|
Philipp Ludwig Von Seidel
Philipp Ludwig von Seidel (; 24 October 1821 in Zweibrücken, Germany – 13 August 1896 in Munich, German Empire) was a German mathematician. He was the son of Julie Reinhold and Justus Christian Felix Seidel. Philosopher & math theorist Imre Lakatos credits von Seidel with discovering, in 1847, the crucial analytic concept of uniform convergence, while analyzing an incorrect proof put forth earlier by Augustin-Louis Cauchy. In 1857, von Seidel contributed to the field of optics when he decomposed the first order monochromatic Aberration in optical systems, aberrations into five constituent aberrations. They are now commonly referred to as Optical telescope#The five Seidel aberrations, the five Seidel Aberrations. The lunar crater Seidel (crater), Seidel is named after him. His doctoral students include Eduard Study and Hermann Wiener. The Gauss–Seidel method is a useful numerical iterative method for solving linear systems. See also *Seidel triangle References Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Telescope
An optical telescope gathers and focus (optics), focuses light mainly from the visible spectrum, visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnification, magnified image for direct visual inspection, to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors. There are three primary types of optical telescope : * ''Refracting telescopes'', which use lens (optics), lenses and less commonly also Prism (optics), prisms (dioptrics) * ''Reflecting telescopes'', which use mirrors (catoptrics) * ''Catadioptric system#Catadioptric telescopes, Catadioptric telescopes'', which combine lenses and mirrors An optical telescope's ability to resolve small details is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (optics), objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light), and its light-gathering power is related to the area of the objective. The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1821 Births
Events January–March * January 21 – Peter I Island in the Antarctic is first sighted, by Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen. * January 26 – Congress of Laibach convenes to deal with outstanding international issues, particularly the outbreak of a revolution in southern Italy. * January 28 – Alexander Island, the largest in Antarctica, is first discovered by Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen. * February 9 – Columbian College in the District of Columbia is chartered by President James Monroe (it becomes George Washington University). * February 10 – In Mexico, the Embrace of Acatempan takes place between Agustín de Iturbide and Vicente Guerrero, which seals the peace between the viceroyalty troops and the insurgents. * February 28 – Congress of Laibach formally comes to an end. However the leading participants remain as fresh uprisings break out in Northern Italy and Greece. * March 7 – The Battle of Rieti is fought in Italy between intervening Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of St
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seidel Triangle
In mathematics, the Bernoulli numbers are a sequence of rational numbers which occur frequently in analysis. The Bernoulli numbers appear in (and can be defined by) the Taylor series expansions of the tangent and hyperbolic tangent functions, in Faulhaber's formula for the sum of ''m''-th powers of the first ''n'' positive integers, in the Euler–Maclaurin formula, and in expressions for certain values of the Riemann zeta function. The values of the first 20 Bernoulli numbers are given in the adjacent table. Two conventions are used in the literature, denoted here by B^_n and B^_n; they differ only for , where B^_1=-1/2 and B^_1=+1/2. For every odd , . For every even , is negative if is divisible by 4 and positive otherwise. The Bernoulli numbers are special values of the Bernoulli polynomials B_n(x), with B^_n=B_n(0) and B^+_n=B_n(1). The Bernoulli numbers were discovered around the same time by the Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli, after whom they are named, and ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauss–Seidel Method
In numerical linear algebra, the Gauss–Seidel method, also known as the Liebmann method or the method of successive displacement, is an iterative method used to solve a system of linear equations. It is named after the German mathematicians Carl Friedrich Gauss and Philipp Ludwig von Seidel. Though it can be applied to any matrix with non-zero elements on the diagonals, convergence is only guaranteed if the matrix is either strictly diagonally dominant, or symmetric and positive definite. It was only mentioned in a private letter from Gauss to his student Gerling in 1823. A publication was not delivered before 1874 by Seidel. Description Let \mathbf A\mathbf x = \mathbf b be a square system of linear equations, where: \mathbf A = \begin a_ & a_ & \cdots & a_ \\ a_ & a_ & \cdots & a_ \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\a_ & a_ & \cdots & a_ \end, \qquad \mathbf = \begin x_ \\ x_2 \\ \vdots \\ x_n \end , \qquad \mathbf = \begin b_ \\ b_2 \\ \vdots \\ b_n \end. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Wiener
Hermann Ludwig Gustav Wiener (15 May 1857, Karlsruhe – 13 June 1939, Darmstadt) was a German mathematician. Education and career Hermann Wiener, whose father was the mathematician Christian Wiener, graduated from the ''Gymnasium'' in Karlsruhe. From 1876 to 1879 he studied mathematics and natural science at the ''Polytechnische Schule Karlsruhe'' (now the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology). From 1879 to 1882 he studied at the Technical University of Munich under Felix Klein and Alexander von Brill and in 1881 at the University of Leipzig. In 1881 he received his ''Promotion'' (PhD) in Munich in mathematics with a thesis ''Über Involutionen auf ebenen Curven'' (On involutions on plane curves) under the supervision of Ludwig Seidel. In Karlsruhe in 1882 he passed the state examination for secondary school teachers. He was from 1882 to 1883 a ''Lehramtspraktikant'' (teaching trainee) at the ''Gymnasium'' in Karlsruhe and from 1882 to 1883 his father's assistant at the ''Polytec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Study
Christian Hugo Eduard Study ( ; 23 March 1862 – 6 January 1930) was a German mathematician known for work on invariant theory of ternary forms (1889) and for the study of spherical trigonometry. He is also known for contributions to space geometry, hypercomplex numbers, and criticism of early physical chemistry. Study was born in Coburg in the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha. Career Eduard Study began his studies in Jena, Strasbourg, Leipzig, and Munich. He loved to study biology, especially entomology. He was awarded the doctorate in mathematics at the University of Munich in 1884. Paul Gordan, an expert in invariant theory was at Leipzig, and Study returned there as Privatdozent. In 1888 he moved to Marburg and in 1893 embarked on a speaking tour in the U.S.A. He appeared at a Congress of Mathematicians in Chicago as part of the World's Columbian Exposition and took part in mathematics at Johns Hopkins University. Back in Germany, in 1894, he was appointed extraordinary professor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seidel (crater)
Seidel is a worn lunar impact crater that lies to the east-northeast of the much larger crater Jules Verne. Farther to the east of Seidel is the western edge of Mare Ingenii, and to the northeast lies the crater O'Day O'Day is a surname of Irish origin. Notable people with the surname include: *Alan O'Day (1940–2013), American singer-songwriter *Anita O'Day (1919–2006), American jazz singer * Aubrey O'Day (born 1984), American singer, dancer, actress, songw .... This is an eroded crater with a small crater overlying the south-southeastern outer rim. The southern rim is overlain by material deposits, most likely ejecta from another impact. The remainder of the rim has survived fairly well, and is marked only by tiny craterlets and general wear. The interior floor is relatively level with a few tiny craterlets marking the surface. Satellite craters By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
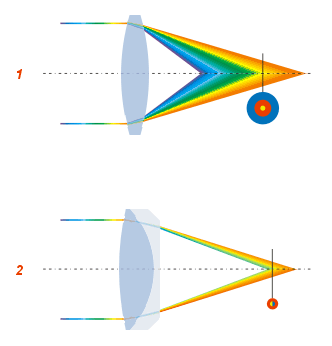
Aberration In Optical Systems
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as Lens (optics), lenses and mirrors, that causes the ''image'' created by the optical system to not be a faithful reproduction of the ''object'' being observed. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred, distorted in shape or have color fringing or other effects not seen in the object, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zweibrücken
Zweibrücken (; ; , ; literally translated as "Two Bridges") is a town in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, on the Schwarzbach (Blies), Schwarzbach River. Name The name ''Zweibrücken'' means 'two bridges'; older forms of the name include Middle High German ''Zweinbrücken'', Latin ''Geminus Pons'' and ''Bipontum'', and French language, French ''Deux-Ponts'', all with the same meaning. History The town was the capital of the former Imperial State of Palatine Zweibrücken owned by the House of Wittelsbach. The ducal castle is now occupied by the high court of the Palatinate (''Oberlandesgericht''). There is a fine Gothic architecture, Gothic Protestant church, Alexander's church, founded in 1493 and rebuilt in 1955. From the end of the 12th century, Zweibrücken was the seat of the County of Zweibrücken, the counts being descended from Henry I, youngest son of Simon I, Count of Saarbrücken (d. 1182). The line became extinct on the death of Count Eberhard II (1394), who in 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible light, visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the Classical electromagnetism, classical electromagnetic description of light, however complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of Ray (optics), rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |