|
Palatine Peasants' War
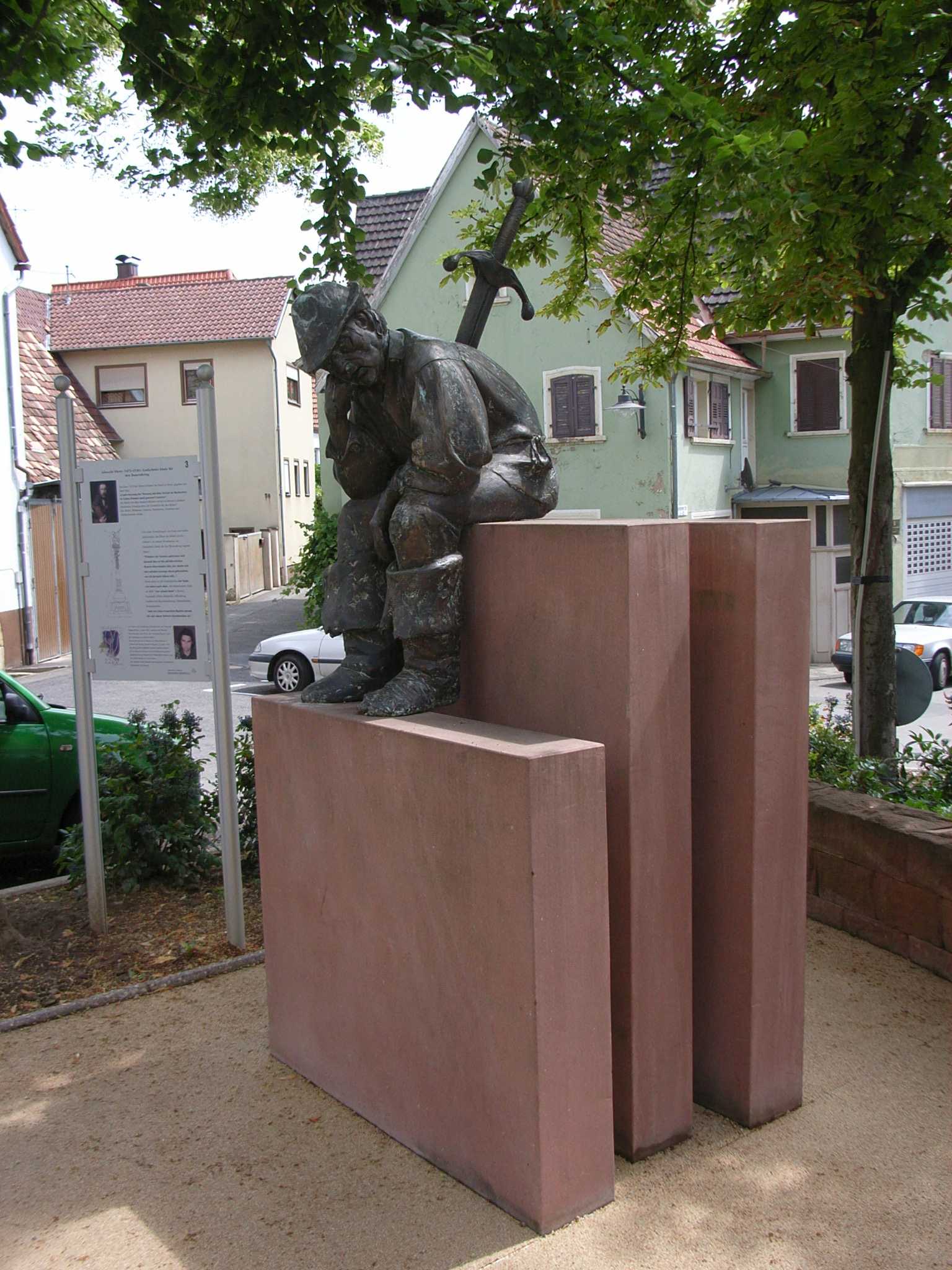
The Palatine Peasants' War (german: pfälzische Bauernkrieg) was part of the general German Peasants' War on the Middle and Upper Rhine. The uprising in the Palatine Electorate and its surrounding area took place in April to June 1525. History The start of the German Peasants' War in West Rhenish Palatinate was marked by the gathering of a band of peasants, a so-called ''Haufe'', at Nußdorf near Landau on 23 April 1525. The Palatine peasant mobs plundered several surrounding monasteries (including the Knights Hospitaller commandry of Heimbach near Zeiskam as well as Hördt, where the provost was killed) and castles, before they took Neustadt on 6 May without a fight. The peasants' programme was based on the Twelve Articles, which were drawn up at Memmingen and of which 25,000 copies were printed. A second ''Haufe'' gathered near Bockenheim. As a result, the Palatine prince-elector, Louis V felt forced into negotiations with the Geilweiler and Bockenheim groups; these began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Articles
The Twelve Articles (German ''Zwölf Artikel'') were part of the peasants' demands of the Swabian League during the German Peasants' War of 1525. They are considered the first draft of human rights and civil liberties in continental Europe after the Roman Empire. The gatherings in the process of drafting them are considered to be the first constituent assembly on German soil. Incidents On 6 March 1525 about 50 representatives of the Upper Swabian Peasants Groups (of the Baltringer Mob, the Allgäuer Mob, and the Lake Constance Mob), met in Memmingen to deliberate upon their common stance against the Swabian League. One day later and after difficult negotiations, they proclaimed the Christian Association, an Upper Swabian Peasants' Confederation. The peasants met again on 15 and 20 March 1525 in Memmingen and, after some additional deliberation, adopted the Twelve Articles and the Federal Order (Bundesordnung). The Articles and the Order are only examples among many similar progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peasant Revolts
This is a chronological list of conflicts in which peasants played a significant role. Background The history of peasant wars spans over two thousand years. A variety of factors fueled the emergence of the peasant revolt phenomenon, including: *Tax resistance *Social inequality *Religious war * National liberation *Resistance against serfdom *Redistribution of land *External factors such as plague and famine Later peasant revolts such as the Telangana Rebellion were also influenced by agrarian socialist ideologies such as Maoism. The majority of peasant rebellions ended prematurely and were unsuccessful. Peasants suffered from limited funding and lacked the training and organisational capabilities of professional armies. Chronological list The list gives the name, the date, the peasant allies and enemies, and the result of these conflicts following this legend: : : : : See also * Servile Wars * Peasant movement * Popular revolts in late-medieval Europe * Maoism * U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pfeddersheim
The Battle of Pfeddersheim (german: Schlacht bei Pfeddersheim) was a battle during the German Peasants' War that took place in June 1525 near Pfeddersheim. The peasants of the Palatinate region had previously joined the uprising in southwest Germany against high taxes and attacked, plundered, and devastated the estates of the nobility and the monasteries. Causes The Battle of Pfeddersheim was part of the Palatine Peasants' War of 1525. The unrest amongst the peasants and townsfolk in and around Worms began before 29 April 1525 and reached its zenith in May that year. They demanded that the town authorities comply with 13 articles and make concessions within four days. These articles were related to three areas: first, in the religious sphere, they demanded a clear and unbiased preaching of the Gospel and the free election of priests and preachers by members of the community. Second, in the economic sphere and where applicable, they demanded that interest, pensions and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the west of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, near the border with Luxembourg and within the important Moselle wine region. Founded by the Celts in the late 4th century BC as ''Treuorum'' and conquered 300 years later by the Romans, who renamed it ''Augusta Treverorum'' ("The City of Augustus among the Treveri"), Trier is considered Germany's oldest city. It is also the oldest seat of a bishop north of the Alps. Trier was one of the four capitals of the Roman Empire during the Tetrarchy period in the late 3rd and early 4th centuries. In the Middle Ages, the archbishop-elector of Trier was an important prince of the Church who controlled land from the French border to the Rhine. The archbishop-elector of Trier also had great si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landtag (historic)
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non-federal matters. The States of Germany and Austria are governed by ''landtage''. In addition, the legislature of the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol is known in German as a ''landtag''. Historically, states of the German Confederation also established ''landtage''. The Landtag of Liechtenstein is the small nation's unicameral assembly. Name The German word Landtag is composed of the words ''Land'' (state, country or territory) and ''Tag'' (day). The German word ''Tagung'' (meeting) is derived from the German word ''Tag'', as such meetings were held at daylight and sometimes spanned several days. Historic Landtag assemblies States of the Holy Roman Empire In feudal society, the formal class system was reflected in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forst An Der Weinstraße
Forst may refer to: Communities In Germany *, in the district of Aachen *Forst (Baden), in Baden-Württemberg *Forst (Lausitz), in Brandenburg * Forst (Unterfranken), part of Schonungen, Bavaria * Forst, Altenkirchen, in the district of Altenkirchen, Rhineland-Palatinate * Forst (Eifel), in the district Cochem-Zell, Rhineland-Palatinate * Forst (Hunsrück), in the district Cochem-Zell, Rhineland-Palatinate * Forst an der Weinstraße, in the district of Bad Dürkheim, Rhineland-Palatinate *Forst, Lower Saxony, a district of Bevern, known for its residents Roedelius and Moebius in the 1970s In Italy * Forst (Foresta), a frazione in the comune of Algund (Lagundo) in South Tyrol, Italy In Switzerland * Forst, Switzerland, in the Canton of Bern People * David Forst (born 1976), American baseball executive * Grete Forst (1878–1942), Austrian soprano * Rainer Forst (born 1964), German philosopher *Willi Forst Willi Forst, born Wilhelm Anton Frohs (7 April 1903 – 11 August 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis V Of The Palatinate
Louis V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (German: ''Ludwig V. von der Pfalz'') (2 July 1478, in Heidelberg – 16 March 1544, in Heidelberg), also Louis the Pacific, was a member of the Wittelsbach dynasty was prince elector of the Palatinate. His parents were Philip, Elector Palatine, and Margaret, a daughter of Louis IX, Duke of Bavaria-Landshut. He converted to Lutheranism in the 1530s. Biography Louis succeeded his father in 1508 and had to cope with the consequences of the lost Landshut War of Succession against Albert IV, Duke of Bavaria. With the Imperial Diet of Augsburg in 1518 Louis achieved the annulment of the Imperial Ban against the Palatinate. In 1519 Louis voted for Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. During the German Peasants' War, Louis found himself surrounded by 8,000 armed peasants in Neustadt, where he invited their leaders to dinner and complied with their demands. Louis married Sibylle, daughter of Albert IV, Duke of Bavaria Albert IV (15 December 1447 & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire. From the 13th century onwards, the prince-electors had the privilege of electing the monarch who would be crowned by the pope. After 1508, there were no imperial coronations and the election was sufficient. Charles V (elected in 1519) was the last emperor to be crowned (1530); his successors were elected emperors by the electoral college, each being titled "Elected Emperor of the Romans" (german: erwählter Römischer Kaiser; la, electus Romanorum imperator). The dignity of elector carried great prestige and was considered to be second only to that of king or emperor. The electors held exclusive privileges that were not shared with other princes of the Empire, and they continued to hold their original titles alongside that of elector. The heir apparent to a secular prince- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bockenheim An Der Weinstraße
Bockenheim an der Weinstraße (or ''Bockenheim an der Weinstrasse'') is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Bad Dürkheim district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Geography The municipality lies in the Palatinate and the Rhine-Neckar urban agglomeration. It belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Leiningerland, whose seat is in Grünstadt, although that town is itself not in the ''Verbandsgemeinde''. Bockenheim lies at the north end of the 85 km-long German Wine Route, and has even adopted an epithet referring to its location there: ''an der Weinstraße'' means “on the Wine Route” in German. The Route runs concurrently here with ''Bundesstraße'' 271. History Bockenheim is made up of two smaller centres called Großbockenheim and Kleinbockenheim (''groß'' means “great” and ''klein'' “little”), which were merged in 1956. The two places arose from small settlements that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
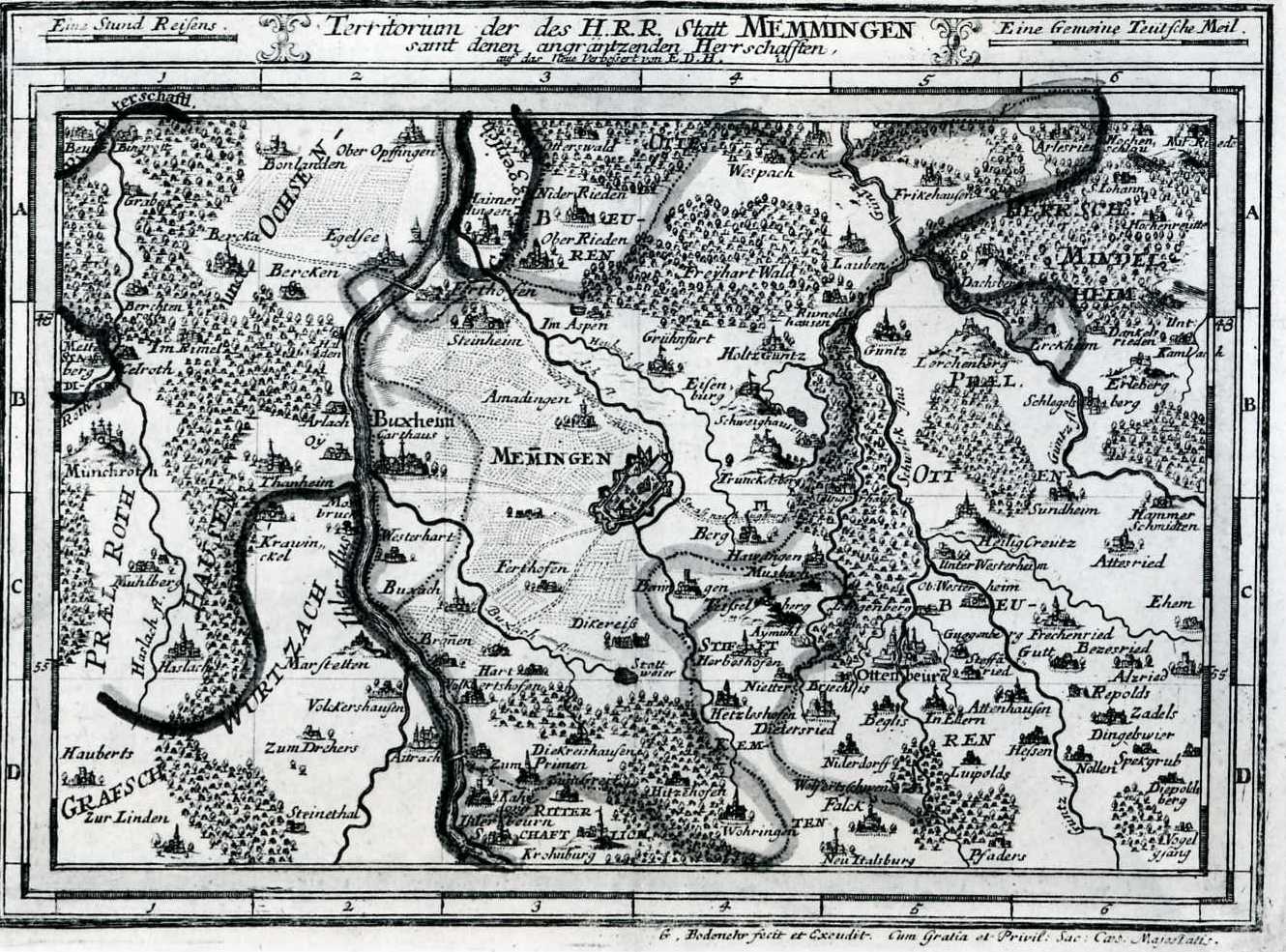
Memmingen
Memmingen (; Swabian: ''Memmenge'') is a town in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is the economic, educational and administrative centre of the Danube-Iller region. To the west the town is flanked by the Iller, the river that marks the Baden-Württemberg border. To the north, east and south the town is surrounded by the district of Unterallgäu (Lower Allgäu). With about 42,000 inhabitants, Memmingen is the 5th biggest town in the administrative region of Swabia. The origins of the town go back to the Roman Empire. The old town, with its many courtyards, castles and patricians' houses, palaces and fortifications is one of the best preserved in southern Germany. With good transport links by road, rail and air, it is the transport hub for Upper Swabia and Central Swabia, and the Allgäu. Due to its proximity to the Allgäu region, Memmingen is often called the Gateway to the Allgäu (''Tor zum Allgäu''). The town motto is ''Memmingen – Stadt mit Perspektiven'' ("Memmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neustadt An Der Weinstraße
Neustadt an der Weinstraße (, formerly known as ; lb, Neustadt op der Wäistrooss ; pfl, Naischdadt) is a town in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. With 53,300 inhabitants , it is the largest town called ''Neustadt''. Geography Location The town itself lies in the western park of the Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region between the Haardt mountains, the eastern edge of the Palatinate Forest, and the western edge of the Upper Rhine Plain in the middle of the Palatinate wine region, an area that is around 10 km wide and 85 km long. The Speyerbach river flows through the town from west to east as does the Rehbach, which separates from the Speyerbach within the town at the ''Winzinger Wassergescheid'' before emptying into the River Rhine several kilometres further north than the Speyerbach. The borough, with its incorporated parishes, measures from west to east and from north to south. Its highest point is at the Hohe Loog House at the top of the Hohe Loog moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |