|
RAR-related Orphan Receptor
The RAR-related orphan receptors (RORs) are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. There are three forms of ROR, ROR-α, -β, and -γ and each is encoded by a separate gene RORA, RORB, and RORC respectively. The RORs are somewhat unusual in that they appear to bind as monomers to hormone response elements as opposed to the majority of other nuclear receptors which bind as dimers. They bind to DNA elements called ROR response elements (RORE). Ligands While the identity of natural ligands for the RORs remains controversial, similar to the liver X receptors (LXRs), it appears that the RORs are activated by oxysterols. Furthermore, the RORs appear to be constitutively active (absence of ligand) and that activity may be due to continuously bound natural ligands. Side chain oxygenated sterols (e.g., 20α-hydroxycholesterol, 22R-hydroxycholesterol, and 25-hydroxycholesterol) are high affinity RORγ agonists while sterols oxygenated at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAR-related Orphan Receptor Alpha
RAR-related orphan receptor alpha (RORα), also known as NR1F1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group F, member 1) is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''RORA'' gene. RORα participates in the transcriptional regulation of some genes involved in circadian rhythm. In mice, RORα is essential for development of cerebellum through direct regulation of genes expressed in Purkinje cells. It also plays an essential role in the development of type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) and mutant animals are ILC2 deficient. In addition, although present in normal numbers, the ILC3 and Th17 cells from RORα deficient mice are defective for cytokine production. Discovery The first three-human isoforms of RORα were initially Molecular cloning, cloned and characterized as nuclear receptors in 1994 by Giguère and colleagues, when their structure and function were first studied. In the early 2000s, various studies demonstrated that RORα displays rhythmic patterns of expressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-trans Retinoic Acid
Tretinoin, also known as all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For leukemia, it is taken by mouth for up to three months. Topical tretinoin is also the most extensively investigated retinoid therapy for photoaging. Common side effects when used as a cream are limited to the skin and include skin redness, peeling, and sun sensitivity. When used by mouth, side effects include shortness of breath, headache, numbness, depression, skin dryness, itchiness, hair loss, vomiting, muscle pains, and vision changes. Other severe side effects include high white blood cell counts and blood clots. Use during pregnancy is contraindicated due to the risk of birth defects. It is in the retinoid family of medications. Tretinoin was patented in 1957, and approved for medical use in 1962. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
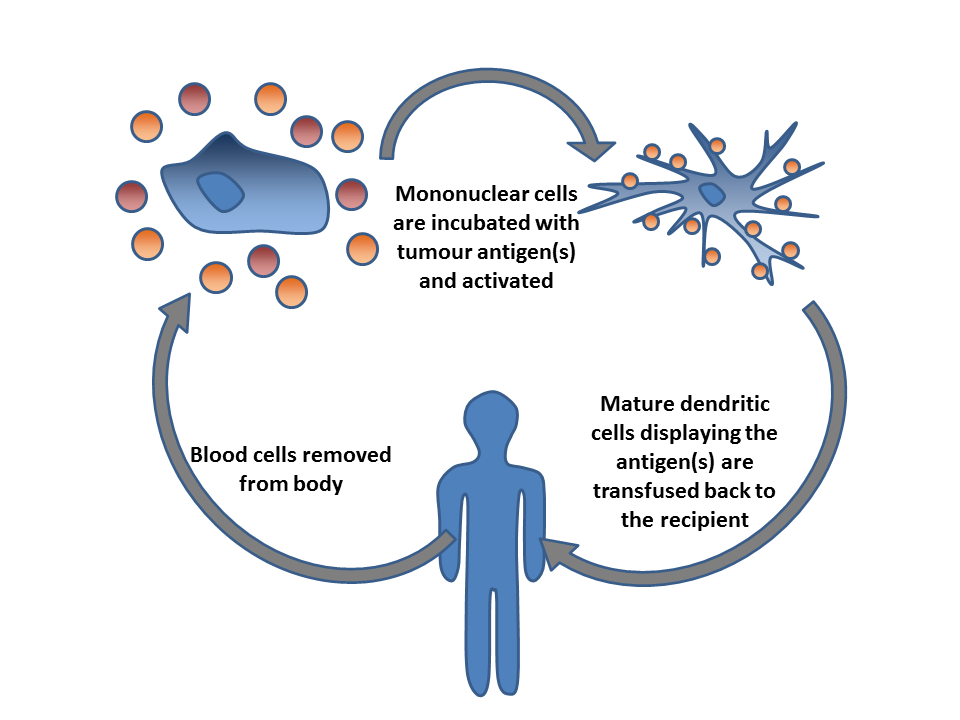
Immunooncology
Cancer immunotherapy (sometimes called immuno-oncology) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology and a growing subspecialty of oncology. Cancer immunotherapy exploits the fact that cancer cells often have tumor antigens, molecules on their surface that can be detected by the antibody proteins of the immune system, binding to them. The tumor antigens are often proteins or other macromolecules (e.g., carbohydrates). Normal antibodies bind to external pathogens, but the modified immunotherapy antibodies bind to the tumor antigens marking and identifying the cancer cells for the immune system to inhibit or kill. Clinical success of cancer immunotherapy is highly variable between different forms of cancer; for instance, certain subtypes of gastric cancer react well to the approach whereas immunotherapy is not effective for oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. In contrast, too much inflammation, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Helper 17 Cell
T helper 17 cells (Th17) are a subset of pro-inflammatory T helper cells defined by their production of interleukin 17 (IL-17). They are related to T regulatory cells and the signals that cause Th17s to differentiate actually inhibit Treg differentiation. However, Th17s are developmentally distinct from Th1 and Th2 lineages. Th17 cells play an important role in maintaining mucosal barriers and contributing to pathogen clearance at mucosal surfaces; such protective and non-pathogenic Th17 cells have been termed as Treg17 cells. They have also been implicated in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. The loss of Th17 cell populations at mucosal surfaces has been linked to chronic inflammation and microbial translocation. These regulatory Th17 cells can be generated by TGF-beta plus IL-6 in vitro. Differentiation Like conventional regulatory T cells (Treg), induction of regulatory Treg17 cells could play an important role in modulating and preventing certain autoimmune disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could cause serious problems to the health of the host organism if not cleared from the body. There are two distinct aspects of the immune response, the innate and the adaptive, which work together to protect against pathogens. The innate branch—the body's first reaction to an invader—is known to be a non-specific and quick response to any sort of pathogen. Components of the innate immune response include physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes, and soluble factors including cytokines and complement. On the other hand, the adaptive branch is the body's immune response which is catered against specific antigens and thus, it takes longer to activate the components invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism is the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells, involving the breakdown or storage of fats for energy and the synthesis of structural and functional lipids, such as those involved in the construction of cell membranes. In animals, these fats are obtained from food or are synthesized by the liver. Lipogenesis is the process of synthesizing these fats. The majority of lipids found in the human body from ingesting food are triglycerides and cholesterol. Other types of lipids found in the body are fatty acids and membrane lipids. Lipid metabolism is often considered as the digestion and absorption process of dietary fat; however, there are two sources of fats that organisms can use to obtain energy: from consumed dietary fats and from stored fat. Vertebrates (including humans) use both sources of fat to produce energy for organs such as the heart to function. Since lipids are hydrophobic molecules, they need to be solubilized before their metabolism can begin. Lipid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomically, the human cerebellum has the appearance of a separate structure attached to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMAL1
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (ARNTL) or brain and muscle ARNT-Like 1 (BMAL1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene on chromosome 11, region p15.3. It's also known as ''BMAL1'', ''MOP3'', and, less commonly, ''bHLHe5'', ''BMAL'', ''BMAL1C'', ''JAP3'', ''PASD3'', and ''TIC''. ''ARNTL'' encodes a transcription factor with a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) and two PAS domains. The human ''ARNTL'' gene has a predicted 24 exons, located on the p15 band of the 11th chromosome. The ARNTL protein is 626 amino acids long and plays a key role as one of the positive elements in the mammalian auto-regulatory transcription-translation negative feedback loop (TTFL), which is responsible for generating molecular circadian rhythms. Research has revealed that ''ARNTL'' is the only clock gene without which the circadian clock fails to function in humans. ''ARNTL'' has also been identified as a candidate gene for susceptibility to hypertension, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to the environment ( entrained by the environment). These 24-hour rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and they have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ''circa'', meaning "approximately", and ''dies'', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous, they are adjusted to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers (German for "time givers"), which include light, temperature and redox cycles. In clinical settings, an abnormal circadian rhythm in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


