|
Pluripotent
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c- Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totipotency
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totipotency
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
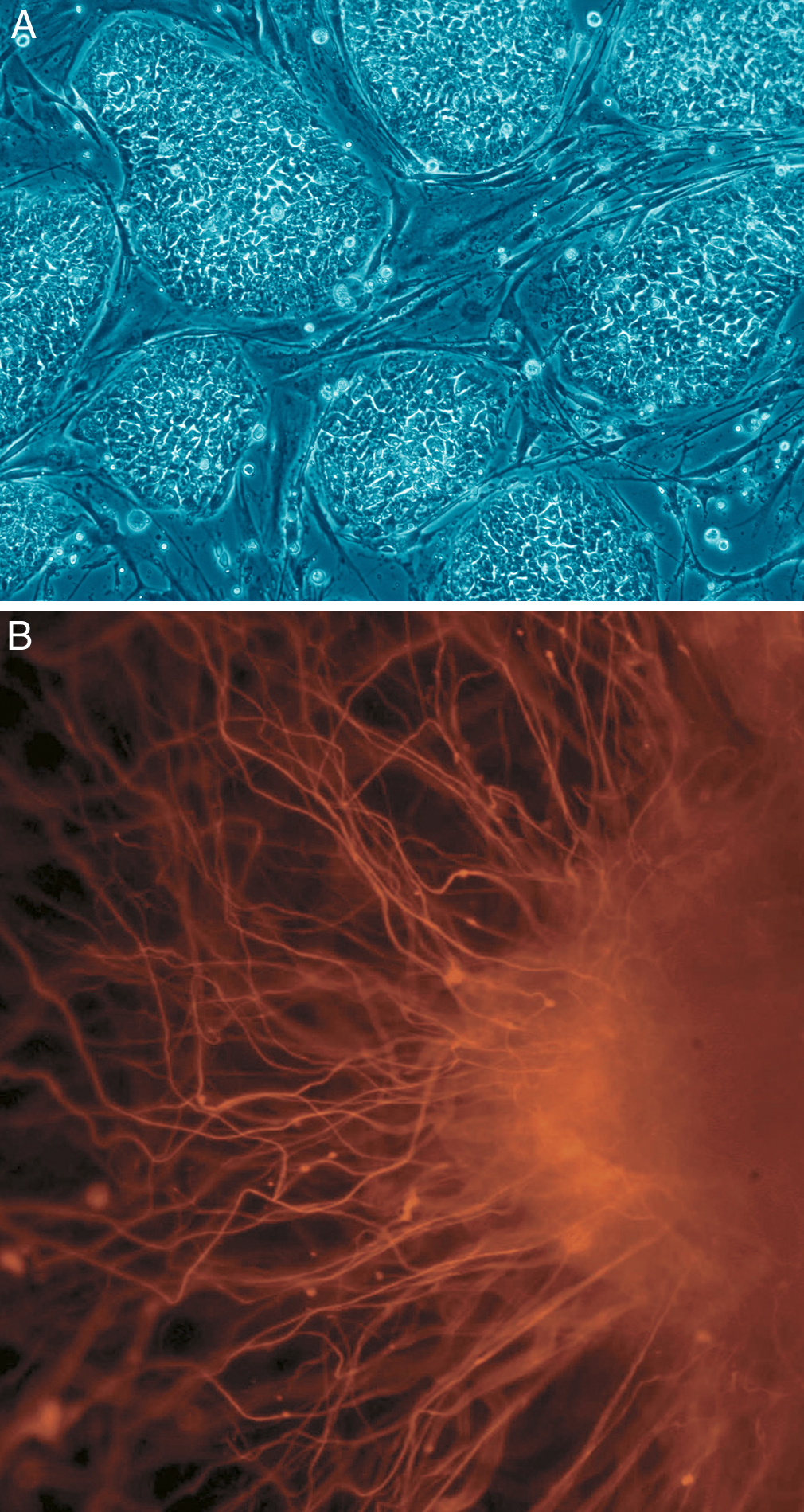
Pluripotency
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c- Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multipotency
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c- Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligopotency
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c- Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unipotency
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta. According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things. We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c- Myc of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration. Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramatical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oct4
Oct-4 (octamer-binding transcription factor 4), also known as POU5F1 (POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''POU5F1'' gene. Oct-4 is a homeodomain transcription factor of the POU family. It is critically involved in the self-renewal of undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. As such, it is frequently used as a marker for undifferentiated cells. Oct-4 expression must be closely regulated; too much or too little will cause differentiation of the cells. Octamer-binding transcription factor 4, OCT-4, is a transcription factor protein that is encoded by the ''POU5F1'' gene and is part of the POU (Pit-Oct-Unc) family. OCT-4 consists of an octamer motif, a particular DNA sequence of AGTCAAAT that binds to their target genes and activates or deactivates certain expressions. These gene expressions then lead to phenotypic changes in stem cell differentiation during the development of a mammalian embryo. It plays a vital role in de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Cell Mass
The inner cell mass (ICM) or embryoblast (known as the pluriblast in marsupials) is a structure in the early development of an embryo. It is the mass of cells inside the blastocyst that will eventually give rise to the definitive structures of the fetus. The inner cell mass forms in the earliest stages of embryonic development, before implantation into the endometrium of the uterus. The ICM is entirely surrounded by the single layer of trophoblast cells of the trophectoderm. Further development The physical and functional separation of the inner cell mass from the trophectoderm (TE) is a special feature of mammalian development and is the first cell lineage specification in these embryos. Following fertilization in the oviduct, the mammalian embryo undergoes a relatively slow round of cleavages to produce an eight-cell morula. Each cell of the morula, called a blastomere, increases surface contact with its neighbors in a process called compaction. This results in a polari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAF-1
Chromatin assembly factor-1 (CAF-1) is a protein complex — including Chaf1a (p150), Chaf1b (p60), and p48 subunits in humans, or Cac1, Cac2, and Cac3, respectively, in yeast— that assembles histone tetramers onto replicating DNA during the S phase of the cell cycle. Function CAF-1 functions as a histone chaperone that mediates the first step in nucleosome formation by tetramerizing and depositing newly synthesized histone H3/ H4 onto DNA rapidly behind replication forks. H3 and H4 are synthesized in the cytoplasm. Several studies have shown that the interaction between CAF-1 and PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen, which stabilizes CAF-1 at replication forks, is important for CAF-1's role in nucleosome assembly The three subunits work together to make the complex function. The human subunit (p150) interacts with PCNA, which acts as a sliding clamp, to help the CAF-1 complex interact with the DNA replication fork. Additionally, p150 along with PCNA performs nucleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophoblast
The trophoblast (from Greek : to feed; and : germinator) is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta. They form during the first stage of pregnancy and are the first cells to differentiate from the fertilized egg to become extraembryonic structures that do not directly contribute to the embryo. After gastrulation, the trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo and is referred to as the trophectoderm. After the first differentiation, the cells in the human embryo lose their totipotency and are no longer totipotent stem cells because they cannot form a trophoblast. They are now pluripotent stem cells. Structure The trophoblast proliferates and differentiates into two cell layers at approximately six days after fertilization for humans. Function Trophoblasts are specialized cells of the placenta that play ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morula
A morula (Latin, ''morus'': mulberry) is an early-stage embryo consisting of a solid ball of cells called blastomeres, contained in mammals, and other animals within the zona pellucida shell. The blastomeres are the daughter cells of the zygote, and when the blastomeres number from 16–32 the ball of cells is called a morula. At the 8-cell stage the blastomeres are round and only loosely adhered. With further division they begin to become flattened, and develop an inside-out polarity that optimises the cell to cell contact. In the human embryo by day four after fertilisation, the morula at about the 32–cell stage begins to take in fluid. The fluid comes about from sodium-potassium pumps (on trophoblasts) that pump sodium into the morula, drawing in water from the maternal environment to become blastocoelic fluid. Hydrostatic pressure of the fluid creates a large cavity in the morula called a blastocoel or blastocyst cavity. Embryoblast cells also known as the inner cell ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |