|
Piegan Blackfeet
The Piegan (Blackfeet language, Blackfeet: ''Piikáni'') are an Algonquian languages, Algonquian-speaking people from the Plains Indians, North American Great Plains. They are the largest of three Blackfeet-speaking groups that make up the Blackfeet Confederacy; the Siksika Nation, Siksika and Kainai Nation, Kainai are the others. The Piegan dominated much of the northern Great Plains during the nineteenth century. After their homelands were divided by the nations of Canada and the United States of America making boundaries between them, the Piegan people were forced to sign treaties with one of those two countries, settle in reservations on one side or the other of the border, and be enrolled in one of two government-like bodies sanctioned by North American nation-states. These two successor groups are the Blackfeet Nation, a List of federally recognized tribes, federally recognized tribe in northwestern Montana, U.S., and the Piikani Nation, a recognized "Band government, ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackfoot (other)
The Blackfoot Confederacy is a group of indigenous peoples in Canada and the United States. Blackfoot or Blackfeet may also refer to: Places Canada * Blackfoot, Alberta * Blackfoot, British Columbia * Blackfoot diatreme, a volcanic pipe in British Columbia, Canada United States * Blackfoot, Idaho * Blackfoot, Montana * Blackfoot, Texas * Blackfoot Creek, a stream in South Dakota * Blackfoot Glacier, in Montana * Blackfoot Mountain, in Montana * Blackfoot Mountains, in Idaho * Blackfoot River (other) * Blackfoot Dam Other uses * Blackfoot language, an Algonquian language spoken by the Blackfoot people * Blackfeet Nation, a Native American tribe in Montana * Blackfoot Sioux, or Sihasapa, a people unrelated to the Blackfoot Confederacy * Blackfoot (band), an American rock band * Black foot disease of grapevine, a plant disease * Blackfoot, a fictional character in the ''Warriors'' novel series * J. Blackfoot (1946–2011), American soul singer * J. D. Blackfoot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Browning, Montana
Browning is a former town and current Census-designated place in Glacier County, Montana, Glacier County, Montana, United States. It is the headquarters for the Blackfeet Indian Reservation and was the only incorporated town on the Reservation. The population was 1,018 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The town was named in 1885 for Commissioner of Indian Affairs Daniel M. Browning. The post office was established in 1895. The town was disincorporated on September 26, 2018, after the town's government collapsed financially. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , all land. Climate Browning has a warm-summer humid continental climate (''Dfb''), bordering on a subarctic climate, as well as cold semi-arid. From January 23 to January 24, 1916, the temperature fell 100 °F (56 °C), from 44 °F (7 °C) to −56 °F (−49 °C), the world record for greatest temperature drop in 24 hours. Brownin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
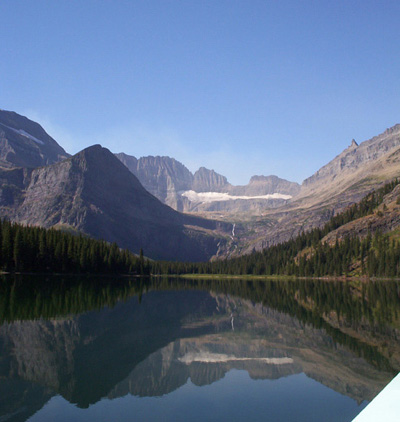
Glacier National Park (U
Glacier National Park may refer to: * Glacier National Park (Canada), in British Columbia, Canada * Glacier National Park (U.S.), in Montana, USA See also * Glacier Bay National Park, in Alaska, USA * Los Glaciares National Park, in Patagonia, Argentina {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Bird Grinnell
George Bird Grinnell (September 20, 1849 – April 11, 1938) was an American anthropologist, historian, naturalist, and writer. Originally specializing in zoology, he became a prominent early conservationist and student of Native American life. Grinnell has been recognized for his influence on public opinion and work on legislation to preserve the American bison. Mount Grinnell in Glacier National Park in Montana is named after him. Early life and education Grinnell was born on September 20, 1849, in Brooklyn, New York, the son of George Blake and Helen Lansing Grinnell. The family moved when he was seven to Audubon Park, the section of Washington Heights in Manhattan which was developed from the estate after noted ornithologist John James Audubon's death in 1851. Containing Drs. Diettert & Hampton's notes in preparing Diettert's thesis and subsequent 1992 book ''Grinnell's Glacier: George Bird Grinnell and Glacier National Park'' Grinnell graduated from Yale University w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Mountain Front
The Rocky Mountain Front is a somewhat unified geologic and ecosystem area in North America where the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains meet the plains. In 1983, the Bureau of Land Management called the Rocky Mountain Front "a nationally significant area because of its high wildlife, recreation, and scenic values". Conservationists Gregory Neudecker, Alison Duvall, and James Stutzman have described the Rocky Mountain Front as an area that warrants "the highest of conservation priorities" because it is largely unaltered by development and contains "unparalleled" numbers of wildlife. Defining the Rocky Mountain Front Although the Rocky Mountain Front is clearly distinct from both plains and mountains, in places like the Wyoming Basin, Montana, and New Mexico it is more ambiguous. One definition of the front is that it is a "transition zone between the Rocky Mountains and the mixed grass prairie ... hatencompasses a wide variety of wetland, riparian, grassland, and forested habi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutinative
In linguistics, agglutination is a morphological process in which words are formed by stringing together morphemes (word parts), each of which corresponds to a single syntactic feature. Languages that use agglutination widely are called agglutinative languages. For example, in the agglutinative Turkish, the word ("from your houses") consists of the morphemes ''ev-ler-i-n-iz-den''. Agglutinative languages are often contrasted with isolating languages, in which words are monomorphemic, and fusional languages, in which words can be complex, but morphemes may correspond to multiple features. Examples of agglutinative languages Although agglutination is characteristic of certain language families, this does not mean that when several languages in a certain geographic area are all agglutinative they are necessarily related phylogenetically. In the past, this assumption led linguists to propose the so-called Ural–Altaic language family, which included the Uralic and Turkic lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, Huron, Lake Erie, Erie, and Lake Ontario, Ontario (though hydrologically, Lake Michigan–Huron, Michigan and Huron are a single body of water, joined at the Straits of Mackinac). The Great Lakes Waterway enables modern travel and shipping by water among the lakes. The lakes connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River, and to the Mississippi River basin through the Illinois Waterway. The Great Lakes are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area and the second-largest by total volume. They contain 21% of the world's surface fresh water by volume. The total surface is , and the total volume (measured at the low water datum) is , slightly less than the volume of Lake Baikal (, 22–23% of the world's surface f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the United States (Montana and North Dakota). Saskatchewan and neighbouring Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2025, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,250,909. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan's total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs, and List of lakes in Saskatchewan, lakes. Residents live primarily in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city, Saskatoon, or the provincial capital, Regina, Saskatchewan, Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Saskatchewan, Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Estevan, Weyburn, Melfort, Saskatchewan, Melfort, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
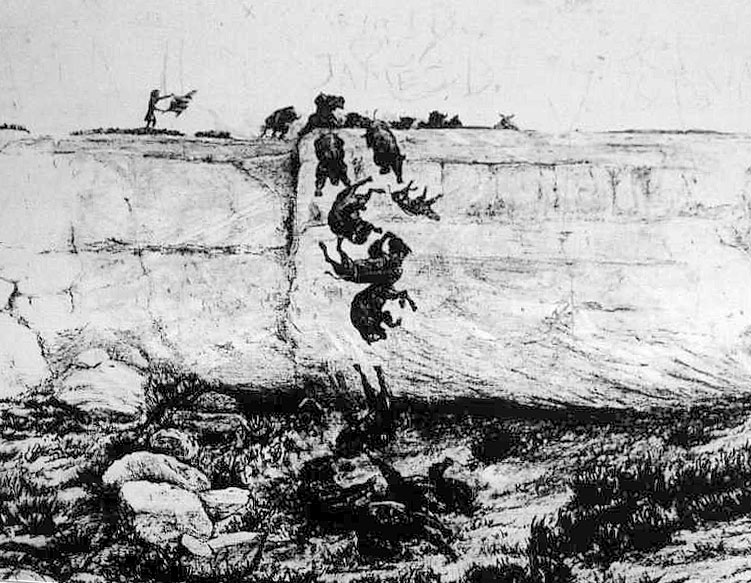
Buffalo Jump
A buffalo jump, or sometimes bison jump, is a cliff formation that Indigenous peoples of North America historically used to hunt and kill plains bison in mass quantities. The broader term game jump refers to a man-made jump or cliff used for hunting other game, such as reindeer. Method of the hunt Hunters herded the bison and drove them over the cliff; this process would serve to break the buffalos' legs and render them immobile, though often still alive and in great pain. Tribe members would wait below the jump and then close in with spears and bows to finish the kill. The Blackfoot people called the buffalo jumps "pishkun", which loosely translates as "deep blood kettle". They believed that if any buffalo escaped these killings then the rest of the buffalo would learn to avoid humans, which would make future hunts more difficult. Due to the large number of buffalo that would be driven over the cliff, the practice has been criticized as having been highly wasteful. Many of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Peoples Buffalo Jump State Park
First Peoples Buffalo Jump State Park is a Montana state park and National Historic Landmark in Cascade County, Montana in the United States. The park is and sits at an elevation of . It is located about northwest of the small town of Ulm, which is near the city of Great Falls. First Peoples Buffalo Jump State Park contains the Ulm Pishkun (also known as the Ulm Buffalo Jump), a historic buffalo jump utilized by the Native American tribes of North America. It has been described as, geographically speaking, either North America's largest buffalo jumpRobison, p. 13.Baumler, p. 15. or the world's largest.Schalla and Johnson, p. 60. There is some evidence that it was the most utilized buffalo jump in the world.Puckett, Karl. "Historic Buffalo Jump Site." ''Great Falls Tribune.'' May 30, 1999. The site was added to the National Register of Historic Places on December 17, 1974,Puckett, Karl. "Bison Kill Site Yields Terrific Old Treasures." ''Great Falls Tribune.'' July 5, 1999. and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clovis Culture
The Clovis culture is an archaeological culture from the Paleoindian period of North America, spanning around 13,050 to 12,750 years Before Present (BP). The type site is Blackwater Draw locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, where stone tools were found alongside the remains of Columbian mammoths in 1929. Clovis sites have been found across North America. The most distinctive part of the Clovis culture toolkit are Clovis points, which are projectile points with a fluted, lanceolate shape.Fluted: Having a flake removed from the base, either on one or both sides.Lanceolate: Tapering to a point at one end, like the head of a lance. Clovis points are typically large, sometimes exceeding in length. These points were multifunctional, also serving as cutting tools. Other stone tools used by the Clovis culture include knives, scrapers, and bifacial tools, with bone tools including beveled rods and shaft wrenches, with possible ivory points also being identified. Hides, wood, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackie Larson Bread Blackfeet
Jackie or Jacky may refer to: People and fictional characters * Jackie (given name), a list of people and fictional characters named Jackie or Jacky ** Jackie, current ring name of female professional wrestler Jacqueline Moore ** Jackie Lee (Irish singer) (born 1936), also known as "Jacky" ** Sagar Alias Jacky, Indian film character * Jarrhan Jacky (born 1989), Australian rules football player Arts and entertainment Films * ''Jackie'' (1921 film), directed by John Ford * ''Jacky'' (film), a 2000 Dutch film * ''Jackie'' (2010 film), an Indian Kannada -language film directed by Kannada director Soori * ''Jackie'' (2012 film), a Dutch film * ''Jackie'' (2016 film), a biographical drama about Jackie Kennedy Music Albums * ''Jackie'' (Jackie DeShannon album) (1972) * ''Jackie'' (Ciara album) (2015) * ''Jacky'' (album), a 2006 album by Joker Xue Songs * "Jacky" (Jacques Brel song) (1965) * "Jackie" (Elisa Fiorillo song) (1987) * "Jackie", a song from the 1987 album ''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |