|
Potassium Nonahydridorhenate
Potassium nonahydridorhenate(VII) is an inorganic compound having the formula . This colourless salt is soluble in water but only poorly soluble in most alcohols. This salt contains the nonahydridorhenate(VII) anion, , which is a rare example of a coordination complex bearing only hydride ligands. History The study of rhenium hydrides can be traced to the 1950s and included reports of the "rhenide" anion, supposedly . These reports led to a series of investigations by A. P. Ginsberg and coworkers on the products from the reduction of perrhenate. The ''rhenide'' anion, , was based on the product of the reduction of perrhenate salts, such as the reduction of potassium perrhenate () by potassium metal. "Potassium rhenide" was shown to exist as a tetrahydrated complex, with the postulated chemical formula (potassium rhenide tetrahydrate). This compound exhibits strongly reducing properties, and slowly yields hydrogen gas when dissolved in water. The lithium and thallous salts were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep Mantle (geology), mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salt (chemistry), salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within life, living things. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
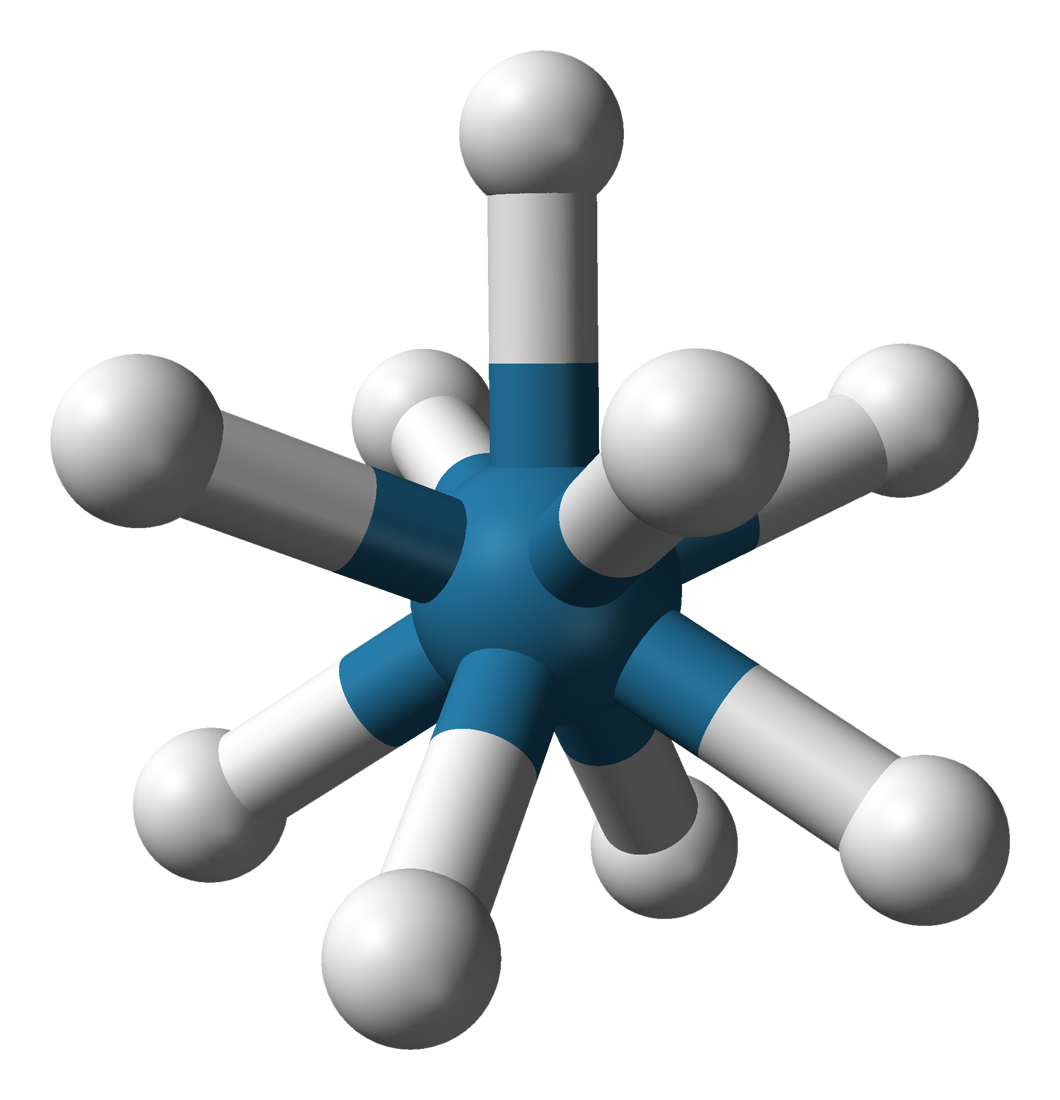
Tricapped Trigonal Prismatic Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, the tricapped trigonal prismatic molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds where nine atoms, groups of atoms, or ligands are arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of a triaugmented triangular prism (a trigonal prism In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The oc ... with an extra atom attached to each of its three rectangular faces). It is very similar to the capped square antiprismatic molecular geometry, and there is some dispute over the specific geometry exhibited by certain molecules. Examples * * (Ln = La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy) * References Stereochemistry Molecular geometry {{Stereochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Phase
In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of material that is chemically uniform, physically distinct, and (often) mechanically separable. In a system consisting of ice and water in a glass jar, the ice cubes are one phase, the water is a second phase, and the humid air is a third phase over the ice and water. The glass of the jar is a different material, in its own separate phase. (See .) More precisely, a phase is a region of space (a thermodynamic system), throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, magnetization and chemical composition. The term ''phase'' is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but there can be several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (as where oil and water separate into distinct phases, both in the liquid state). Types of phases Distinct phases may be described as different states of matter such as gas, liquid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Symmetry
In chemistry, molecular symmetry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of these molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it can be used to predict or explain many of a molecule's chemical property, chemical properties, such as whether or not it has a molecular dipole moment, dipole moment, as well as its allowed spectroscopy, spectroscopic transitions. To do this it is necessary to use group theory. This involves classifying the states of the molecule using the irreducible representations from the character table of the symmetry group of the molecule. Symmetry is useful in the study of molecular orbitals, with applications to the Hückel method, to ligand field theory, and to the Woodward–Hoffmann rules. Many university level textbooks on physical chemistry, quantum chemistry, spectroscopy and inorganic chemistry discuss symmetry. Another framework on a larger scale is the use of crystal sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Functional Theory
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals - that is, functions that accept a function as input and output a single real number. In the case of DFT, these are functionals of the spatially dependent electron density. DFT is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry. DFT has been very popular for calculations in solid-state physics since the 1970s. However, DFT was not considered accurate enough for calculations in quantum chemistry until the 1990s, when the approximations used in the theory were greatly refined to better m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isostructural
Isostructural chemical compounds have similar chemical structures. " Isomorphous" when used in the relation to crystal structures is not synonymous: in addition to the same atomic connectivity that characterises isostructural compounds, isomorphous substances crystallise in the same space group and have the same unit cell dimensions. The IUCR definition used by crystallographers is: Examples include: *I- Gold(I) bromide is isostructural with gold(I) chloride *Borazine is isostructural with benzene * Indium(I) bromide is isostructural with β- thallium(I) iodide and has a distorted rock salt structure. Many minerals are isostructural when they differ only in the nature of a cation. Compounds which are isoelectronic usually have similar chemical structures. For example, methane, CH4, and the ammonium ion, NH4+, are isoelectric and are isostructural as both have a tetrahedral structure. The C-H and N-H bond lengths are different and crystal structures are completely different bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraethylammonium
Tetraethylammonium (TEA) is a quaternary ammonium cation with the chemical formula , consisting of four ethyl groups (, denoted Et) attached to a central nitrogen atom. It is a counterion used in the research laboratory to prepare lipophilic salts of inorganic anions. It is used similarly to tetrabutylammonium, the difference being that its salts are less lipophilic, more easily crystallized and more Toxicity, toxic. Preparation The halide salt is prepared by the reaction of triethylamine and an ethyl halide: : This method works well for the preparation of tetraethylammonium iodide (where X = I). Most tetraethylammonium salts are prepared by salt metathesis reactions. For example, the synthesis of tetraethylammonium perchlorate, a salt that has been useful as a supporting electrolyte for polarography, polarographic studies in non-aqueous solvents, is carried out by mixing the water-soluble salts tetraethylammonium bromide and sodium perchlorate in water, from which the water-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cation Exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one species of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid. Ion exchange is used in softening or demineralizing of water, purification of chemicals, and separation of substances. Ion exchange usually describes a process of purification of aqueous solutions using solid polymeric ion-exchange resin. More precisely, the term encompasses a large variety of processes where ions are exchanged between two electrolytes. Aside from its use to purify drinking water, the technique is widely applied for purification and separation of a variety of industrially and medicinally important chemicals. Although the term usually refers to applications of synthetic (human-made) resins, it can include many other materials such as soil. Typical ion exchangers are ion-exchange resins (functionalized porous or gel polymer), zeolites, montmorillonite, clay, and soil humus. Ion exchangers are eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Metal
Sodium is a chemical element; it has symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including humans. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Perrhenate
Sodium perrhenate (also known as sodium rhenate(VII)) is the inorganic compound with the formula NaReO4. It is a white salt that is soluble in water. It is a common precursor to other rhenium compounds. Its structure resembles that of sodium perchlorate and sodium permanganate. Preparation It can be prepared by treatment of rhenium heptoxide with base or by ion exchange Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one species of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid. Ion exchange is used in softening or demineralizing of water, purification of ch ... from the potassium salt. Sodium perrhenate can be prepared from rhenium metal with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of base. : Reactions It reacts with sodium in ethanol to give nonahydridorhenate. Sodium perrhenate has been used as a precursor of rhenium nitrides (such as Re3N, Re2N, Re3N2, ReN2, ReN3, ReN4), which can be used as catalysts for ammonia synthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl group, ethyl. Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technetium
Technetium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tc and atomic number 43. It is the lightest element whose isotopes are all radioactive. Technetium and promethium are the only radioactive elements whose neighbours in the sense of atomic number are both stable. All available technetium is produced as a synthetic element. Naturally occurring technetium is a spontaneous fission product in uranium ore and thorium ore (the most common source), or the product of neutron capture in molybdenum ores. This silvery gray, crystalline transition metal lies between manganese and rhenium in group 7 element, group 7 of the periodic table, and its chemical properties are intermediate between those of both adjacent elements. The most common naturally occurring isotope is 99Tc, in traces only. Many of technetium's properties had been predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev before it was discovered; Mendeleev noted a gap in his periodic table and gave the undiscovered element the provis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |