|
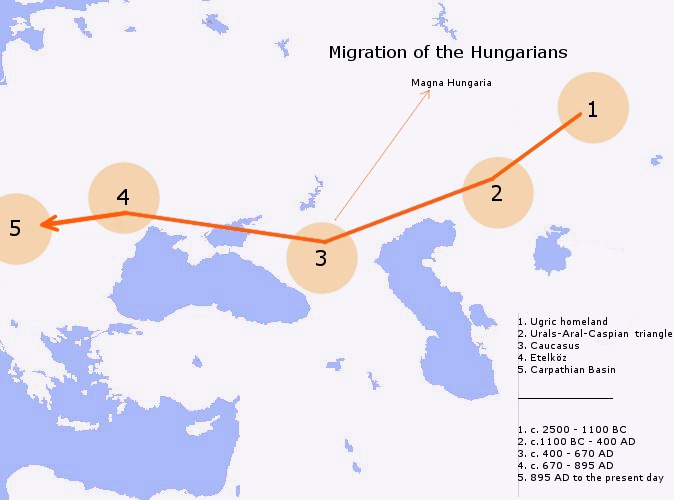
Principality Of Hungary
The Grand Principality of Hungary or Duchy of Hungary (: "Hungarian Grand Principality", ) was the earliest documented Hungarian state in the Carpathian Basin, established in 895 or 896, following the 9th century Magyar invasion of the Carpathian Basin. The Hungarians, a semi-nomadic people, formed a tribal alliance led by Árpád (founder of the Árpád dynasty) who arrived from Etelköz, their earlier principality east of the Carpathians.Paul Lendvai''The Hungarians: a thousand years of victory in defeat'' C. Hurst & Co., 2003, pp. 15–29, 533 During the period, the power of the Hungarian Grand Prince seemed to be decreasing irrespective of the success of the Hungarian military raids across Europe. The tribal territories, ruled by Hungarian warlords (chieftains), became semi-independent polities (e.g., the domains of Gyula the Younger in Transylvania). These territories were united again only under the rule of St. Stephen. The semi-nomadic Hungarian population adop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchy, monarchical state or feudalism, feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "principality" is often used to describe small monarchies, particularly those in Europe, where the ruler holds the title of prince or an equivalent. Historically, principalities emerged during the Middle Ages as part of the feudal system, where local princes gained significant power within a king's domain. This led to political fragmentation and the creation of mini-states. Over time, many of these principalities consolidated into larger Monarchy, kingdoms and empires, while others retained their independence and prospered. Sovereign principalities which exist today include Liechtenstein, Monaco, and the co-principality of Andorra. Additionally, some royal primogenitures, such as Asturias in Spain, are styled as principalities. The term is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamanistic Remnants In Hungarian Folklore
Hungarian shamanism is discovered through comparative methods in ethnology, designed to analyse and search ethnographic data of Hungarian folktales, songs, language, comparative cultures, and historical sources. Research Studies of files of witch trials reveal that some features of Hungarian folklore are remnants of shamanistic beliefs, maintained from the deep past, or possibly borrowed from Turkic peoples with whom Hungarians lived before wandering to the Pannonian Basin;Diószegi 1998 or maybe is an effect of Eastern influence thereafter (Cuman immigration). These remnants are partly conserved as fragments by some features of customs and beliefs, for example * refrains of certain folksongs accompanying some customs; * certain motifs of folktales, e.g. sky-reaching tree, which was a specific belief among several central Eurasian peoples, having some resemblances to the world tree concept, but it was also related to the shaman's tree and had some other peculiarities as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magyar Tribes
The Magyar or Hungarian tribes ( , ) or Hungarian clans were the fundamental political units within whose framework the Hungarians (Magyars) lived, before the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin and the subsequent establishment of the Principality of Hungary.George H. HodosThe East-Central European region: an historical outline Greenwood Publishing Group, 1999, p. 19 Etymology The origin of the term "Hungary", the ethnonym of the Hungarian tribal alliance, is uncertain. According to one view, following the description in the 13th-century chronicle, ''Gesta Hungarorum'', the federation was called "Hetumoger" (modern Hungarian: ''hét magyar'', ), as in the Latin phrase, "''VII principales persone qui Hetumoger dicuntur''" ("seven princely persons who are called Seven Magyars"). The word "Magyar" possibly comes from the name of the most prominent Hungarian tribe, called ''Megyer'', which became used to refer to the Hungarians, Hungarian people as a whole. Written sources cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphological term Pannonian Plain was also used for roughly the same region, referring to the lowlands in the area occupied by the Pannonian Sea during the Pliocene Epoch, however some consider the term "Pannonian Plain" not only unhistorical but also topologically erroneous. Terminology The term Pannonian Plain refers to the lowland parts of the Pannonian Basin as well as those of some adjoining regions like Lower Austria, Moravia, and Silesia (Czech Republic and Poland). The lands adjoining the plain proper are sometimes also called ''peri-Pannonian''. In English language, the terms "Pannonian Basin" and "Carpathian Basin" may sometimes be used synonymously, although the latter holds an irredentist Hungarian connotation. The name "Pannonian" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Géza, Grand Prince Of The Hungarians
Géza ( 940 – 997), also Gejza, was Grand Prince of the Hungarians from the early 970s. He was the son of Grand Prince Taksony of Hungary, Taksony and his OrientalKhazars, Khazar, Pechenegs, Pecheneg or Volga Bulgarianwife. He married Sarolt, a daughter of an Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Hungarian chieftain. After ascending the throne, Géza made peace with the Holy Roman Empire. Within Hungary, he consolidated his authority with extreme cruelty, according to the unanimous narration of nearly contemporaneous sources. He was the first Hungarian monarch to support Christian missionaries from Western Europe. Although he was baptised (his baptismal name was Stephen), his Christian faith remained shallow and he continued to perform acts of pagan worship. He was succeeded by his son Stephen I of Hungary, Stephen, who was crowned the first King of Hungary in 1000 or 1001. Early life Géza was the elder son of Taksony of Hungary, Taksony, Grand Prince of the Hungarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taksony Of Hungary
Taksony (, also Taxis or Tocsun; before or around 931 – early 970s) was the Grand Prince of the Hungarians after their catastrophic defeat in the 955 Battle of Lechfeld. In his youth he had participated in plundering raids in Western Europe, but during his reign the Hungarians only targeted the Byzantine Empire. The ''Gesta Hungarorum'' recounts that significant Muslim and Pecheneg groups settled in Hungary under Taksony. Early life Taksony was the son of Zoltán, according to the ''Gesta Hungarorum'' (written around 1200). The same source adds that Taksony's mother was an unnamed daughter of Menumorut, a local ruler defeated by the conquering Hungarians shortly before 907. Its unknown author also says that Taksony was born "in the year of Our Lord's incarnation 931". The ''Gesta Hungarorum'' reports that Zoltán abdicated in favor of Taksony in 947, three years before his own death. However, modern historians have challenged existing information on Taksony's early li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fajsz
Fajsz (), also Falicsi (), was Grand Prince of the Hungarians from about 950 to around 955. All information on him comes from ''De administrando imperio'', a book written by the Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus. No other contemporary source or later Hungarian chronicle preserved his name, suggesting that he did not take an active role in the politics of the Hungarian tribes' confederation. Life Fajsz was the only known son of Jutotzas, the third son of Árpád who led the Hungarian tribes' confederation at the time of their conquest of the Carpathian Basin between around 895 and 907. After Árpád's death, fundamental changes happened in the government of the tribal confederation. Although the various tribes could even thereafter act in concert for raids, they did not obey a strong central authority any more. Even so, as the historian Miklós Molnár emphasizes, "the supremacy of the House of Árpád seems to have remained unshaken." For instance, Hungaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoltán Of Hungary
Zoltán (; 880 or 903 – 950), also Zolta, Zsolt, Solt or Zaltas is mentioned in the '' Gesta Hungarorum'' as the third Grand Prince of the Hungarians who succeeded his father Árpád around 907. Although modern historians tend to deny this report on his reign, because other chronicles do not list him among the Hungarian rulers, there is consensus that even if Zoltán never ascended the throne, all monarchs ruling in Hungary from the House of Árpád after around 955 were descended from him. Life Zoltán in the ''Gesta Hungarorum'' Modern historians' main source of Zoltán's life is the ''Gesta Hungarorum'', a late 12th-century chronicle whose writer is now known as Anonymus. According to this source, Zoltán was the only son of Árpád, Grand Prince of the Hungarians. In contrast, the nearly contemporary Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus writes that "Zaltas" was Árpád's fourth son. Zoltán's name seemingly derived from the Arabian sultan title wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Árpád
Árpád (; 845 – 907) was the head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries. He might have been either the sacred ruler or '' kende'' of the Hungarians, or their military leader or '' gyula'', although most details of his life are debated by historians, because different sources contain contradictory information. Despite this, many Hungarians refer to him as the "founder of our country", and Árpád's preeminent role in the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin has been emphasized by some later chronicles. The dynasty descending from Árpád ruled the Kingdom of Hungary until 1301. Biography Early life Árpád was the son of Álmos who is mentioned as the first head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes by all Hungarian chronicles. His mother's name and family are unknown. According to historian Gyula Kristó, Árpád was born around 845. His name derived from the Hungarian word for barley, ''árpa''. The B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Prince Of The Hungarians
Grand Prince () was the title used by contemporary sources to name the leader of the federation of the Hungarian tribes in the tenth century.Constantine VII mentioned Árpád in his book De Administrando Imperio as ', while Bruno of Querfurt referred to Géza in his ''Sancti Adalberti Pragensis episcopi et martyris vita altera'' as '. The grand prince (') was probably elected by the leaders of the federation of the seven Hungarian tribes and the three Kabar tribes (dissident Khazar tribes) that joined the Hungarians before 830. However, the first grand prince, Álmos, father of Árpád, was more likely appointed by the khagan of the Khazars. It is still under discussion whether the grand prince was the spiritual leader of the federation ('), the military commander of the Hungarian tribes (') or the title was a new creation. When the Hungarians were pushed out of ' and moved to the Carpathian Basin ('), the grand prince's power seemed to be decreasing. By the time of Gé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurszán
Kurszán or Kusál (died 904), was a Hungarian (Magyar) chieftain at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries, who had a crucial role in the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin. He was '' kende'' of the Magyars in the dual leadership with Árpád serving as a '' gyula'' - according to a mainstream theory. While ''kende'' probably corresponded roughly to the Khazar title ''khagan'', Kurszán's role equated to the Khazar military title '' bek''. In Latin sources he was referred to as '' rex'' and some scholars say he had a political status as a sacred king until he was massacred in a political plot of Western rulers and was temporarily succeeded by Árpád. There is also arguments that Kurszán, who appears as an active actor in Western and Byzantine sources, rather held the dignity of ''gyula'', while Álmos then Árpád served as ''kende'', the "sacred king". The name of Kurszán According to some historians, such as Gyula Kristó, it is wrong to call the conquering princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |