|
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics encompasses a variety of Statistics, statistical techniques from data mining, Predictive modelling, predictive modeling, and machine learning that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about future or otherwise unknown events. In business, predictive models exploit Pattern detection, patterns found in historical and transactional data to identify risks and opportunities. Models capture relationships among many factors to allow assessment of risk or potential associated with a particular set of conditions, guiding decision-making for candidate transactions. The defining functional effect of these technical approaches is that predictive analytics provides a predictive score (probability) for each individual (customer, employee, healthcare patient, product SKU, vehicle, component, machine, or other organizational unit) in order to determine, inform, or influence organizational processes that pertain across large numbers of individuals, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cash Flow
Cash flow, in general, refers to payments made into or out of a business, project, or financial product. It can also refer more specifically to a real or virtual movement of money. *Cash flow, in its narrow sense, is a payment (in a currency), especially from one central bank account to another. The term 'cash flow' is mostly used to describe payments that are expected to happen in the future, are thus uncertain, and therefore need to be forecast with cash flows. *A cash flow is determined by its time , nominal amount , currency , and account ; symbolically, . Cash flows are narrowly interconnected with the concepts of value, interest rate, and liquidity. A cash flow that shall happen on a future day can be transformed into a cash flow of the same value in . This transformation process is known as discounting, and it takes into account the time value of money by adjusting the nominal amount of the cash flow based on the prevailing interest rates at the time. Cash flow analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Management
Decision management refers to the process of designing, building, and managing automated decision-making systems that support or replace human decision-making in organizations. It integrates business rules, predictive analytics, and decision modeling to streamline and automate operational decisions. These systems combine business rules and potentially machine learning to automate routine business decisions and are typically embedded in business operations where large volumes of routine decisions are made, such as fraud detection, customer service routing, and claims processing. Decision management differs from decision support systems in that its primary focus is on automating ''operational'' decisions, rather than solely providing information to assist human decision-makers. It incorporates technologies designed for real-time decision-making with minimal human intervention. Historical background The roots of decision management can be traced back to the expert systems and mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criminal Reduction Utilising Statistical History
Criminal Reduction Utilising Statistical History (CRUSH) is an IBM predictive analytics system that attempts to predict the location of future crimes. It was developed as part of the Blue CRUSH program in conjunction with Memphis Police Department and the University of Memphis Criminology and Research department. In Memphis it was “credited as a key factor behind a 31 per cent fall in crime and 15 per cent drop in violent crime.” , it was being trialed by two British police forces. In 2014 a modified version of the system, called CRASH (Crash Reduction Analysing Statistical History) became operational in Tennessee aimed at preventing vehicle accidents. See also * Crime mapping Crime mapping is used by analysts in law enforcement agency, law enforcement agencies to map, visualize, and analyze crime incident patterns. It is a key component of crime analysis and the CompStat policing strategy. Mapping crime, using Geogr ... References {{IBM Crime mapping Crime pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Sociology
Computational sociology is a branch of sociology that uses computationally intensive methods to analyze and model social phenomena. Using computer simulations, artificial intelligence, complex statistical methods, and analytic approaches like social network analysis, computational sociology develops and tests theories of complex social processes through bottom-up modeling of social interactions. It involves the understanding of social agents, the interaction among these agents, and the effect of these interactions on the social aggregate. Although the subject matter and methodologies in social science differ from those in natural science or computer science, several of the approaches used in contemporary social simulation originated from fields such as physics and artificial intelligence. Some of the approaches that originated in this field have been imported into the natural sciences, such as measures of network centrality from the fields of social network analysis and network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
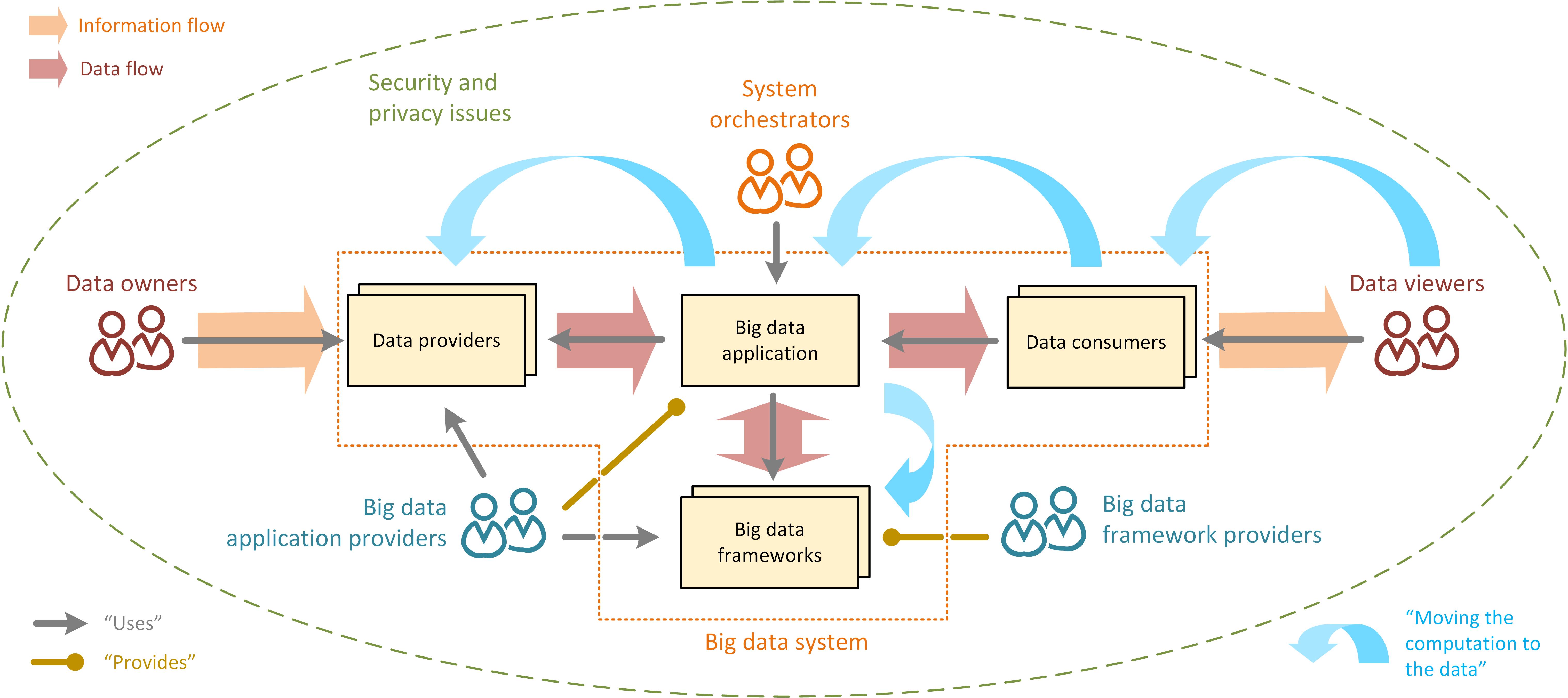
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Procedures (finance Auditing)
Analytical procedures are one of many financial audit procedures which help an auditor understand an entity's business and changes in the business, and to identify potential risk areas to plan other audit procedures. It can also be an audit substantive test involving the evaluation of financial information made by a study of plausible relationships among both financial and non-financial data. Analytical procedures also encompass such investigation as is necessary of identified fluctuations or relationships that are inconsistent with other relevant information or that differ from expected values by a significant amount. Use and stage Analytical procedures are performed at three stages of the audit: at the start, in the middle and at the end of the audit. These three stages are risk assessment procedures, substantive analytical procedures, and final analytical procedures. * Risk assessment procedures are used to assist the auditor to better understand the business and to plan the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence In Healthcare
Artificial intelligence in healthcare is the application of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze and understand complex medical and healthcare data. In some cases, it can exceed or augment human capabilities by providing better or faster ways to diagnose, treat, or prevent disease. As the widespread use of AI in healthcare is still relatively new, research is ongoing into its applications across various medical subdisciplines and related industries. AI programs are being applied to practices such as Medical diagnosis, diagnostics, Medical guideline, treatment protocol development, drug development, personalized medicine, and patient monitoring and care. Since Radiography, radiographs are the most commonly performed imaging tests in radiology, the potential for AI to assist with triage and interpretation of radiographs is particularly significant. Using AI also presents unprecedented ethical concerns related to issues such as Information privacy, data privacy, automation of j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actuarial Science
Actuarial science is the discipline that applies mathematics, mathematical and statistics, statistical methods to Risk assessment, assess risk in insurance, pension, finance, investment and other industries and professions. Actuary, Actuaries are professionals trained in this discipline. In many countries, actuaries must demonstrate their competence by passing a series of rigorous professional examinations focused in fields such as probability and predictive analysis. Actuarial science includes a number of interrelated subjects, including mathematics, probability theory, statistics, finance, economics, financial accounting and computer science. Historically, actuarial science used deterministic models in the construction of tables and premiums. The science has gone through revolutionary changes since the 1980s due to the proliferation of high speed computers and the union of stochastic actuarial models with modern financial theory. Many universities have undergraduate and gradu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor. Bankrupt is not the only legal status that an insolvent person may have, meaning the term ''bankruptcy'' is not a synonym for insolvency. Etymology The word ''bankruptcy'' is derived from Italian language, Italian , literally meaning . The term is often described as having originated in Renaissance Italy, where there allegedly existed the tradition of smashing a banker's bench if he defaulted on payment. However, the existence of such a ritual is doubted. History In Ancient Greece, bankruptcy did not exist. If a man owed and he could not pay, he and his wife, children or servants were forced into "debt slavery" until the creditor recouped losses through their Manual labour, physical labour. Many city-states in ancient Greece lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Default (finance)
In finance, default is failure to meet the legal obligations (or conditions) of a loan, for example when a home buyer fails to make a mortgage payment, or when a corporation or government fails to pay a bond which has reached maturity. A national or sovereign default is the failure or refusal of a government to repay its national debt. The biggest private default in history is Lehman Brothers, with over $600 billion when it filed for bankruptcy in 2008 (equivalent to over $ billion in ). The biggest sovereign default is Greece, with $138 billion in March 2012 (equivalent to $ billion in ). Distinction from insolvency, illiquidity and bankruptcy The term "default" should be distinguished from the terms "insolvency", illiquidity and "bankruptcy": * Default: Debtors have been passed behind the payment deadline on a debt whose payment was due. * Illiquidity: Debtors have insufficient cash (or other "liquefiable" assets) to pay debts. * Insolvency: A legal term meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underwrite
Underwriting (UW) services are provided by some large financial institutions, such as banks, insurance companies and investment houses, whereby they guarantee payment in case of damage or financial loss and accept the financial risk for liability arising from such guarantee. An underwriting arrangement may be created in a number of situations including insurance, issues of security in a public offering, and bank lending, among others. The person or institution that agrees to sell a minimum number of securities of the company for commission is called the underwriter. History The term "underwriting" derives from the Lloyd's of London insurance market. Financial backers (or risk takers), who would accept some of the risk on a given venture (historically a sea voyage with associated risks of shipwreck) in exchange for a premium, would literally write their names under the risk information that was written on a Lloyd's slip created for this purpose. Securities underwriting In the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |