|
Roth Spots
Roth's spots, also known as Litten spots or the Litten sign, are non-specific red lesions with white or pale centres, seen on the retina of the eye and although traditionally associated with infective endocarditis, can occur in a number of other conditions including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, collagen vascular disease, extreme hypoxia, leukemia and HIV. Red and white retinal spots were first observed in 1872 by Swiss physician Moritz Roth, and named "Roth spots" six years later by Moritz Litten. They are typically observed via fundoscopy (using an ophthalmoscope to view inside the eye) or slit lamp exam. The original retinal spots identified in 1872 were attributed to nerve-fibres that had burst. Present-day analysis shows that they can be composed of coagulated fibrin including platelets, focal ischaemia, inflammatory infiltrate, infectious organisms, or neoplastic cells. Cause Roth's spots occur in conditions that predispose to endothelial damage of retinal capillarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. In the United States, following graduation from medical school, one must complete a four-year residency in ophthalmology to become an ophthalmologist. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat ailments, such as eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care—medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelets
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activation''. Third, they connect to each other throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
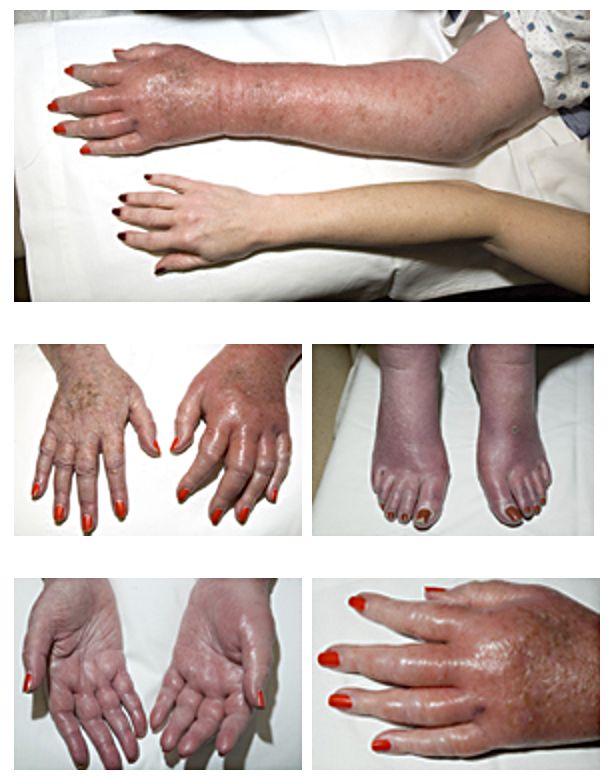
Vascular Disease
Vascular disease is a class of diseases of the vessels of the circulatory system in the human body, body, including blood vessels – the arteries and veins, and the lymphatic vessels. Vascular disease is a subgroup of cardiovascular disease. Disorders in this vast network of blood and lymph vessels can cause a range of health problems that can sometimes become severe, and fatal. Coronary heart disease for example, is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States. Types There are several types of vascular disease, including venous diseases, and arterial diseases, and signs and symptoms vary depending on the disease. Those of the arterial system are associated with blood supply to tissues and its obstruction due to blockages or narrowing. In the venous system disorders are often caused by a slow return of blood due to insufficient valves, or to a thrombus, blood clot. Venous disease Most disorders of the veins involve obstruction such as a thrombus or insuffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candida Albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus '' Candida'' that cause the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. ''C. albicans'' is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. ''C. albicans'', ''C. tropicalis'', ''C. parapsilosis'', and ''C. glabrata'' are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to ''C. albicans''. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abusive Head Trauma
Shaken baby syndrome (SBS), also known as abusive head trauma (AHT), is a controversial and scientifically disputed medical condition in children younger than five years old, hypothesized to be caused by blunt trauma, vigorous shaking, or a combination of both. According to literature, the condition is caused by violent shaking with or without blunt impact that can lead to long-term health consequences for infants or children. Diagnosis can be difficult, but is generally characterized by the "triad" of findings: retinal hemorrhage, encephalopathy, and subdural hematoma. A CT scan of the head is typically recommended if a concern is present. If there are concerning findings on the CT scan, a full work-up for child abuse often occurs, including an eye exam and skeletal survey. Retinal hemorrhage is highly associated with AHT, occurring in 78% of cases of AHT versus 5% of cases of non-abusive head trauma, although such findings rely on contested methodology. A 2023 review conclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, the average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the Subtypes of HIV, HIV subtype. In most cases, HIV is a sexually transmitted infection and HIV/AIDS#Transmission, occurs by contact with or transfer of blood, pre-ejaculate, semen, and Vaginal lubrication, vaginal fluids. Non-sexual transmission can occur from an infected mother to her infant during pregnancy, during childbirth by exposure to her blood or vaginal fluid, and through breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected White blood cell, immune cells. Research has s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a multi-system disorder specific to pregnancy, characterized by the new onset of hypertension, high blood pressure and often a significant amount of proteinuria, protein in the urine or by the new onset of high blood pressure along with significant end-organ damage, with or without the proteinuria. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 Gestational age (obstetrics), weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease there may be hemolysis, red blood cell breakdown, a thrombocytopenia, low blood platelet count, impaired liver function, kidney dysfunction, edema, swelling, pulmonary edema, shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs, or visual disturbances. Pre-eclampsia increases the risk of undesirable as well as lethal outcomes for both the mother and the fetus including preterm labor. If left untreated, it may result in seizures at which point it is known as eclampsia. Risk factors for pre-eclampsia include obesity, prior hypertension, older age, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy (also known as diabetic eye disease) is a medical condition in which damage occurs to the retina due to diabetes. It is a leading cause of blindness in developed countries and one of the lead causes of sight loss in the world, even though there are many new therapies and improved treatments for helping people live with diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy affects up to 80 percent of those who have had both Type 1 diabetes, type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, type 2 diabetes for 20 years or more. In at least 90% of new cases, progression to more aggressive forms of sight threatening retinopathy and maculopathy could be reduced with proper treatment and monitoring of the eyes. The longer a person has diabetes, the higher their chances of developing diabetic retinopathy. Each year in the United States, diabetic retinopathy accounts for 12% of all new cases of blindness. It is also the leading cause of blindness in people aged 20 to 64. Signs and symptoms Nearly all peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertensive Retinopathy
Hypertensive retinopathy is damage to the retina and retinal circulation due to high blood pressure (i.e. hypertension). Signs and symptoms Most patients with hypertensive retinopathy have no symptoms. However, some may report decreased or blurred vision, and headaches. Signs Signs of damage to the retina caused by hypertension include: * Arteriolar changes, such as generalized arteriolar narrowing, focal arteriolar narrowing, arteriovenous nicking, changes in the arteriolar wall (arteriosclerosis) and abnormalities at points where arterioles and venules cross. Manifestations of these changes include ''Copper wire arterioles'' where the central light reflex occupies most of the width of the arteriole and ''Silver wire arterioles'' where the central light reflex occupies all of the width of the arteriole, and "arterio-venular (AV) nicking" or "AV nipping", due to venous constriction and banking. * Advanced retinopathy lesions, such as microaneurysms, blot hemorrhages and/or flam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia—acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myelo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen Vascular Disease
Connective tissue diseases (also termed connective tissue disorders, or collagen vascular diseases), are medical conditions that affect connective tissue. Connective tissues protect, support, and provide structure for the body's other tissues and structures. They hold the body's structures together. Connective tissues consist of two distinct proteins: elastin and collagen. Tendons, ligaments, skin, cartilage, bone, and blood vessels are all made of collagen. Skin and ligaments also contain elastin. These proteins and the surrounding tissues may suffer damage when the connective tissues become inflamed. The two main categories of connective tissue diseases are (1) a set of relatively rare genetic disorders affecting the primary structure of connective tissue, and (2) a variety of acquired diseases where the connective tissues are the site of multiple, more or less distinct immunological and inflammatory reactions. Diseases in which inflammation or weakness of collagen tends to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care units, intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μL) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μL. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood – thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually asymptomatic, has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |