|
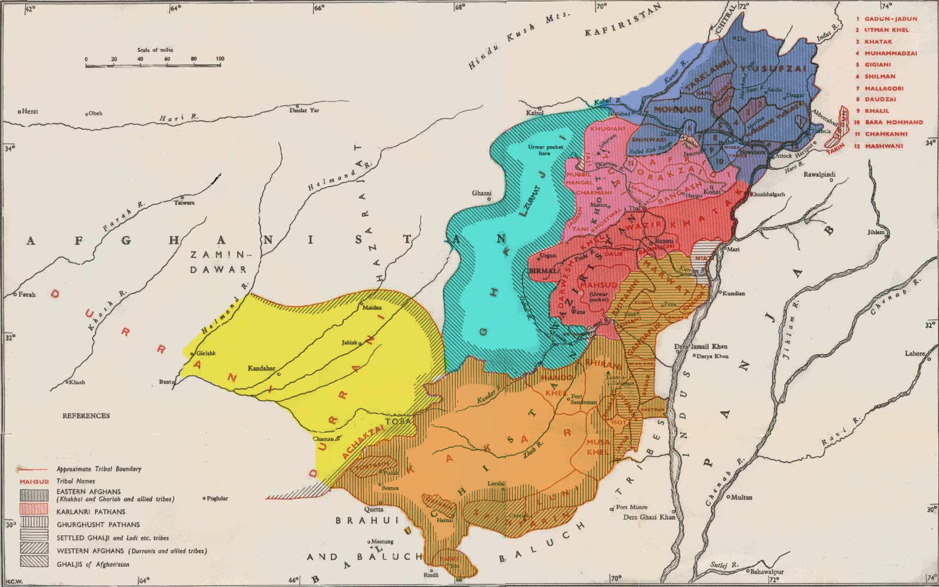
Pashtun Tribes
The Pashtun tribes ( ps, پښتانه قبايل), historically also known as Afghan tribes, are the tribes of the Pashtun people, a large Eastern Iranian ethnic group who use the Pashto language and follow Pashtunwali code of conduct. They are found primarily in Afghanistan and Pakistan and form the world's largest tribal society, comprising over 49 million people and between 350 and 400 tribes and clans. They are traditionally divided into four tribal confederacies: the Sarbani (), the Bettani (), the Gharghashti () and the Karlani (). Folkloric genealogies trace the descendants of the Pashtuns to Qais Abdur Rashid and his three sons ''Saṛban'' (), ''Bēṭ'' (), and ''Gharghax̌t'' () as well as an adopted son, not directly adopted by Qais Abdul Rashid, therefore, the identity of Karlan himself and the man who adopted him, according to some books written on the history of the Pashtuns, is either unclear or controversial, the Karlani confederacy Ormur Baraki, who b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashtun People
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically referred to as Afghans () or xbc, αβγανο () until the 1970s, when the term's meaning officially evolved into that of a demonym for all residents of Afghanistan, including those outside of the Pashtun ethnicity. The group's native language is Pashto, an Iranian language in the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family. Additionally, Dari Persian serves as the second language of Pashtuns in Afghanistan while those in the Indian subcontinent speak Urdu and Hindi (see Hindustani language) as their second language. Pashtuns are the 26th-largest ethnic group in the world, and the largest segmentary lineage society; there are an estimated 350–400 Pashtun tribes and clans with a variety of origin theories. The total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlani
Karlāṇī ( ps, کرلاڼي) is a Pashtun tribal confederacy. They primarily inhabit the FATA region of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan and certain parts of eastern Afghanistan. In the 16th century the Karlani founded the Karrani dynasty, the last dynasty to rule the Bengal Sultanate. The legend of Karlani in the folklore says: "In his infancy he became an orphan and after losing his family he alone survived and was adopted by the Ormur Tribe. The tribe gave him shelter & protection & raised him like their own son. When he reached a marriageable age, the chief of the Ormur tribe made Karlan his son in law." by Muhammad Qāsim Hindū Šāh Astarābādī Firištah, The |
Ghilji
The Ghiljī ( ps, غلجي, ; fa, خیلجی, Xelji) also spelled Khilji, Khalji, or Ghilzai or Ghilzay (), are one of the largest Pashtun tribes. Their traditional homeland is Ghazni and Qalati Ghilji in Afghanistan but they have also settled in other regions throughout the Afghanistan-Pakistan Pashtun belt. The Khilji dynasty was a dynasty in Delhi Sultanate founded by Jalaluddin Khalji and expanded by Alauddin Khalji who were from Ghilji tribe. The modern nomadic Kochi people are predominantly made up of Ghilji tribes. The Ghilji make up around 20-25% of Afghanistan's total population. They mostly speak the central dialect of Pashto with transitional features between the southern and northern varieties of Pashto. Etymology According to historian C.E. Bosworth, the tribal name "Ghilji" is derived from the name of the '' Khalaj'' () tribe. According to historian V. Minorsky, the ancient Turkic form of the name was ''Qalaj'' (or ''Qalach''), but the Turkic / q/ chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashto Dialects
Pashto dialects ( ps, د پښتو ژبګوټي də Pəx̌tó žәbgóṭi) can be divided into two large varieties: Northern Pashto and Southern Pashto. Each of the two varieties of Pashto is further divided into a number of dialects. Northern Pashto is spoken in eastern Afghanistan, and central, northern and eastern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (including Peshawar). Southern Pashto is spoken to the south of it, in southern and western Afghanistan (including Kandahar), southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and northern Balochistan (including Quetta). ' Ethnologue' divides Pashto into Northern, Southern and Central Pashto, and Wanetsi. Overview According to David Neil MacKenzie , a consonant shift took place in the northern parts of Pashtunistan in several phases in the medieval era. During the shift, the retroflex fricative ''ṣ̌'' changed to ''x̌'' or to ''x'' , while ''ẓ̌'' changed to ''ǵ'' or to ''g'' . That is supported by the linguist Georg Morgenstierne's assertion that the Pashto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIA Afghanistan Ethnic Groups Map
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, and analyzing national security information from around the world, primarily through the use of human intelligence (HUMINT) and performing covert actions. As a principal member of the United States Intelligence Community (IC), the CIA reports to the Director of National Intelligence and is primarily focused on providing intelligence for the President and Cabinet of the United States. President Harry S. Truman had created the Central Intelligence Group under the direction of a Director of Central Intelligence by presidential directive on January 22, 1946, and this group was transformed into the Central Intelligence Agency by implementation of the National Security Act of 1947. Unlike the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which is a dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Iranian
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau. The Iranian languages are grouped in three stages: Old Iranian (until 400 BCE), Middle Iranian (400 BCE–900 CE) and New Iranian (since 900 CE). The two directly-attested Old Iranian languages are Old Persian (from the Achaemenid Empire) and Old Avestan (the language of the Avesta). Of the Middle Iranian languages, the better understood and recorded ones are Middle Persian (from the Sasanian Empire), Parthian (from the Parthian Empire), and Bactrian (from the Kushan and Hephthalite empires). , there were an estimated 150–200 million native speakers of the Iranian languages. ''Ethnologue'' estimates that there are 86 languages in the group, with the largest among them being Persian (Farsi, Dari, and Tajik dialects), Pashto, Kurdish, Luri, and Balochi. Terminolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactrian Language
Bactrian (, , ) is an extinct Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (in present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan, and the Hephthalite empires. Name It was long thought that Avestan represented "Old Bactrian", but this notion had "rightly fallen into discredit by the end of the 19th century". Bactrian, which was written predominantly in an alphabet based on the Greek script, was known natively as ("Arya"; an endonym common amongst Indo-Iranian peoples). It has also been known by names such as Greco-Bactrian, Kushan or Kushano-Bactrian. Under Kushan rule, Bactria became known as ''Tukhara'' or ''Tokhara'', and later as ''Tokharistan''. When texts in two extinct and previously unknown Indo-European languages were discovered in the Tarim Basin of China, during the early 20th century, they were linked circumstantially to Tokharistan, and Bactrian was sometimes referred to as "Eteo-Tocharian" (i.e. "true" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Crooke
William Crooke (6 August 1848 – 25 October 1923) was a British orientalist and a key figure in the study and documentation of Anglo-Indian folklore. He was born in County Cork, Ireland, and was educated at Erasmus Smith's Tipperary Grammar School and Trinity College, Dublin. Crooke joined the Indian Civil Service. While an administrator in India, he found abundant material for his researches in the ancient civilizations of the country. He found ample time to write much on the people of India, their religions, beliefs and customs. He was also an accomplished hunter. Although Crooke was a gifted administrator, his career in the ICS lasted only 25 years because of personality clashes with his superiors. He returned to England and in 1910, he was chosen to be the president of the Anthropological Section of the British Association. In 1911, having been for many years a member of the council of the Folklore Society, he was elected its president. Re-elected as president of the soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zai (tribe)
Zai (), are Pashtun tribes in Pakistan and Afghanistan. The title of tribe end in Zai and their clans end in Khel. Pashtuns (/ˈpʌʃˌtʊn/, /ˈpɑːʃˌtʊn/, /ˈpæʃˌtuːn/; Pashto: پښتانه, Pəx̌tānə́), 7also known as Pakhtuns 8or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group 2who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. 334] They were historically referred to as Afghans until the 1970s, 0when the term's meaning evolved into that of a demonym for all residents of Afghanistan, including those outside of the Pashtun ethnicity. Some of the Pashtun tribes * Samozai * Esapzai (ايسپزی) * Kamalzai * Duryazai * Alakozai * Alizai * Barakzai * Dawlatzai * Ghilzai * Kakar * Kakazai * Khudiadadzai * Khulozai * Mohammadzai * Niazi or Niazai * Nurzai * Omarzai * Popalzai * Sadduzai * Salarzai * Stanikzai * Utmankhel * Yousafzai * Zazai See also * Khel * Pashtun tribes * Pashtun Pashtuns (, , ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khel (clan)
Khel ( ps, خیل) are sub-tribes of Pashtun tribes in Afghanistan and Pakistan. The title of the tribe ends in '' Zai'' and its sub-tribe name ends in ''Khel''. ''Khel'' is also a common final element in the names of villages in Afghanistan and in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa of Pakistan, such as Darra Adam Khel. Some of the clans of Pashtun tribes: * Daulat Khel * Ghoryakhel * Isakhel (sub-tribe) * Khan Khel * Khizar Khel * Khwaja Khel * Maghdud Khel * Mahmud Khel * Musakhel * Sahib Khel * Umar Khel * Utmankhel See also * Zai (tribe) * Pashtun people Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ... References {{Pashtun tribes Pashtun tribes Pashto words and phrases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |