|
Purple Forbidden Enclosure
The Purple Forbidden enclosure ( Zǐ wēi yuán) is one of the San Yuan ( Sān yuán) or Three Enclosures. Stars and constellations of this group lie near the north celestial pole and are visible all year from temperate latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere. Asterisms The asterisms are: See also * Twenty-Eight Mansions The Twenty-Eight Mansions (), also called or , are part of the Chinese constellations system. They can be considered as the equivalent to the Zodiac, zodiacal constellations in Western astronomy, though the Twenty-eight Mansions reflect the move ... References Chinese constellations Chinese astrology Purple {{china-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Constellations
Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" ( Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic tradition. The Song dynasty (13th-century) Suzhou planisphere shows a total of 283 asterisms, comprising a total of 1,565 individual stars. The asterisms are divided into four groups, the Twenty-Eight Mansions (, ''Èrshíbā Xiù'') along the ecliptic, and the Three Enclosures of the northern sky. The southern sky was added as a fifth group in the late Ming dynasty based on European star charts, comprising an additional 23 asterisms. The Three Enclosures (, ''Sān Yuán'') include the Purple Forbidden Enclosure, which is centered on the north celestial pole and includes those stars which could be seen year-round,Needham, J.Astronomy in Ancient and Medieval China. ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London''. Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Emperor Of Heaven
The Great Emperor of the Curved Array). ( zh, c=勾陳大帝, p= gōuchén dàdì), also called the Gouchen Emperor and Tianhuang Emperor, is one of the highest sky deities of Taoism. He is one of the Four Sovereigns (; ) and is in charge of heaven, earth, and human and of wars in the human world. Chinese mythology The "Curved Array" is a constellation in the Purple Forbidden enclosure, equivalent to the European constellation called ''Ursa Minor'' or the ''Little Dipper''. In Taoism, the Great Emperor of Curved Array is the eldest son of Doumu and the brother of the Ziwei Emperor. History Emperor Gaozong of Tang was called by the title Emperor Tianhuang as his Posthumous name given by Wu Zetian. Liu Yan was also given the posthumous name. Constellation There is a constellation named after the Tianhuang Emperor. See also * North Star * Myōken * Wufang Shangdi The Wǔfāng Shàngdì ( "Five Regions' Highest Deities" or "Highest Deities of the Five Regions" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-Eight Mansions
The Twenty-Eight Mansions (), also called or , are part of the Chinese constellations system. They can be considered as the equivalent to the Zodiac, zodiacal constellations in Western astronomy, though the Twenty-eight Mansions reflect the movement of the Moon through a Lunar month, sidereal month rather than the Sun in a tropical year. The lunar mansion system was in use in other parts of East Asia, such as ancient Japan; the ''Bansenshūkai'', written by Fujibayashi Yasutake, mentions the system several times and includes an image of the twenty-eight mansions. A similar system, called nakshatra, is used in traditional Indian astronomy. Overview Ancient Chinese astronomers divided the sky ecliptic into four regions, collectively known as the Four Symbols, each assigned a mysterious animal. They are Azure Dragon (青龍) on the east, Black Tortoise (玄武) on the north, White Tiger (mythology), White Tiger (白虎) on the west, and Vermilion Bird (朱雀) on the south. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boötes
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from , which comes from 'herder, herdsman' or 'plowman' (literally, 'ox-driver'; from ''boûs'' 'cow'). One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the List of brightest stars, fourth-brightest star in the night sky, the orange giant Arcturus. Epsilon Boötis, or Izar, is a colourful multiple star popular with amateur astronomers. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye. History and mythology In ancient Babylon, the stars of Boötes were known as SHU.PA. They were apparently depicted as the god Enlil, who was the leader of the Babylonian religion, Babyloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Minor
Leo Minor is a small and faint constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for "the smaller lion", in contrast to Leo, the larger lion. It lies between the larger and more recognizable Ursa Major to the north and Leo to the south. Leo Minor was not regarded as a separate constellation by classical astronomers; it was designated by Johannes Hevelius in 1687. There are 37 stars brighter than apparent magnitude 6.5 in the constellation; three are brighter than magnitude 4.5. 46 Leonis Minoris, an orange giant of magnitude 3.8, is located some 95 light-years from Earth. At magnitude 4.4, Beta Leonis Minoris is the second-brightest star and the only one in the constellation with a Bayer designation. It is a binary star, the brighter component of which is an orange giant and the fainter a yellow-white main sequence star. The third-brightest star is 21 Leonis Minoris, a rapidly rotating white main-sequence star of avera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canes Venatici
Canes Venatici ( ) is one of the 88 constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for 'hunting dogs', and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighboring constellation. Cor Caroli is the constellation's brightest star, with an apparent magnitude of 2.9. La Superba (Y CVn) is one of the reddest naked-eye stars and one of the brightest carbon stars. The Whirlpool Galaxy is a spiral galaxy tilted face-on to observers on Earth, and was the first galaxy whose spiral nature was discerned. In addition, quasar TON 618 is one of the most massive black holes with the mass of 66 billion solar masses. History The stars of Canes Venatici are not bright. In classical times, they were listed by Ptolemy as unfigured stars below the constellation Ursa Major in his star catalogu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules (constellation)
Hercules is a constellation named after Hercules, the Roman mythology hero adapted from the Greek mythology, Greek hero Heracles. Hercules was one of the 48 constellations listed by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations today. It is the fifth-largest of the modern constellations and is the largest of List of brightest stars, the 50 which have no stars brighter than apparent Magnitude (astronomy), magnitude +2.5. Characteristics Hercules is bordered by Draco (constellation), Draco to the north; Boötes, Corona Borealis, and Serpens, Serpens Caput to the west; Ophiuchus to the south; Aquila (constellation), Aquila to the southwest; and Sagitta, Vulpecula, and Lyra to the east. Covering 1225.1 square degrees and 2.970% of the night sky, it ranks fifth among the 88 constellations in size. The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
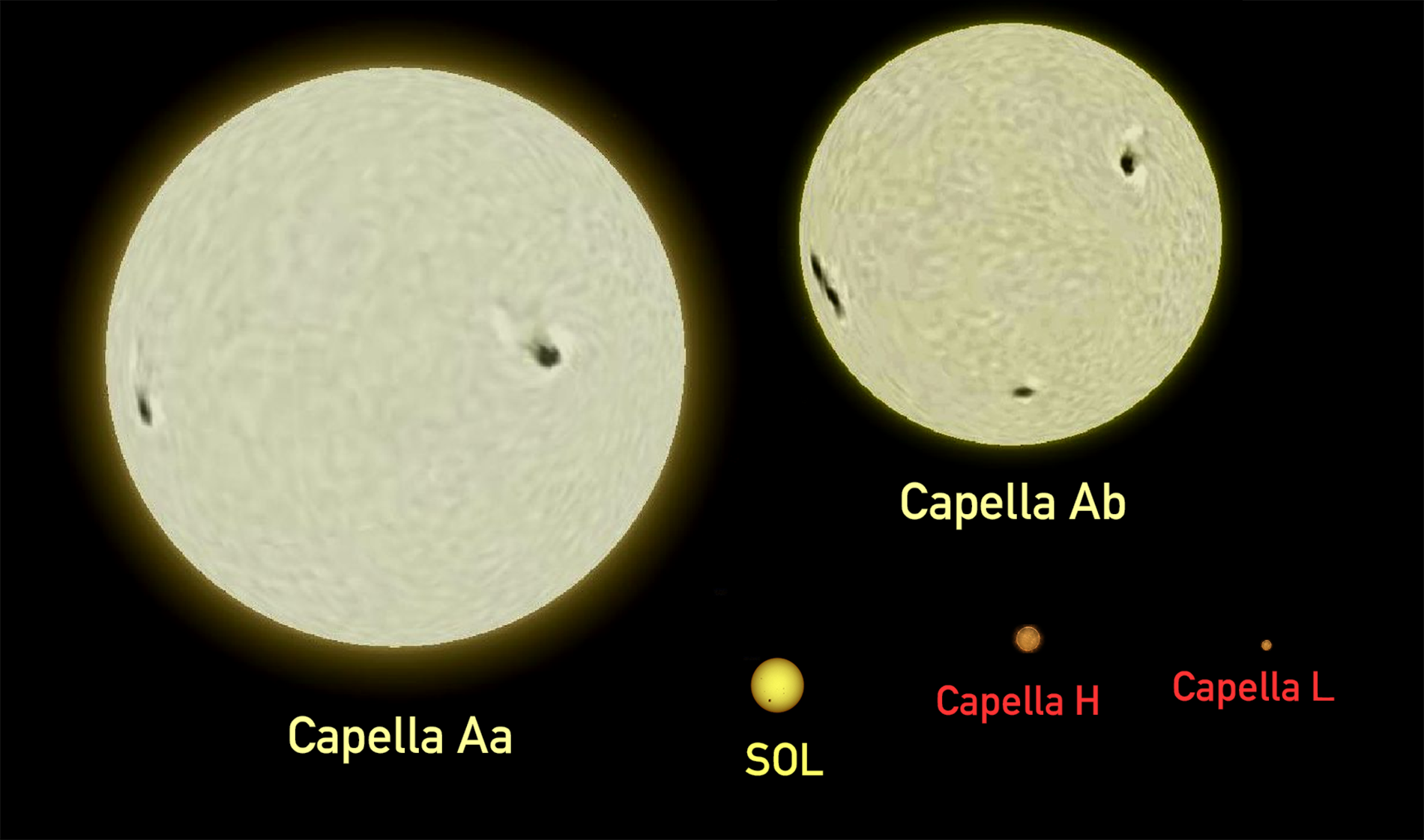
Auriga (constellation)
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the List of constellations, 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius of Athens, Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism (astronomy), asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as −34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra (constellation), Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella (star), Capella, is an unusual Star system, multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, drawing on earlier works by Greek, Egyptian, Babylonian, and Assyrian astronomers. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Major is primarily known from the asterism of its main seven stars, which has been called the "Big Dipper", "the Wagon", "Charles's Wain", or "the Plough", among other names. In particular, the Big Dipper's stellar configuration mimics the shape of the " Little Dipper". Two of its stars, named Dubhe and Merak ( α Ursae Majoris and β Ursae Majoris), can be used as the navigational pointer towards the place of the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Pole
Northern Pole (北极 in Simplified Chinese, ''běi jí'' in Pinyin) is a traditional Chinese asterism found in the Purple Forbidden enclosure (紫微垣 in Simplified Chinese, ''zǐ wēi yuán'' in Pinyin). It consists of five stars found in the modern constellations of Ursa Minor and Camelopardalis and represents the five stars of the North Pole. During the Qing dynasty, a total of four stars from the constellation Ursa Minor was added to the asterism. {, class="wikitable" , - ! Order !! English name !! Chinese name !! Corresponding star , - , 1 (北极一) , , The Crown Prince , , 太子 , , Gamma Ursae Minoris (Pherkad) , - , 2 (北极二) , , The Emperor , , 帝 , , Beta Ursae Minoris (Kochab) , - , 3 (北极三) , , The Son of Concubine , , 庶子 , , 5 Ursae Minoris , - , 3+1 (庶子增一) , , The Son of Concubine , , 庶子 , , unclear, in Ursa Minor , - , 3+2 (庶子增二) , , The Son of Concubine , , 庶子 , , 3 Ursae Minoris , - , 3+3 (庶子� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia (constellation)
Cassiopeia () is a constellation and Asterism (astronomy), asterism in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia (mother of Andromeda), Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda (mythology), Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. Cassiopeia is located in the northern sky and from latitudes above 34th parallel north, 34°N it is visible year-round. In the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November, and at low southern, tropical, latitudes of less than 25th parallel south, 25°S it can be seen, seasonally, low in the North. At magnitude 2.2, Alpha Cassiopeiae, or Schedar, is the brightest star in Cassiopeia. The constellation hosts some of the most luminous stars known, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cepheus (constellation)
Cepheus is a constellation in the deep northern sky, named after Cepheus, King of Aethiopia, Cepheus, a king of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the second century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 constellations in the modern times. The constellation's brightest star is Alderamin (Alpha Cephei), with an apparent magnitude of 2.5. Delta Cephei is the prototype of an important class of star known as a Cepheid variable. RW Cephei, an orange hypergiant, together with the red supergiants Mu Cephei, MY Cephei, VV Cephei, V381 Cephei, and V354 Cephei are among the List of largest stars, largest stars known. In addition, Cepheus also has the hyperluminous quasar S5 0014+81, which hosts an ultramassive black hole in its core, reported at 40 billion solar masses, about 10,000 times more massive than the Sagittarius A*, central black hole of the Milky Way, making this among the most List of most massive black holes, massive black ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |