|
Pliensbachian-Toarcian Extinction
The Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (TOAE), also known as the Jenkyns Event, was a global anoxic event during the early part of the Toarcian age, approximately 183 million years ago, during the Early Jurassic. The TOAE is believed to be possibly the most extreme case of widespread ocean deoxygenation in the entire Phanerozoic eon. It is documented by a high amplitude negative carbon isotope excursion, as well as the widespread deposition of black shales and a major extinction event of marine life associated with a major rise in global temperatures. This anoxic event was responsible for the deposition of commercially extracted oil shales, particularly in China. Timing The TOAE lasted for approximately 500,000 years. The extinction event occurred in two distinct pulses. The first, more recently identified pulse occurred during the ''mirabile'' subzone of the ''tenuicostatum'' ammonite zone, coinciding with a slight drop in oxygen concentrations and the beginning of warming followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth-Science Reviews
''Earth-Science Reviews'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. It covers all aspects of Earth sciences. The editors-in-chief for this journal are A. Chin, C. Doglioni, J.L. Florsheim, M.F.J. Flower, G.R. Foulger, A. Gómez-Tuena, S. Khan, S. Marriott, A.D. Miall, G.F. Panza, J.A. Sanchez-Cabeza, M. Strecker, E.S. Takle, M. Widdowson, and P.B. Wignall. Abstracting and indexing This journal is abstracted and indexed by: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2012 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 7.339. References External links {{Authority control Earth and atmospheric sciences journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Monthly journals Publications establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth And Planetary Science Letters
''Earth and Planetary Science Letters'' (EPSL) is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on physical, chemical and mechanical processes of the Earth and other planets, including extrasolar ones. Topics covered range from deep planetary interiors to atmospheres. The journal was established in 1966 and is published by Elsevier. The co-editors-in-chief are J. Adkins (California Institute of Technology), J.P. Avouac (California Institute of Technology), R. Bendick (University of Montana), L. Derry (Cornell University), M. Ishii (Harvard University), T.A. Mather (University of Oxford), W.B. McKinnon (Washington University in St. Louis), F. Moynier ( Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris), Chiara Maria Petrone, Hans Thybo (Istanbul Technical University and University of Oslo), Alexander Webb. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Geoscience
''Nature Geoscience'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Nature Publishing Group. The Chief Editor is Tamara Goldin, who took over from Heike Langenberg in February 2020. It was established in January 2008. Scope The journal covers all aspects of the Earth sciences, including theoretical research, modelling, and field work. Significant related work in other fields, such as atmospheric sciences, geology, geophysics, climatology, oceanography, palaeontology, and space science, is also published. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed by: * ''CAB Abstracts'' * ''Chemical Abstracts Service/CASSI'' * ''Science Citation Index'' * ''Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences'' * ''GeoRef'' According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Asian Earth Sciences
The ''Journal of Asian Earth Sciences'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal specializing in Earth processes with a focus on aspects of research related to Asia. The journal is published by Elsevier. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 3.449. As of May 2022 the editor-in-chief is Mei-Fu Zhou (Chinese Academy of Sciences The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS); ), known by Academia Sinica in English until the 1980s, is the national academy of the People's Republic of China for natural sciences. It has historical origins in the Academia Sinica during the Republi ...). References English-language journals Online-only journals Earth and atmospheric sciences journals {{journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrological Cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time but the partitioning of the water into the major reservoirs of ice, fresh water, saline water (salt water) and atmospheric water is variable depending on a wide range of climatic variables. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, surface runoff, and subsurface flow. In doing so, the water goes through different forms: liquid, solid (ice) and vapor. The ocean plays a key role in the water cycle as it is the source of 86% of global evaporation. The water cycle involves the exchange of energy, which leads to temperature changes. When water evaporates, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate–silicate Cycle
The carbonate–silicate geochemical cycle, also known as the inorganic carbon cycle, describes the long-term transformation of silicate rocks to carbonate rocks by weathering and sedimentation, and the transformation of carbonate rocks back into silicate rocks by metamorphism and volcanism. Urey, H. C. (1952). The planets: their origin and development. Mrs. Hepsa Ely Silliman Memorial Lectures. Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere during burial of weathered minerals and returned to the atmosphere through volcanism. On million-year time scales, the carbonate-silicate cycle is a key factor in controlling Earth's climate because it regulates carbon dioxide levels and therefore global temperature. However the rate of weathering is sensitive to factors that modulate how much land is exposed. These factors include sea level, topography, lithology, and vegetation changes. Furthermore, these geomorphic and chemical changes have worked in tandem with solar forcing, whether due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
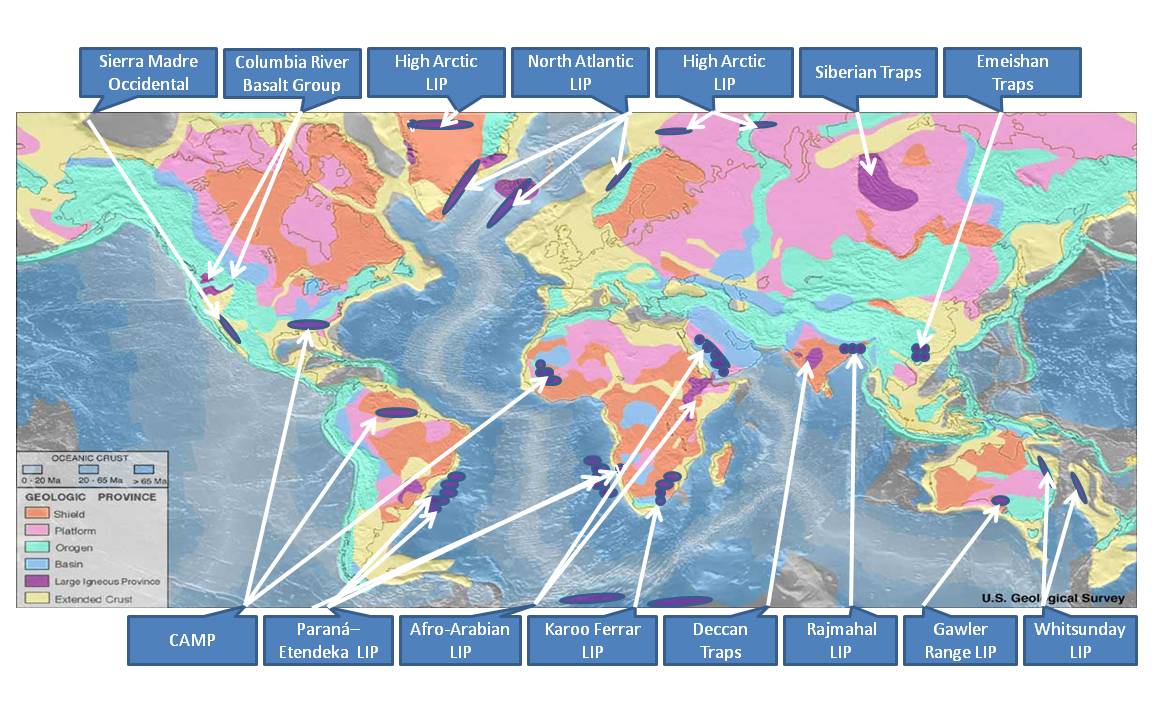
Large Igneous Province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely the scientific validity of a submitted paper, rather than its perceived importance, significance, or impact. In September 2016, the journal became the largest in the world by number of articles, overtaking '' PLOS ONE''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Chemical Abstracts Service, the Science Citation Index Expanded, and selectively in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor 4.996. Reviewing policy The ''Guide to Referees'' states that to be published, "a paper must be scientifically valid and technically sound in methodology and analysis", and reviewers have to ensure manuscripts "are not assessed based on their perceived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse And Icehouse Earth
Throughout Earth's climate history (Paleoclimate) its climate has fluctuated between two primary states: greenhouse and icehouse Earth. Both climate states last for millions of years and should not be confused with glacial and interglacial periods, which occur as alternate phases within an icehouse period and tend to last less than 1 million years. There are five known Icehouse periods in Earth's climate history, which are known as the Huronian, Cryogenian, Andean-Saharan, Late Paleozoic, and Late Cenozoic glaciations. The main factors involved in changes of the paleoclimate are believed to be the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (), changes in Earth's orbit, long-term changes in the solar constant, and oceanic and orogenic changes from tectonic plate dynamics. Greenhouse and icehouse periods have played key roles in the evolution of life on Earth by directly and indirectly forcing biotic adaptation and turnover at various spatial scales across time. Greenhouse Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeobotany
Paleobotany, which is also spelled as palaeobotany, is the branch of botany dealing with the recovery and identification of plant remains from geological contexts, and their use for the biological reconstruction of past environments (paleogeography), and the evolutionary history of plants, with a bearing upon the evolution of life in general. A synonym is paleophytology. It is a component of paleontology and paleobiology. The prefix ''palaeo-'' means "ancient, old", and is derived from the Greek adjective , . Paleobotany includes the study of terrestrial plant fossils, as well as the study of prehistoric marine photoautotrophs, such as photosynthetic algae, seaweeds or kelp. A closely related field is palynology, which is the study of fossilized and extant spores and pollen. Paleobotany is important in the reconstruction of ancient ecological systems and climate, known as paleoecology and paleoclimatology respectively; and is fundamental to the study of green plant develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Journal Of Science
The ''American Journal of Science'' (''AJS'') is the United States of America's longest-running scientific journal, having been published continuously since its conception in 1818 by Professor Benjamin Silliman, who edited and financed it himself. Until 1880, it was also known as the ''American Journal of Science and Arts'', but its focus was always on natural sciences and especially on geology and related subjects. In early years, the journal was often referred to as "Silliman's Journal", and the publication became associated with Yale University due to his long tenure there (1804–1853). The editorship long remained in the family of Professor Silliman, as he was assisted by his son, Benjamin Silliman Jr., from 1838. On the death of the elder Silliman in 1864, he was succeeded as chief editor by his son-in-law, James Dwight Dana, and then from 1895 till 1926 by Dana's son Edward Salisbury Dana. Associate editors included the botanist Asa Gray and the zoologist Louis Agassiz. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)