|
Radiation Hormesis
Radiation hormesis is the hypothesis that low doses of ionizing radiation (within the region of and just above natural background levels) are beneficial, stimulating the activation of repair mechanisms that protect against disease, that are not activated in absence of ionizing radiation. The reserve repair mechanisms are hypothesized to be sufficiently effective when stimulated as to not only cancel the detrimental effects of ionizing radiation but also inhibit disease not related to radiation exposure (see hormesis). It has been advertised by the British physicist Wade Allison in a book published in 2009. While the effects of high and acute doses of ionising radiation are easily observed and understood in humans (''e.g.'' Japanese atomic bomb survivors), the effects of low-level radiation are very difficult to observe and highly controversial. This is because the baseline cancer rate is already very high and the risk of developing cancer fluctuates 40% because of individual l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiations At Low Doses
An evolutionary radiation is an increase in taxonomic diversity that is caused by elevated rates of speciation, that may or may not be associated with an increase in morphological disparity. A significantly large and diverse radiation within a relatively short geologic time scale (e.g. a period or epoch) is often referred to as an explosion. Radiations may affect one clade or many, and be rapid or gradual; where they are rapid, and driven by a single lineage's adaptation to their environment, they are termed adaptive radiations. Examples Perhaps the most familiar example of an evolutionary radiation is that of placental mammals immediately after the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs at the end of the Cretaceous, about 66 million years ago. At that time, the placental mammals were mostly small, insect-eating animals similar in size and shape to modern shrews. By the Eocene (58–37 million years ago), they had evolved into such diverse forms as bats, whales, and horses. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Council On Radiation Protection And Measurements
The National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP), formerly the National Committee on Radiation Protection and Measurements, and before that the Advisory Committee on X-Ray and Radium Protection (ACXRP), is a U.S. organization. It has a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code, but this does not imply any sort of oversight by Congress; NCRP is not a government entity. History The Advisory Committee on X-Ray and Radium Protection was established in 1929. Initially, the organization was an informal collective of scientists seeking to proffer accurate information and appropriate recommendations for radiation protection. In 1946, the organization changed its name to the National Committee on Radiation Protection and Measurements. In 1964, the U.S. Congress The United States Congress is the legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a bicameral legislature, including a lower body, the U.S. House of Repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells can cause toxic effects through the production of peroxides and free radicals that damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. Oxidative stress from oxidative metabolism causes base damage, as well as strand breaks in DNA. Base damage is mostly indirect and caused by the reactive oxygen species generated, e.g., (superoxide radical), OH ( hydroxyl radical) and (hydrogen peroxide). Further, some reactive oxidative species act as cellular messengers in redox signaling. Thus, oxidative stress can cause disruptions in normal mechanisms of cellular signaling. In humans, oxidative stress is thought to be involved in the development of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, cancer, Parkin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl radical (OH.), and singlet oxygen(1O2). ROS are pervasive because they are readily produced from O2, which is abundant. ROS are important in many ways, both beneficial and otherwise. ROS function as signals, that turn on and off biological functions. They are intermediates in the redox behavior of O2, which is central to fuel cells. ROS are central to the photodegradation of organic pollutants in the atmosphere. Most often however, ROS are discussed in a biological context, ranging from their effects on aging and their role in causing dangerous genetic mutations. Inventory of ROS ROS are not uniformly defined. All sources include superoxide, singlet oxygen, and hydroxyl radical. Hydrogen peroxide is not nearly as reactive as these species, but is readily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenic
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and Biological agent, biologic agents such as viruses and carcinogenic bacteria, bacteria. Most carcinogens act by creating mutations in DNA that disrupt a cell's normal processes for regulating growth, leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation. This occurs when the cell's DNA repair processes fail to identify DNA damage allowing the defect to be passed down to daughter cells. The damage accumulates over time. This is typically a multi-step process during which the regulatory mechanisms within the cell are gradually dismantled allowing for unchecked Cell division, cellular division. The specific mechanisms for carcinogenic activity is unique to each agent and cell type. Carcinogens can be broadly categorized, however, as activation-dependent and activation-independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Académie Nationale De Médecine
Situated at 16 Rue Bonaparte in the 6th arrondissement of Paris, the Académie nationale de médecine (National Academy of Medicine) was created in 1820 by King Louis XVIII at the urging of baron Antoine Portal. At its inception, the institution was known as the Académie royale de médecine (or ''Royal Academy of Medicine''). This academy was endowed with the legal status of two institutions which preceded it—the Académie royale de chirurgie (or ''Royal Academy of Surgery''), which was created in 1731 and of the Société royale de médecine (or ''Royal Society of Medicine''), which was created in 1776. Background Academy members initially convened at the ''Paris Faculty of Medicine (or Faculté de Médecine de Paris)''. Four years later, the academy acquired its own headquarters, in the form of a mansion in the rue where it was located until 1850. The office was then relocated to a vaulted hall of the Hospital of Charity on rue Saint Pierre. Their current facility o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Response
The adaptive response is a DNA damage response pathway prevalent across bacteria that protects DNA from damage by external agents or by errors during replication.Landini, P, Volkert MR. (2000Regulatory Responses of the Adaptive Response to Alkylation Damage: a Simple Regulon with Complex Regulatory Features''J. Bacteriol.'' 182(23): 6543–6549. It is initiated specifically against alkylation, particularly methylation, of guanine or thymine nucleotides or phosphate groups on the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA. Under sustained exposure to low-level treatment with alkylating mutagens, bacteria can adapt to the presence of the mutagen, rendering subsequent treatment with high doses of the same agent less effective.Volkert MR. (1988)Adaptive response of ''Escherichia coli'' to alkylation damage.''Environ Mol Mutagen'' 11(2):241-55. Function Environmental influence plays a crucial role in the developmental plasticity of genotypes due to the introduction of DNA damaging agents. This p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
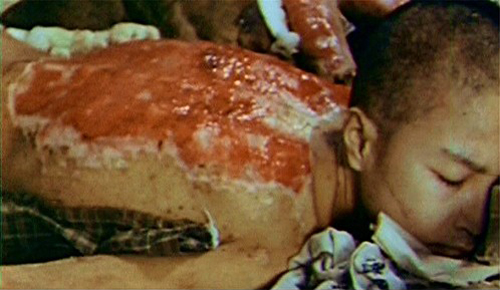
Hibakusha
' ( or ; or ; or ) is a word of Japanese origin generally designating the people affected by the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki by the United States at the end of World War II. Definition The word is Japanese, originally written in kanji. While the term ( + + ) has been used before in Japanese to designate any victim of bombs, its worldwide democratization led to a definition concerning the survivors of the atomic bombs dropped in Japan by the United States Army Air Forces on 6 and 9 August 1945. Anti-nuclear movements and associations, among others of ', spread the term to designate any direct victim of nuclear disaster, including the ones of the nuclear plant in Fukushima. They, therefore, prefer the writing (replacing with the homophonous ) or . This definition tends to be adopted since 2011. The legal status of is allocated to certain people, mainly by the Japanese government. Official recognition The Atomic Bomb Survivors Relief Law defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent diseases. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying Risk factor (epidemiology), risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission (medicine), transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'' is the peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' cover the full range of List of academ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |