|
Rams (other)
In engineering, reliability, availability, maintainability and safety (RAMS) Norwegian University of Science and Technology is used to characterize a product or system: * : Ability to perform a specific function and may be given as design reliability or operational reliability * : Ability to keep a functioning state in the given environment * : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, Materials engineering, materials, and energy systems. The Academic discipline, discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more Academic specialization, specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis for applications of applied mathematics, mathematics and applied science, science. See glossary of engineering. The word '':wikt:engineering, engineering'' is derived from the Latin . Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (the predecessor of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology aka ABET) has defined "engineering" as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure Mode, Effects, And Criticality Analysis
Failure mode effects and criticality analysis (FMECA) is an extension of failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA). FMEA is a bottom-up, inductive analytical method which may be performed at either the functional or piece-part level. FMECA extends FMEA by including a ''criticality analysis'', which is used to chart the probability of failure modes against the severity of their consequences. The result highlights failure modes with relatively high probability and severity of consequences, allowing remedial effort to be directed where it will produce the greatest value. FMECA tends to be preferred over FMEA in space and NATO military applications, while various forms of FMEA predominate in other industries. History FMECA was originally developed in the 1940s by the U.S military, which published MIL–P–1629 in 1949. By the early 1960s, contractors for the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) were using variations of FMECA under a variety of names. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability, Availability And Serviceability
Reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS), also known as reliability, availability, and maintainability (RAM), is a computer hardware engineering term involving reliability engineering, high availability, and serviceability design. The phrase was originally used by IBM as a term to describe the robustness of their mainframe computers. Computers designed with higher levels of RAS have many features that protect data integrity and help them stay available for long periods of time without failure. This data integrity and uptime is a particular selling point for mainframes and fault-tolerant systems. Definitions While RAS originated as a hardware-oriented term, systems thinking has extended the concept of reliability-availability-serviceability to systems in general, including software: * ''Reliability'' can be defined as the probability that a system will produce correct outputs up to some given time ''t''. Reliability is enhanced by features that help to avoid, detec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Instrumented System
In functional safety a safety instrumented system (SIS) is an engineered set of hardware and software controls which provides a protection layer that shuts down a chemical, nuclear, electrical, or mechanical system, or part of it, if a hazardous condition is detected. Requirement specification An SIS performs a safety instrumented function (SIF). The SIS is credited with a certain measure of reliability depending on its safety integrity level (SIL). The required SIL is determined from a quantitative process hazard analysis (PHA), such as a Layers of Protection Analysis (LOPA). The SIL requirements are verified during the design, construction, installation, and operation of the SIS. The required functionality may be verified by design reviews, factory acceptance testing, site acceptance testing, and regular functional testing. The PHA is in turn based on a hazard identification exercise. In the process industries (oil and gas production, refineries, chemical plants, etc.), this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability-centered Maintenance
Reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) is a concept of maintenance planning to ensure that systems continue to do what their users require in their present operating context. Successful implementation of RCM will lead to increase in cost effectiveness, reliability, machine uptime, and a greater understanding of the level of risk that the organization is managing. Context It is generally used to achieve improvements in fields such as the establishment of safe minimum levels of maintenance, changes to operating procedures and strategies and the establishment of capital maintenance regimes and plans. Successful implementation of RCM will lead to increase in cost effectiveness, machine uptime, and a greater understanding of the level of risk that the organization is managing. John Moubray characterized RCM as a process to establish the safe minimum levels of maintenance. This description echoed statements in the Nowlan and Heap report from United Airlines. It is defined by the tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
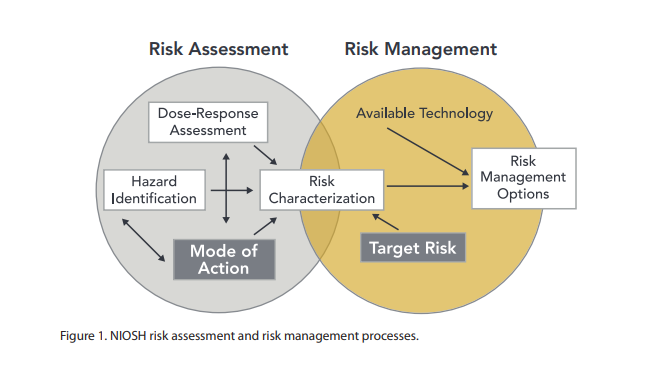
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a process for identifying hazards, potential (future) events which may negatively impact on individuals, assets, and/or the environment because of those hazards, their likelihood and consequences, and actions which can mitigate these effects. The output from such a process may also be called a risk assessment. Hazard analysis forms the first stage of a risk assessment process. Judgments "on the tolerability of the risk on the basis of a risk analysis" (i.e. risk evaluation) also form part of the process. The results of a risk assessment process may be expressed in a quantitative or qualitative fashion. Risk assessment forms a key part of a broader risk management strategy to help reduce any potential risk-related consequences. Categories Individual risk assessment Risk assessments can be undertaken in individual cases, including in patient and physician interactions. In the narrow sense chemical risk assessment is the assessment of a health risk in response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Availability
High availability (HA) is a characteristic of a system that aims to ensure an agreed level of operational performance, usually uptime, for a higher than normal period. There is now more dependence on these systems as a result of modernization. For example, to carry out their regular daily tasks, hospitals and data centers need their systems to be highly available. Availability refers to the ability of the user to access a service or system, whether to submit new work, update or modify existing work, or retrieve the results of previous work. If a user cannot access the system, it is considered ''unavailable from the user's perspective''. The term '' downtime'' is generally used to refer to describe periods when a system is unavailable. Resilience High availability is a property of network resilience, the ability to "provide and maintain an acceptable level of service in the face of faults and challenges to normal operation." Threats and challenges for services can range from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazard Analysis And Critical Control Points
Hazard analysis and critical control points, or HACCP (), is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological hazard, biological, chemical hazard, chemical, and physical hazards in production processes that can cause the finished product to be unsafe and designs measures to reduce these risks to a safe level. In this manner, HACCP attempts to avoid hazards rather than attempting to inspect finished products for the effects of those hazards. The HACCP system can be used at all stages of a food chain, from food processing, food production and preparation processes including packaging, distribution, etc. The United States Food and Drug Administration, Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) require mandatory HACCP programs for juice and meat as an effective approach to food safety and protecting public health. Meat HACCP systems are regulated by the USDA, while seafood and juice are regulated by the FDA. All other food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure Rate
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. One person might consider a failure what another person considers a success, particularly in cases of direct competition or a zero-sum game. Similarly, the degree of success or failure in a situation may be differently viewed by distinct observers or participants, such that a situation that one considers to be a failure, another might consider to be a success, a qualified success or a neutral situation. It may also be difficult or impossible to ascertain whether a situation meets criteria for failure or success due to ambiguous or ill-defined definition of those criteria. Finding useful and effective criteria or heuristics to judge the success or failure of a situation may itself be a significant task. Sociology Cultural historian Sco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability is defined as the probability that a product, system, or service will perform its intended function adequately for a specified period of time, OR will operate in a defined environment without failure. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The ''reliability function'' is theoretically defined as the probability of success. In practice, it is calculated using different techniques, and its value ranges between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates no probability of success while 1 indicates definite success. This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets, or through reliability testing and reliability modeling. Availability, testability, maintainability, and maintenance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure Mode
Failure causes are defects in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying cause of a failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Where failure depends on the user of the product or process, then human error must be considered. Component failure/failure modes A part failure mode is the way in which a component failed "functionally" on the component level. Often a part has only a few failure modes. For example, a relay may fail to open or close contacts on demand. The failure mechanism that caused this can be of many different kinds, and often multiple factors play a role at the same time. They include corrosion, welding of contacts due to an abnormal electric current, return spring fatigue failure, unintended command failure, dust accumulation and blockage of mechanism, etc. Seldom only one cause (hazard) can be identified that creates system failures. The real root causes can in theory in most cases be traced back to some kind of human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |