|
Position-specific Scoring Matrix
A position weight matrix (PWM), also known as a position-specific weight matrix (PSWM) or position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM), is a commonly used representation of motifs (patterns) in biological sequences. PWMs are often derived from a set of aligned sequences that are thought to be functionally related and have become an important part of many software tools for computational motif discovery. Background Creation Conversion of sequence to position probability matrix A PWM has one row for each symbol of the alphabet (4 rows for nucleotides in DNA sequences or 20 rows for amino acids in protein sequences) and one column for each position in the pattern. In the first step in constructing a PWM, a basic position frequency matrix (PFM) is created by counting the occurrences of each nucleotide at each position. From the PFM, a position probability matrix (PPM) can now be created by dividing that former nucleotide count at each position by the number of sequences, thereb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
LexA Gram Positive Bacteria Sequence Logo
The LexA repressor or LexA (Locus for X-ray sensitivity A) is a transcriptional repressor () that represses SOS response genes coding primarily for error-prone DNA polymerases, DNA repair enzymes and cell division inhibitors. LexA forms ''de facto'' a two-component regulatory system with RecA, which senses DNA damage at stalled replication forks, forming monofilaments and acquiring an active conformation capable of binding to LexA and causing LexA to cleave itself, in a process called autoproteolysis. LexA polypeptides contains a two domains: a DNA-binding domain and a dimerization domain. The dimerization domain binds to other LexA polypeptides to form dumbbell shaped dimers. The DNA-binding domain is a variant form of the helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif, and is usually located at the N-terminus of the protein. This domain is bound to an SOS box upstream of SOS response genes until DNA damage stimulates autoproteolysis. Clinical significance DNA damage can be inflicte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Information Content
In information theory, the information content, self-information, surprisal, or Shannon information is a basic quantity derived from the probability of a particular event occurring from a random variable. It can be thought of as an alternative way of expressing probability, much like odds or log-odds, but which has particular mathematical advantages in the setting of information theory. The Shannon information can be interpreted as quantifying the level of "surprise" of a particular outcome. As it is such a basic quantity, it also appears in several other settings, such as the length of a message needed to transmit the event given an optimal source coding of the random variable. The Shannon information is closely related to ''entropy'', which is the expected value of the self-information of a random variable, quantifying how surprising the random variable is "on average". This is the average amount of self-information an observer would expect to gain about a random variable whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
UniPROBE
The Universal PBM Resource for Oligonucleotide-Binding Evaluation (UniPROBE) is database of DNA-binding proteins determined by Protein microarray, protein-binding microarrays. See also * Protein microarray * DNA-binding domain References External links Official website Protein databases Microarrays Proteomics {{Biodatabase-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
ScerTF
ScerTF is a comprehensive database of position weight matrices for the transcription factors of Saccharomyces. See also *Transcription factor In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ... * Gary Stormo References External links * http://stormo.wustl.edu/ScerTF. Biological databases Gene expression {{Biodatabase-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Pfam
Pfam is a database of protein families that includes their annotations and multiple sequence alignments generated using hidden Markov models. The latest version of Pfam, 37.0, was released in June 2024 and contains 21,979 families. It is currently provided through InterPro website. Uses The general purpose of the Pfam database is to provide a complete and accurate classification of protein families and domains. Originally, the rationale behind creating the database was to have a semi-automated method of curating information on known protein families to improve the efficiency of annotating genomes. The Pfam classification of protein families has been widely adopted by biologists because of its wide coverage of proteins and sensible naming conventions. It is used by experimental biologists researching specific proteins, by structural biologists to identify new targets for structure determination, by computational biologists to organise sequences and by evolutionary biologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Hidden Markov Model
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is a Markov model in which the observations are dependent on a latent (or ''hidden'') Markov process (referred to as X). An HMM requires that there be an observable process Y whose outcomes depend on the outcomes of X in a known way. Since X cannot be observed directly, the goal is to learn about state of X by observing Y. By definition of being a Markov model, an HMM has an additional requirement that the outcome of Y at time t = t_0 must be "influenced" exclusively by the outcome of X at t = t_0 and that the outcomes of X and Y at t < t_0 must be conditionally independent of at given at time . Estimation of the parameters in an HMM can be performed using maximum likelihood estimation. For linear chain HMMs, the Baum–Welch algorithm can be used to estimate parameters. Hidden Markov models are known for their applications to thermodynamics, statistical mechanics, physics, chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
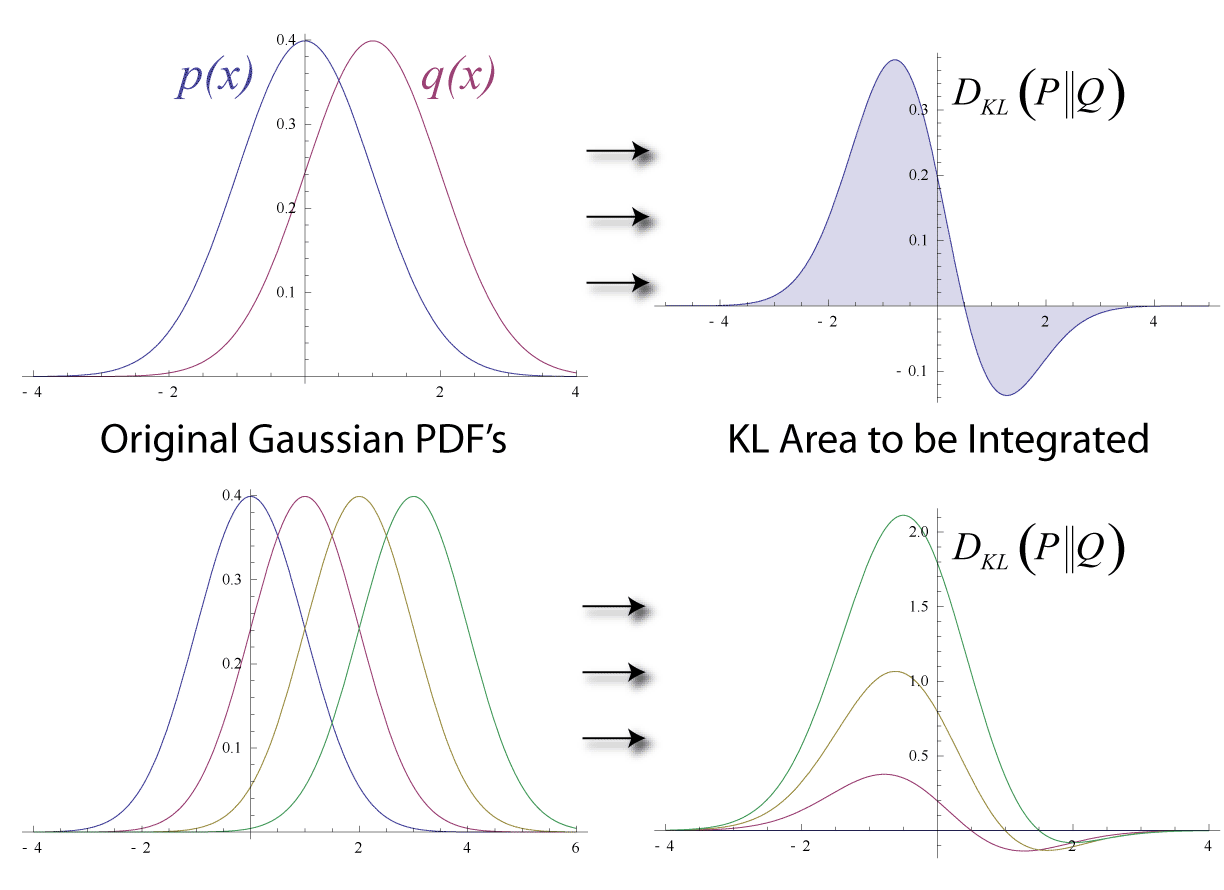 |
Kullback–Leibler Divergence
In mathematical statistics, the Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence (also called relative entropy and I-divergence), denoted D_\text(P \parallel Q), is a type of statistical distance: a measure of how much a model probability distribution is different from a true probability distribution . Mathematically, it is defined as D_\text(P \parallel Q) = \sum_ P(x) \, \log \frac\text A simple interpretation of the KL divergence of from is the expected excess surprise from using as a model instead of when the actual distribution is . While it is a measure of how different two distributions are and is thus a distance in some sense, it is not actually a metric, which is the most familiar and formal type of distance. In particular, it is not symmetric in the two distributions (in contrast to variation of information), and does not satisfy the triangle inequality. Instead, in terms of information geometry, it is a type of divergence, a generalization of squared distance, and for cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Thermophilic
A thermophile is a type of extremophile that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between . Many thermophiles are archaea, though some of them are bacteria and fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earliest bacteria. Thermophiles are found in geothermally heated regions of the Earth, such as hot springs like those in Yellowstone National Park and deep sea hydrothermal vents, as well as decaying plant matter, such as peat bogs and compost. They can survive at high temperatures, whereas other bacteria or archaea would be damaged and sometimes killed if exposed to the same temperatures. The enzymes in thermophiles function at high temperatures. Some of these enzymes are used in molecular biology, for example the ''Taq'' polymerase used in PCR. "Thermophile" is derived from the (''thermotita''), meaning heat, and (''philia''), love. Comparative surveys suggest that thermophile diversity is principally driven by pH, not temperature. Clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Self-information
In information theory, the information content, self-information, surprisal, or Shannon information is a basic quantity derived from the probability of a particular event occurring from a random variable. It can be thought of as an alternative way of expressing probability, much like odds or log-odds, but which has particular mathematical advantages in the setting of information theory. The Shannon information can be interpreted as quantifying the level of "surprise" of a particular outcome. As it is such a basic quantity, it also appears in several other settings, such as the length of a message needed to transmit the event given an optimal source coding of the random variable. The Shannon information is closely related to ''entropy'', which is the expected value of the self-information of a random variable, quantifying how surprising the random variable is "on average". This is the average amount of self-information an observer would expect to gain about a random variable wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Uniform Distribution (discrete)
In probability theory and statistics, the discrete uniform distribution is a symmetric probability distribution wherein each of some finite whole number ''n'' of outcome values are equally likely to be observed. Thus every one of the ''n'' outcome values has equal probability 1/''n''. Intuitively, a discrete uniform distribution is "a known, finite number of outcomes all equally likely to happen." A simple example of the discrete uniform distribution comes from throwing a fair six-sided die. The possible values are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and each time the die is thrown the probability of each given value is 1/6. If two dice were thrown and their values added, the possible sums would not have equal probability and so the distribution of sums of two dice rolls is not uniform. Although it is common to consider discrete uniform distributions over a contiguous range of integers, such as in this six-sided die example, one can define discrete uniform distributions over any finite set. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
GC-content
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out of an implied four total bases, also including adenine and thymine in DNA and adenine and uracil in RNA. GC-content may be given for a certain fragment of DNA or RNA or for an entire genome. When it refers to a fragment, it may denote the GC-content of an individual gene or section of a gene (domain), a group of genes or gene clusters, a non-coding region, or a synthetic oligonucleotide such as a primer. Structure Qualitatively, guanine (G) and cytosine (C) undergo a specific hydrogen bonding with each other, whereas adenine (A) bonds specifically with thymine (T) in DNA and with uracil (U) in RNA. Quantitatively, each GC base pair is held together by three hydrogen bonds, while AT and AU base pairs are held together by two hydrogen bonds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Sequence Motif
In biology, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and usually assumed to be related to biological function of the macromolecule. For example, an ''N''-glycosylation site motif can be defined as ''Asn, followed by anything but Pro, followed by either Ser or Thr, followed by anything but Pro residue''. Overview When a sequence motif appears in the exon of a gene, it may encode the " structural motif" of a protein; that is a stereotypical element of the overall structure of the protein. Nevertheless, motifs need not be associated with a distinctive secondary structure. " Noncoding" sequences are not translated into proteins, and nucleic acids with such motifs need not deviate from the typical shape (e.g. the "B-form" DNA double helix). Outside of gene exons, there exist regulatory sequence motifs and motifs within the " junk", such as satellite DNA. Some of these are believed to affect the shape of nucleic acids (see for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |