|
Rostral Interstitial Nucleus Of Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
The rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF) is a collection of neurons in the medial longitudinal fasciculus in the midbrain. It is responsible for mediating vertical conjugate eye movements (vertical gaze (physiology), gaze) and vertical saccades. It mostly projects efferents to the ipsilateral oculomotor and trochlear nuclei. To mediate downgaze, it projects efferents to the ipsilateral oculomotor nucleus and trochlear nucleus; mediate upgaze, it projects efferents to the contralateral aforementioned nuclei through the posterior commissure. It is one of the accessory oculomotor nuclei. Anatomy Structure The riMLF is a wing-shaped nucleus. The riMLF contains two populations of neurons: excitatory burst neurons mediating vertical gaze/saccades, as well as omnipause neurons which are functionally similar to those mediating horizontal gaze. Relations It is situated at the caudal extremity of the mesencephalon at its junction with the telenceph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a prominent bundle of nerve fibres which pass within the ventral/anterior portion of periaqueductal gray of the mesencephalon (midbrain). It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement. The MLF interconnects interneurons of each abducens nucleus with motor neurons of the contralateral oculomotor nucleus; thus, the MLF mediates coordination of horizontal (side to side) eye movements, ensuring the two eyes move in unison (thus also enabling saccadic eye movements). The MLF also contains fibers projecting from the vestibular nuclei to the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei as well as the interstitial nucleus of Cajal; these connections ensure that eye movements are coordinated with head movements (as sensed by the vestibular system). The medial longitudinal fasciculus is the main central connection for the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, and abduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstitial Nucleus Of Cajal
The interstitial nucleus of Cajal is a collection of neurons in the mesencephalon (midbrain) which are involved in integrating eye position-velocity information in order to coordinate head-eye movements - especially those related to vertical and torsional conjugate eye movements (gaze). It also mediates vertical gaze holding. Bilateral projections to the oculomotor (cranial nerve III) and trochlear (cranial nerve IV) nuclei represent its principal outputs. It forms reciprocal connections with vestibular nuclei. It also has additional afferents and efferents. Some of the nucleus' connections pass through the medial longitudinal fasciculus, and the posterior commissure. It is one of the accessory oculomotor nuclei. Anatomy The interstitial nucleus of Cajal is a diffuse collection of mid-sized, parvalbumin-containing premotor neurons of the midbrain reticular formation. Connections The nucleus forms reciprocal connections with the vestibular nuclei (through the MLF). It f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
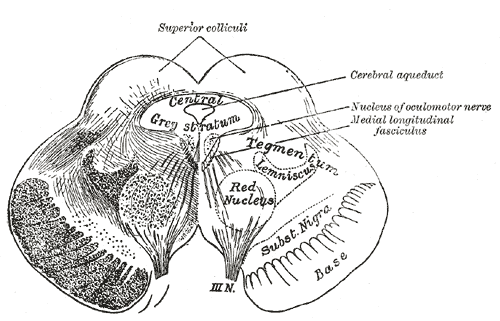
Red Nucleus
The red nucleus or nucleus ruber is a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination. The red nucleus is pale pink, which is believed to be due to the presence of iron in at least two different forms: hemoglobin and ferritin. The structure is located in the midbrain tegmentum next to the substantia nigra and comprises caudal magnocellular and rostral parvocellular components. The red nucleus and substantia nigra are subcortical centers of the extrapyramidal motor system. Function In a vertebrate without a significant corticospinal tract, gait is mainly controlled by the red nucleus. However, in primates, where the corticospinal tract is dominant, the rubrospinal tract may be regarded as vestigial in motor function. Therefore, the red nucleus is less important in primates than in many other mammals. Nevertheless, the crawling of babies is controlled by the red nucleus, as is arm swinging in typical walking. The red nucleus may play an additional role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
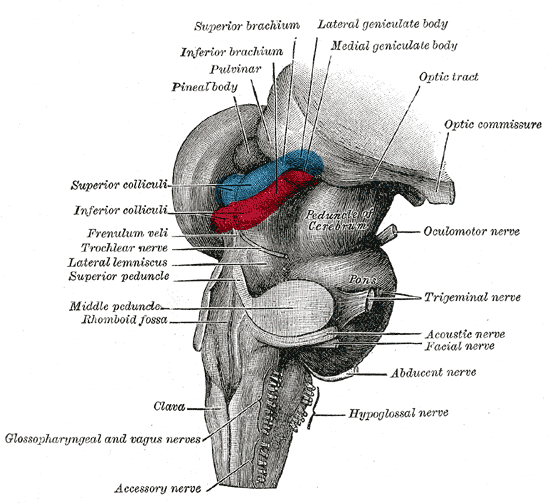
Superior Colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the tectum, roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the Homology (biology), homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectum, tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar in all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers (retinal nerve fiber layer, stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telencephalon
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal, it lies either in front or on top of the brainstem. In humans, the cerebrum is the largest and best-developed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostral and caudal, Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while Rostral and caudal, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Oculomotor Nuclei
The accessory oculomotor nuclei are a group of nuclei situated in the rostral mesencephalon (midbrain) near its junction with the diencephalon, and consist of: * Interstitial nucleus of Cajal * Rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus * Nucleus of Darkschewitsch * Nucleus of the posterior commissure These nuclei are involved in vertical and rotatory gaze (physiology), and smooth pursuit. They receive afferents from the visual association area; they project efferents through the medial longitudinal fasciculus The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a prominent bundle of nerve fibres which pass within the ventral/anterior portion of periaqueductal gray of the mesencephalon (midbrain). It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible ... to the nuclei of cranial nerves controlling extrinsic eye muscles. References {{Reflist Brainstem nuclei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostral and caudal, Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while Rostral and caudal, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Commissure
The posterior commissure (also known as the epithalamic commissure) is a rounded band of white fibers crossing the middle line on the dorsal aspect of the rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct. It is important in the bilateral pupillary light reflex. It constitutes part of the epithalamus. Its fibers acquire their medullary sheaths early, but their connections have not been definitively determined. Most of them have their origin in a nucleus, the ''nucleus of the posterior commissure'' (nucleus of Darkschewitsch), which lies in the periaqueductal grey at rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct, in front of the oculomotor nucleus. Some are thought to be derived from the posterior part of the thalamus and from the superior colliculus, whereas others are believed to be continued downward into the medial longitudinal fasciculus The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a prominent bundle of nerve fibres which pass within the ventral/anterior portion of periaqueductal gray of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochlear Nucleus
The trochlear nucleus () is the motor nucleus of the trochlear nerve ( cranial nerve IV). It is located in the medial midbrain. Structure The trochlear nucleus is located in the midbrain, at an intercollicular level between the superior colliculus and inferior colliculus. As with all motor nuclei of cranial nerves, it is located near the midline (i.e. in the medial midbrain). It is embedded within the medial longitudinal fasciculus. It is situated immediately below the nucleus of the oculomotor nerve (CN III) (the only other cranial nerve with a nucleus in the midbrain besides the mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve, which functions in preserving dentition). The trochlear nucleus is unique in that its axons run dorsally and cross the midline at the trochlear decussation (located in the superior medullary velum) in the midbrain before emerging from the brainstem posteriorly/dorsally. In other words, trochlear nucleus on one side gives rise to the trochlear nerve on the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |