|
Rural Municipality Of Lipton No. 217
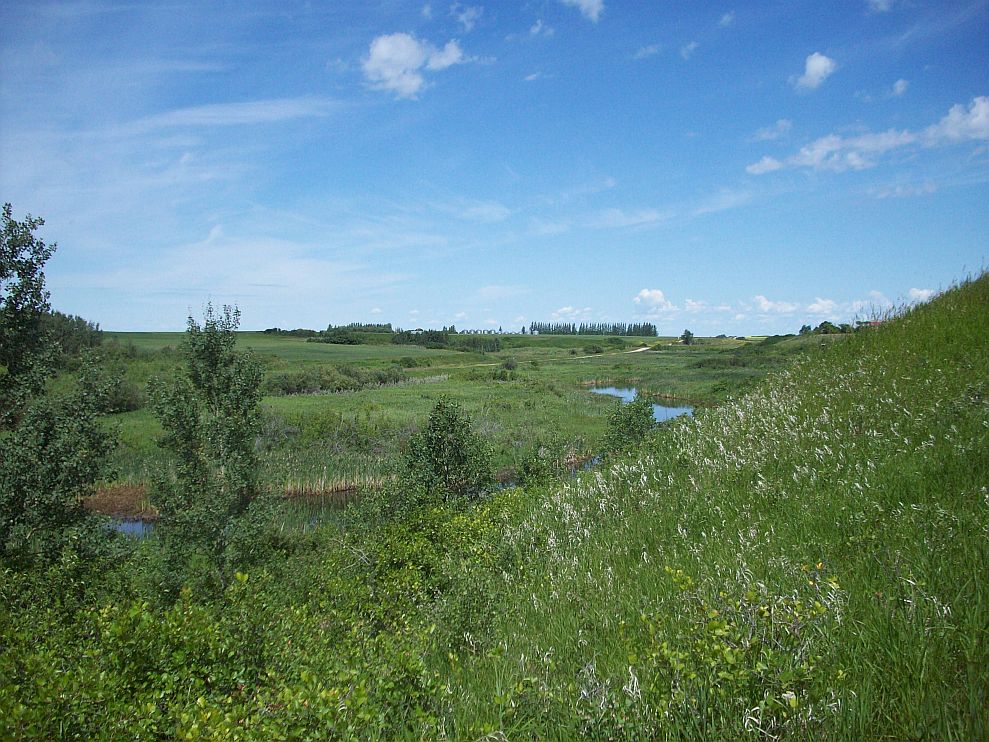
The Rural Municipality of Lipton No. 217 (Canada 2016 Census, 2016 population: ) is a List of rural municipalities in Saskatchewan, rural municipality (RM) in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan within Division No. 6, Saskatchewan, Census Division No. 6 and SARM Division No. 1, Division No. 1. History The RM of Lipton No. 217 incorporated as a rural municipality on December 11, 1911. ;Heritage properties There are three historical sites located within the RM. *''Hayward School'' – Constructed in 1904–1952, the site contains a one-room school house and barns. *''Lipton Jewish Cemetery'' – Established in 1902, the cemetery is the resting place for early Jewish immigrants. *''Tomecko House'' – Constructed in 1917–18, by Mr. Stephen Tomecko, the house served as a gathering place for dances after harvest. Fort Qu'Appelle-Touchwood Hills Trail A section of the Carlton Trail from the Touchwood Hills to the Fishing Lakes in Qu'App ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rural Municipalities In Saskatchewan
A Rural municipality (Canada), rural municipality (RM) is a type of incorporated municipality in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. A rural municipality is created by the Minister of Municipal Relations by ministerial order via section 49 of ''The Municipalities Act''. Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities, which are located in the central and southern portions of the province. They had a cumulative population of and an average population of in the 2016 Canadian Census, 2016 Census of Population. Saskatchewan's largest and smallest rural municipalities are the Rural Municipality of Corman Park No. 344, RM of Corman Park No. 344 and the Rural Municipality of Glen McPherson No. 46, RM of Glen McPherson No. 46 with populations of 8,568 and 72 respectively. The northern half of the province does not lie within any rural municipality, but is rather administered by the provincial government through the Northern Saskatchewan Adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area Codes 306 And 639
Area codes 306, 639, and 474 are telephone area codes in the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) for the entire Canadian province of Saskatchewan. Area code 306 is one of the original North American area codes assigned in 1947. Area codes 639 and 474 were added to the numbering plan area in creation of an overlay complex for the entire province in 2013 and 2021, respectively. The incumbent local exchange carrier is SaskTel. History When the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) created the first nationwide telephone numbering plan in the second half of the 1940s, the United States and Canada were divided into 86 numbering plan areas. Saskatchewan received area code 306 in 1947. By the mid-2000s, area code 306 came under the threat of central office code exhaustion because of demand for telecommunication services from the proliferation of cell phones and other mobile devices requiring unique telephone numbers, particularly in Regina and Saskatoon. In long-term nationw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities In Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is the Population of Canada by province and territory, sixth-most populous Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province with 1,132,505 residents as of Canada 2021 Census, 2021 and is the fifth-largest in land area at . In 2021, Saskatchewan's 774 municipality, municipalities covered of the province's land mass and were home to of its population. These 774 municipalities are local government "creatures of provincial jurisdiction" with natural persons power. One of the key purposes of Saskatchewan's municipalities are "to provide services, facilities and other things that, in the opinion of council, are necessary or desirable for all or a part of the municipality". Other purposes are to: "provide good government"; "develop and maintain a safe and viable community"; "foster economic, social and environmental well-being" and "provide wise stewardship of public assets." The Government of Saskatchewan's Ministry of Municipal Relations recognizes three gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Qu'Appelle
Fort Qu'Appelle () is a town in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan located in the Qu'Appelle River valley north-east of Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina, between Echo Lake (Saskatchewan), Echo and Mission Lakes of the Fishing Lakes. It is not to be confused with the once-significant nearby town of Qu'Appelle, Saskatchewan, Qu'Appelle. It was originally established in 1864 as a Hudson's Bay Company trading post. Fort Qu'Appelle, with its 1,919 residents in 2006, is at the junction of Saskatchewan Highway 35, Highway 35, Saskatchewan Highway 10, Highway 10, Saskatchewan Highway 22, Highway 22, Saskatchewan Highway 56, Highway 56, and Highway 215. The 1897 Hudson's Bay Company store, 1911 Grand Trunk Pacific Railway station, Fort Qu'Appelle Sanatorium (Fort San, Saskatchewan, Fort San), and the Treaty 4 Governance Centre in the shape of a Tipi, teepee are all landmarks of this community. Additionally, the Noel Pinay sculpture of a man praying c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan Highway 35
Highway 35 is a paved, undivided Numbered highways in Canada, provincial highway in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It runs from the Canada–United States border, U.S. border at the Fortuna–Oungre Border Crossing, Port of Oungre (where it meets U.S. Route 85) north to a dead end near the north shore of Tobin Lake. The southern end of Highway 35 is one segment of the CanAm Highway, which is an international highway connecting Canada, the United States, and Mexico. Highway 35 is about long. Highway 35 connects with the following major List of Saskatchewan provincial highways, Saskatchewan highways: Saskatchewan Highway 18, 18, Saskatchewan Highway 39, 39, Saskatchewan Highway 33, 33, Saskatchewan Highway 48, 48, Saskatchewan Highway 1, 1, Saskatchewan Highway 22, 22, Saskatchewan Highway 15, 15, Saskatchewan Highway 16, 16, Saskatchewan Highway 5, 5, Saskatchewan Highway 3, 3, and Saskatchewan Highway 55, 55. Major List of communitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Register Of Historic Places
The Canadian Register of Historic Places (CRHP; , ), also known as Canada's Historic Places, is an online directory of historic places in Canada which have been formally recognized for their heritage value by a federal, provincial, territorial or municipal authority. It is administered by Parks Canada. Background The Canadian Register of Historic Places was created as part of Canada's "Historic Places Initiative". Commencing in 2001, the Historic Places Initiative was a collaboration between the federal, provincial and territorial governments to improve protection of the country's historic sites and to "promote and foster a culture of heritage conservation in Canada". The CRHP and the Standards and Guidelines for the Conservation of Historic Places in Canada (a common set of guidelines for the restoration and rehabilitation of historic sites throughout Canada) are the two major tools developed to assist in achieving the initiative's main objectives. The CRHP was official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North-West Rebellion
The North-West Rebellion (), was an armed rebellion of Métis under Louis Riel and an associated uprising of Cree and Assiniboine mostly in the District of Saskatchewan, against the Government of Canada, Canadian government. Important events included the Frog Lake Massacre, Frog Lake incident, and the Battle of Batoche, capture of Batoche. The North-West Rebellion began in March 1885 after Louis Riel returned from political exile in the U.S. With the assistance of Métis leader Gabriel Dumont (Métis leader), Gabriel Dumont, Riel declared a Provisional Government of Saskatchewan, provisional government on March 18, and rebel territory was carved out. As government forces responded, fighting broke out, with the last shooting over by the end of June. Rebel forces included roughly 250 Métis and 250 Indigenous Peoples of North America, First Nations men, largely Cree and Assiniboine, who were led by Big Bear and Poundmaker and other First Nations chiefs. A non-Indigenous man, Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batoche, Saskatchewan
Batoche, which lies between Prince Albert and Saskatoon in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan, was the site of the historic Battle of Batoche during the North-West Rebellion of 1885. The battle resulted in the defeat of Louis Riel and his Métis forces by Major General Frederick Middleton and his Northwest Field Force. Batoche was then a small village of some 500 residents. The site has since become depopulated and now has few residents. The 1885 church building and a few other historic buildings have been preserved, and the site is a National Historic Site. History The Métis settlement of Batoche (named after Xavier Letendre ''dit'' Batoche) was established in 1872. By 1885 it numbered 500 people. The Métis of the area settled on river lots, and the community contained several stores as well as the Roman Catholic Church of St. Antoine de Padoue at the time of the Rebellion. Batoche was the de facto capital of Riel's Provisional Government of Saskatchewan. Batoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Dobson Middleton
Sir Frederick Dobson Middleton (4 November 1825 – 25 January 1898) was a British general noted for his service throughout the Empire and particularly in the North-West Rebellion in Canada. Imperial military career Middleton was born in London, the third son of Major General Charles Middleton and Fanny Wheatley. Educated at Maidstone Grammar School and the Royal Military College, Sandhurst, Middleton was commissioned into the 58th Regiment of Foot in 1842. He served in the New Zealand Wars, and in 1845 he was mentioned in dispatches for his part in the capture of the stronghold of Māori chief Te Ruki Kawiti. In 1848 he transferred to the 96th Regiment of Foot in India and took part in the suppression of the Indian Mutiny in which campaign he was recommended for, but not awarded, the Victoria Cross. He went on to be Commandant of the Royal Military College, Sandhurst, in 1879. Canadian military career He was appointed General Officer Commanding the Militia of Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qu'Appelle River
The Qu'Appelle River is a river in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba that flows east from Lake Diefenbaker in south-western Saskatchewan to join the Assiniboine River in Manitoba, just south of Shellmouth Reservoir, Lake of the Prairies, near the village of St. Lazare, Manitoba, St. Lazare. It is in a region called the Prairie Pothole Region of North America, which extends throughout three Canadian provinces and five U.S. states. It is also within Palliser's Triangle and the Great Plains ecoregion. With the construction of the Qu'Appelle River Dam and the Gardiner Dam upstream, water flow was significantly increased and regulated. Most of the Qu'Appelle's present flow is actually water diverted from the South Saskatchewan River. Upper and lower watersheds According to the Saskatchewan Water Security Agency, the Qu'Appelle Valley is made up of two watersheds with the dividing point being Craven Dam on the east side of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing Lakes
The Fishing Lakes, also called the Calling Lakes or the Qu'Appelle Lakes, are a chain of four lakes in the Qu'Appelle Valley cottage country about to the north-east of Regina in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The lakes are in a region called the Prairie Pothole Region of North America, which extends throughout three Canadian provinces and five U.S. states. It is also within Palliser's Triangle and the Great Plains ecoregion. The Fishing Lakes all follow the course of the Qu'Appelle River, which flows from the west to the east and is part of the Hudson Bay drainage basin. The lakes sit in the deep-cut Qu'Appelle Valley that was formed about 14,000 years ago during the last ice age. Meltwater from the glaciers carved out the valley and as water levels rose and fell, alluvium was left in the wake. These piles of alluvium are what created the separations between the lakes. The name ''Qu'Appelle'' is French for "Who's calling?" The name comes from First Nations people hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchwood Hills
Touchwood Hills are a range of hills in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The hills are composed of the "Big" Touchwood Hills and the Little Touchwood Hills. Together they are referred to as the Touchwood Uplands. The hills are in the Prairie Pothole Region of North America, which extends throughout three Canadian provinces and five U.S. states, and within Palliser's Triangle and the Great Plains ecoregion of Canada. The hills make up a large plateau that is north-east of Saskatchewan's capital city, Regina. To the west of the hills is Last Mountain Lake; to the north are the Quill Lakes, Foam Lake, and Fishing Lake; to the east is Good Spirit Lake; and to the south is the Qu'Appelle Valley. Several rivers flow out of the hills, such as the south flowing Qu'Appelle River tributaries of East Loon Creek (via Loon Creek), Jumping Deer Creek, Pheasant Creek, and Pearl Creek. To the north, rivers such as Dafoe Brook, Birch Creek, Bevcar Brook, Beckett Brook, and Milliga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |