an indicator such as phenol red. The urease produced by ''H. pylori'' hydrolyzes urea to ammonia, which raises the pH of the medium, and changes the color of the specimen from yellow (NEGATIVE) to red (POSITIVE). Among different kinds of rapid urease tests (liquid-based, gel-based, dry cool) there is a design type with single-layer sensitive element — a layer impregnated simultaneously with urea and an indicator composition. Such a design bears the risk of false-positive result due to the pH value of the gastric bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Strep Test
The rapid strep test (RST) is a rapid antigen detection test (RADT) that is widely used in clinics to assist in the diagnosis of bacterial pharyngitis caused by group A streptococci (GAS), sometimes termed strep throat. There are currently several types of rapid strep test in use, each employing a distinct technology. However, they all work by detecting the presence of GAS in the throat of a person by responding to GAS-specific antigens on a throat swab. Medical use A rapid strep test may assist a clinician in deciding whether to prescribe an antibiotic to a person with pharyngitis, a common infection of the throat. Viral infections are responsible for the majority of pharyngitis, but a significant proportion (20% to 40% in children and 5% to 15% in adults) is caused by bacterial infection. The symptoms of viral and bacterial infection may be indistinguishable, but only bacterial pharyngitis can be effectively treated by antibiotics. Since the major cause of bacterial pharyngiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria Antigen Detection Tests
Malaria antigen detection tests are a group of commercially available rapid diagnostic tests of the rapid antigen test type that allow quick diagnosis of malaria by people who are not otherwise skilled in traditional laboratory techniques for diagnosing malaria or in situations where such equipment is not available. There are currently over 20 such tests commercially available (WHO product testing 2008). The first malaria antigen suitable as target for such a test was a soluble glycolytic enzyme Glutamate dehydrogenase. None of the rapid tests are currently as sensitive as a thick blood film, nor as cheap. A major drawback in the use of all current dipstick methods is that the result is essentially qualitative. In many endemic areas of tropical Africa, however, the quantitative assessment of parasitaemia is important, as a large percentage of the population will test positive in any qualitative assay. Antigen-based Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests Malaria is a curable disease if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Influenza Diagnostic Test
A rapid influenza diagnostic test (RIDT) tells whether a person has a current influenza infection by detecting the influenza viral nucleoprotein antigen In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons .... Commercially available RIDTs can provide results within 30 minutes. These results can be observed by a color change or other visual signals. For clinicians, RIDTs serve as a first-line test that can be confirmed (especially if negative) by traditional diagnostic tests. RIDTs also allow clinicians to promptly start antiviral treatment in high-risk populations, to formulate effective infection control measures, and to make informed decisions regarding diagnostic investigations. RIDTs have been shown to reduce chest radiography and blood tests in ambulatory care settings, but not antibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
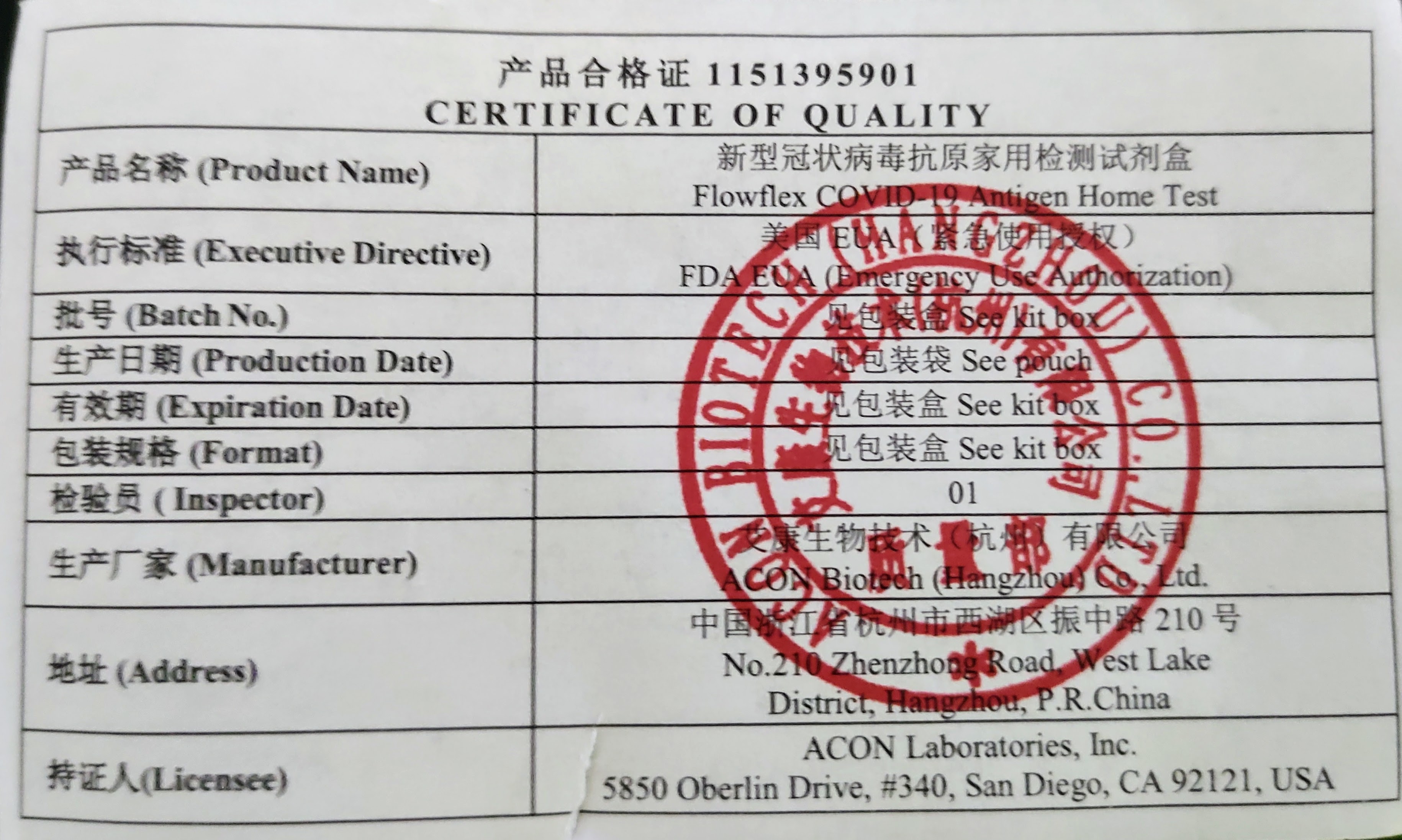
COVID-19 Rapid Antigen Test
COVID-19 rapid antigen tests or RATs, also frequently called COVID-19 lateral flow tests or LFTs, are rapid antigen tests used to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). They are quick to implement with minimal training, cost a fraction of other forms of COVID-19 testing, and give users a result within 5–30 minutes. RATs have been used in several countries as part of mass testing or population-wide screening approaches. Many RATs can be used for self-testing, in which an individual "collects their own specimen… and interpret their test result themselves". False positives are very rare; the tests' specificity is 98%-99%. However, the tests have a sensitivity of 70%-72%, which is lower than COVID-19 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests' sensitivity of 88%-96%. Despite this, COVID-19 RATs remain valuable in finding people who would otherwise not know they were infected, helping to prevent further transmission. The tests are more sensitive in the symptomatic and transmissive s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
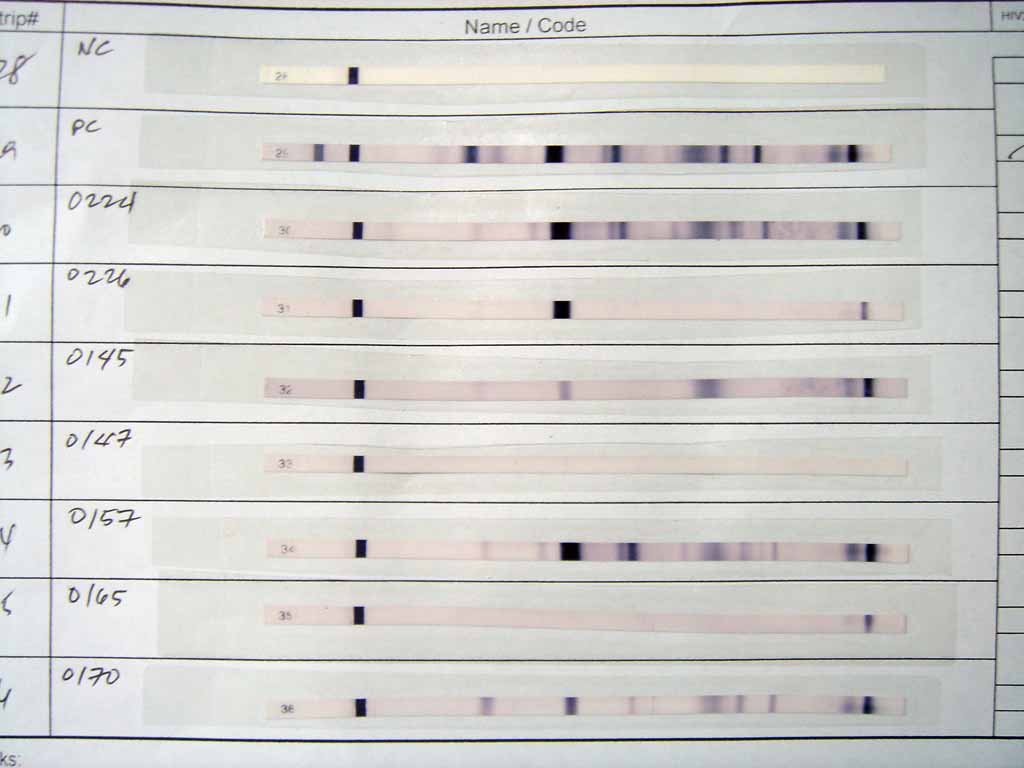
Rapid Antigen Test
A rapid antigen test (RAT), sometimes called a rapid antigen detection test (RADT), antigen rapid test (ART), or loosely just a rapid test, is a rapid diagnostic test suitable for point-of-care testing that directly detects the presence or absence of an antigen. Such tests are a type of lateral flow test that detect antigens, distinguishing them from other medical tests that detect antibodies ( antibody tests) or nucleic acid (nucleic acid tests), of either laboratory or point-of-care types. Rapid tests generally give a result in 5 to 30 minutes, require minimal training or infrastructure, and have significant cost advantages. Rapid antigen tests for the detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, have been commonly used during the COVID-19 pandemic. For many years, an early and major class of RATs—the rapid strep tests for streptococci—were so often the referent when RATs or RADTs were mentioned that the two latter terms were often loosely treated as synonymous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnosis Of HIV/AIDS
HIV tests are used to detect the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), in serum, saliva, or urine. Such tests may detect antibodies, antigens, or RNA. AIDS diagnosis AIDS is diagnosed separately from HIV. Terminology The window period is the time from infection until a test can detect any change. The average window period with HIV-1 antibody tests is 25 days for subtype B. Antigen testing cuts the window period to approximately 16 days and nucleic acid testing (NAT) further reduces this period to 12 days. Performance of medical tests is often described in terms of: * Sensitivity: The percentage of the results that will be positive when HIV is present * Specificity: The percentage of the results that will be negative when HIV is not present. All diagnostic tests have limitations, and sometimes their use may produce erroneous or questionable results. * False positive: The test incorrectly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, the most common of which are diagnosis, screening and evaluation. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood sugar in a person suspected of having diabetes mellitus af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-of-care
Clinical point of care (POC) is the point in time when clinicians deliver healthcare products and services to patients at the time of care. Clinical documentation Clinical documentation is a record of the critical thinking and judgment of a health care professional, facilitating consistency and effective communication among clinicians. Documentation performed at the time of clinical point of care can be conducted using paper or electronic formats. This process aims to capture medical information pertaining to patient's healthcare needs. The patient's health record is a legal document that contains details regarding patient's care and progress. The types of information captured during the clinical point of care documentation include the actions taken by clinical staff including physicians and nurses, and the patient's healthcare needs, goals, diagnosis and the type of care they have received from the healthcare providers. Such documentations provide evidence regarding safe, effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |