|
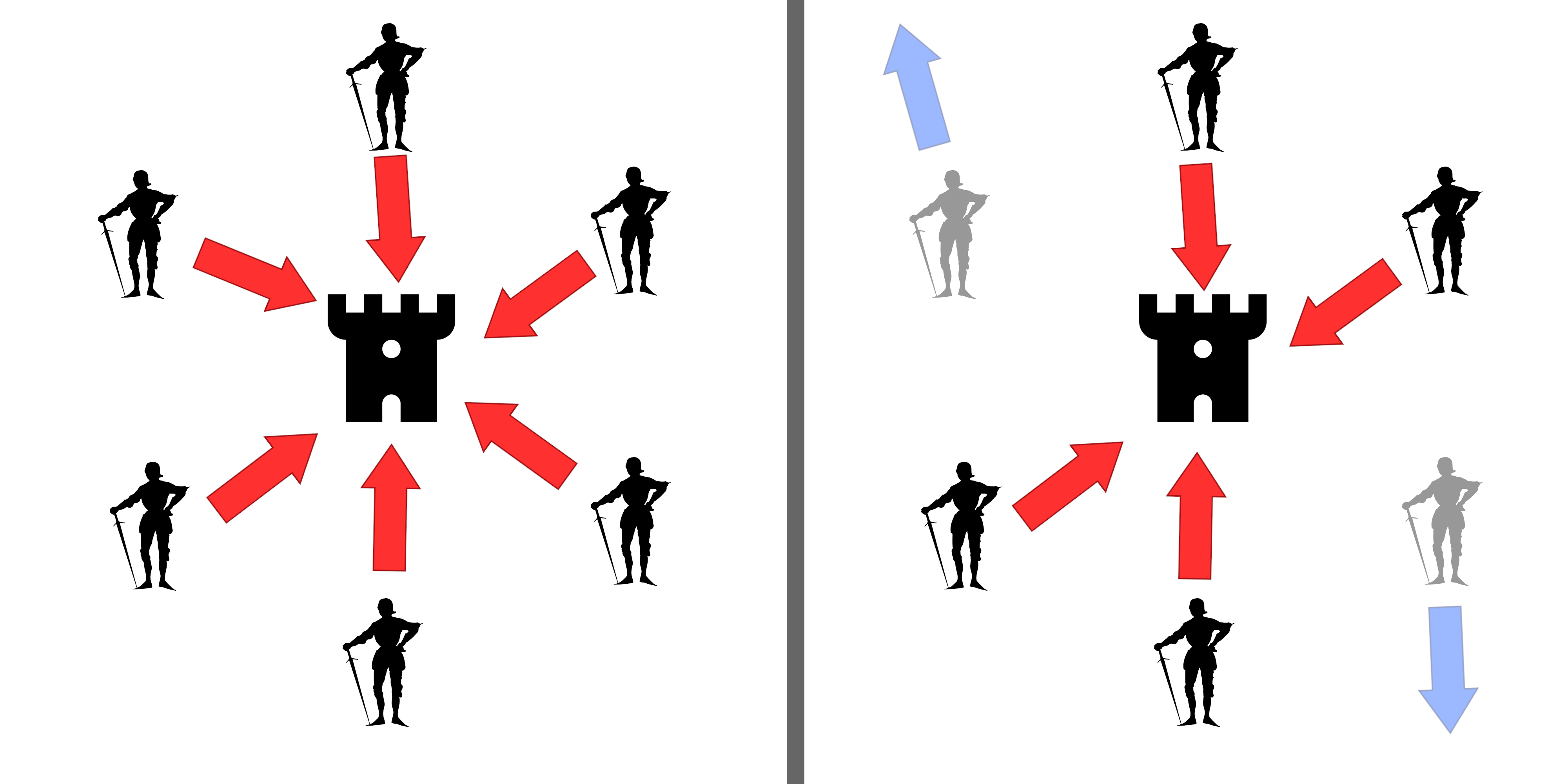
Proactive Secret Sharing
Proactive secret sharing is an underlying technique in Proactive Security Protocols. It is a method to update distributed keys (shares) in a secret sharing scheme periodically such that an attacker has less time to compromise shares and as long as the attacker visits less than a threshold or a quorum group, the system remains secure. This contrasts to a non-proactive scheme where if the threshold number of shares are compromised during the lifetime of the secret, the secret is compromised. The model which takes time constraints into account was originally suggested as an extension of the notion of Byzantine fault tolerance where redundancy of sharing allows robustness into the time domain (periods) and was proposed by Rafail Ostrovsky and Moti Yung in 1991. The method has been used in the areas of cryptographic protocols in secure multi-party computation and in threshold cryptosystems. Motivation If the players (holders of the shared secret) store their shares on insecure compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key (cryptography)
A key in cryptography is a piece of information, usually a string of numbers or letters that are stored in a file, which, when processed through a cryptographic algorithm, can encode or decode cryptographic data. Based on the used method, the key can be different sizes and varieties, but in all cases, the strength of the encryption relies on the security of the key being maintained. A key's security strength is dependent on its algorithm, the size of the key, the generation of the key, and the process of key exchange. Scope The key is what is used to encrypt data from plaintext to ciphertext. There are different methods for utilizing keys and encryption. Symmetric cryptography Symmetric cryptography refers to the practice of the same key being used for both encryption and decryption. Asymmetric cryptography Asymmetric cryptography has separate keys for encrypting and decrypting. These keys are known as the public and private keys, respectively. Purpose Since the key ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Distribution
In symmetric key cryptography, both parties must possess a secret key which they must exchange prior to using any encryption. Distribution of secret keys has been problematic until recently, because it involved face-to-face meeting, use of a trusted courier, or sending the key through an existing encryption channel. The first two are often impractical and unsafe, while the third depends on the security of a previous key exchange. In public key cryptography, the key distribution of public keys is done through public key servers. When a person creates a key-pair, they keep one key private and the other, known as the ''public-key'', is uploaded to a server where it can be accessed by anyone to send the user a private, encrypted, message. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) uses Diffie–Hellman key exchange if the client does not have a public-private key pair and a published certificate in the public key infrastructure, and Public Key Cryptography if the user does have both the keys and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secret Sharing
Secret sharing (also called secret splitting) refers to methods for distributing a secrecy, secret among a group, in such a way that no individual holds any intelligible information about the secret, but when a sufficient number of individuals combine their 'shares', the secret may be reconstructed. Whereas ''insecure'' secret sharing allows an attacker to gain more information with each share, ''secure'' secret sharing is 'all or nothing' (where 'all' means the necessary number of shares). In one type of secret sharing scheme there is one ''dealer'' and ''n'' ''players''. The dealer gives a share of the secret to the players, but only when specific conditions are fulfilled will the players be able to reconstruct the secret from their shares. The dealer accomplishes this by giving each player a share in such a way that any group of ''t'' (for ''threshold'') or more players can together reconstruct the secret but no group of fewer than ''t'' players can. Such a system is called a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secret
Secrecy is the practice of hiding information from certain individuals or groups who do not have the "need to know", perhaps while sharing it with other individuals. That which is kept hidden is known as the secret. Secrecy is often controversial, depending on the content or nature of the secret, the group or people keeping the secret, and the motivation for secrecy. Secrecy by government entities is often decried as excessive or in promotion of poor operation; excessive revelation of information on individuals can conflict with virtues of privacy and confidentiality. It is often contrasted with social transparency. Secrecy can exist in a number of different ways: encoding or encryption (where mathematical and technical strategies are used to hide messages), true secrecy (where restrictions are put upon those who take part of the message, such as through government security classification) and obfuscation, where secrets are hidden in plain sight behind complex idiosyncrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Fault Tolerance
A Byzantine fault is a condition of a system, particularly a distributed computing system, where a fault occurs such that different symptoms are presented to different observers, including imperfect information on whether a system component has failed. The term takes its name from an allegory, the "Byzantine generals problem", developed to describe a situation in which, to avoid catastrophic failure of a system, the system's actors must agree on a strategy, but some of these actors are unreliable in such a way as to cause other (good) actors to disagree on the strategy and they may be unaware of the disagreement. A Byzantine fault is also known as a Byzantine generals problem, a Byzantine agreement problem, or a Byzantine failure. Byzantine fault tolerance (BFT) is the resilience of a fault-tolerant computer system or similar system to such conditions. Definition A Byzantine fault is any fault presenting different symptoms to different observers. A Byzantine failure is the los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rafail Ostrovsky
Rafail Ostrovsky is a distinguished professor of computer science and mathematics at University of California, Los Angeles, UCLA and a well-known researcher in algorithms and cryptography. Biography Rafail Ostrovsky received his Ph.D. from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT in 1992. He is a member of the editorial board of Algorithmica Editorial Board of Journal of Cryptologand Editorial and Advisory Board of the International Journal of Information and Computer Securit Awards * 2022 W. Wallace McDowell Award "for visionary contributions to computer security theory and practice, including foreseeing new cloud vulnerabilities and then pioneering corresponding novel solutions" * 2021 AAAS Fellow * 2021 Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery "for contributions to the foundations of cryptography" * 2019 Academia Europaea Foreign Member * 2018 RSA Award for Excellence in Mathematics "for contributions to the theory and to new variants of secure multi-party comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moti Yung
Mordechai M. "Moti" Yung is a cryptographer and computer scientist known for his work on cryptovirology and kleptography. Career Yung earned his PhD from Columbia University in 1988 under the supervision of Zvi Galil. In the past, he worked at the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center, CertCo, RSA Laboratories, and Google. In 2016, Yung moved from Google to Snap Inc. Yung is currently a research scientist at Google. Yung is an adjunct senior research faculty member at Columbia University, and has co-advised PhD students including Gödel Prize winner Matthew K. Franklin, Jonathan Katz, and Aggelos Kiayias. Research Yung research covers primarily the area of cryptography and its applications to information security and data privacy. He has worked on defining and implementing malicious (offensive) cryptography: cryptovirology and kleptography, and on various other foundational and applied fields of cryptographic research, including: user and entity electronic authent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Multi-party Computation
Secure multi-party computation (also known as secure computation, multi-party computation (MPC) or privacy-preserving computation) is a subfield of cryptography with the goal of creating methods for parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. Unlike traditional cryptographic tasks, where cryptography assures security and integrity of communication or storage and the adversary is outside the system of participants (an eavesdropper on the sender and receiver), the cryptography in this model protects participants' privacy from each other. The foundation for secure multi-party computation started in the late 1970s with the work on mental poker, cryptographic work that simulates game playing/computational tasks over distances without requiring a trusted third party. Traditionally, cryptography was about concealing content, while this new type of computation and protocol is about concealing partial information about data while computing with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Cryptosystem
A threshold cryptosystem, the basis for the field of threshold cryptography, is a cryptosystem that protects information by encrypting it and distributing it among a cluster of fault-tolerant computers. The message is encrypted using a public key, and the corresponding private key is shared among the participating parties. With a threshold cryptosystem, in order to decrypt an encrypted message or to sign a message, several parties (more than some threshold number) must cooperate in the decryption or signature protocol. History Perhaps the first system with complete threshold properties for a trapdoor function (such as RSA) and a proof of security was published in 1994 by Alfredo De Santis, Yvo Desmedt, Yair Frankel, and Moti Yung. Historically, only organizations with very valuable secrets, such as certificate authorities, the military, and governments made use of this technology. One of the earliest implementations was done in the 1990s by Certco for the planned deployment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adversary (cryptography)
In cryptography, an adversary (rarely opponent, enemy) is an entity whose aim is to prevent the users of the cryptosystem from achieving their goal (primarily privacy, integrity, and availability of data), often with malicious intent. An adversary's efforts might take the form of attempting to discover secret data, corrupting some of the data in the system, spoofing the identity of a message sender or receiver, or forcing system downtime. Actual adversaries, as opposed to idealized ones, are referred to as ''attackers''. The former term predominates in the cryptographic and the latter in the computer security literature. Eavesdropper Eve, malicious attacker Mallory, opponent Oscar, and intruder Trudy are all adversarial characters widely used in both types of texts. This notion of an adversary helps both intuitive and formal reasoning about cryptosystems by casting security analysis of cryptosystems as a 'game' between the users and a ''centrally co-ordinated'' enemy. The notion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor involved in some term of a polynomial, a series, or any other type of expression. It may be a number without units, in which case it is known as a numerical factor. It may also be a constant with units of measurement, in which it is known as a constant multiplier. In general, coefficients may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the combination of variables and constants is not necessarily involved in a product, it may be called a ''parameter''. For example, the polynomial 2x^2-x+3 has coefficients 2, −1, and 3, and the powers of the variable x in the polynomial ax^2+bx+c have coefficient parameters a, b, and c. A , also known as constant term or simply constant, is a quantity either implicitly attached to the zeroth power of a variable or not attached to other variables in an expression; for example, the constant coefficients of the expressions above are the number 3 and the parameter ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |