|
Plug-in Electric Vehicles In Finland
, there were about 27,000 battery electric vehicles and 84,000 plug-in hybrid vehicles in Finland. , 31% of new cars sold in Finland were electric. Statistics , the Volkswagen ID.4 was the best-selling electric vehicle in Finland. Government policy , the Finnish government offers tax rebates of up to €2,000 for electric vehicle purchases. Charging stations , there were 1,302 public charging station locations in Finland. Public opinion In a 2022 poll conducted by Tori Auto, slightly more than half of respondents in Finland said that they were unwilling to buy an electric car for their next vehicle purchase, compared with 30% for Plug-in electric vehicles in Norway, Norway and Plug-in electric vehicles in Sweden, Sweden, and 23% for Plug-in electric vehicles in Denmark, Denmark. By region Central Finland , 18% of new cars registered in Central Finland were electric. North Ostrobothnia , there were about 900 electric vehicles in Oulu. Pirkanmaa , there were about 1,500 elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Electric Vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, with no secondary source of propulsion (a hydrogen fuel cell, internal combustion engine, etc.). BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of internal combustion engines (ICEs) for propulsion. They derive all power from battery packs and thus have no internal combustion engine, fuel cell, or fuel tank. BEVs include – but are not limited to – motorcycles, bicycles, scooters, skateboards, railcars, watercraft, forklifts, buses, trucks, and cars. In 2016, there were 210 million electric bikes worldwide used daily. Cumulative global sales of highway-capable light-duty pure electric car vehicles passed the one million unit milestone in September 2016. , the world's top selling all-electric car in history is the Tesla Model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery pack can be recharged by plugging a charging cable into an external electric power source, in addition to internally by its on-board internal combustion engine-powered generator. Most PHEVs are passenger cars, but there are also PHEV versions of commercial vehicles and vans, utility trucks, buses, trains, motorcycles, mopeds, and even military vehicles. Similar to all-electric vehicles (BEVs), PHEVs displace greenhouse gas emissions from the car tailpipe exhaust to the power station generators powering the electricity grid. These centralized generators may be of renewable energy (e.g. solar, wind or hydroelectric) and largely emission-free, or have an overall lower emission intensity than individual internal combustion engines. Compared to conventional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), PHEVs have a larger battery pack that can be charged from the power grid, which is also more efficient and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkswagen ID
The Volkswagen ID. series is a family of battery electric cars from Volkswagen (VW), built on the MEB platform (German: ''Modularer E-Antriebs-Baukasten;'' English'': modular electric-drive toolkit'') that is developed by the Volkswagen Group for a range of electric cars manufactured by its subsidiaries. Most of its production vehicles were adapted from several concept car A concept car (also known as a concept vehicle, show vehicle or prototype) is a car made to showcase new styling and/or new technology. They are often exhibited at motor shows to gauge customer reaction to new and radical designs which may or ... models. History and etymology The ID. series is the first series of electric cars from VW that are purpose built from the ground up to be electric vehicles. According to Volkswagen, ID. stands for "intelligent design, identity and visionary technologies". Production models Upcoming models Concept vehicles See also * Volkswagen Group MEB platfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charging Station
A charging station, also known as a charge point or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), is a piece of equipment that supplies electrical power for charging plug-in electric vehicles (including electric cars, electric trucks, electric buses, neighborhood electric vehicles, and plug-in hybrids). There are two main types: AC charging stations and DC charging stations. Batteries can only be charged with direct current (DC) electric power, while most electricity is delivered from the power grid as alternating current (AC). For this reason, most electric vehicles have a built-in AC-to-DC converter, commonly known as the "onboard charger". At an AC charging station, AC power from the grid is supplied to this onboard charger, which produces DC power to charge the battery. DC chargers facilitate higher power charging (which requires much larger AC-to-DC converters) by building the converter into the charging station instead of the vehicle to avoid size and weight restrictions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
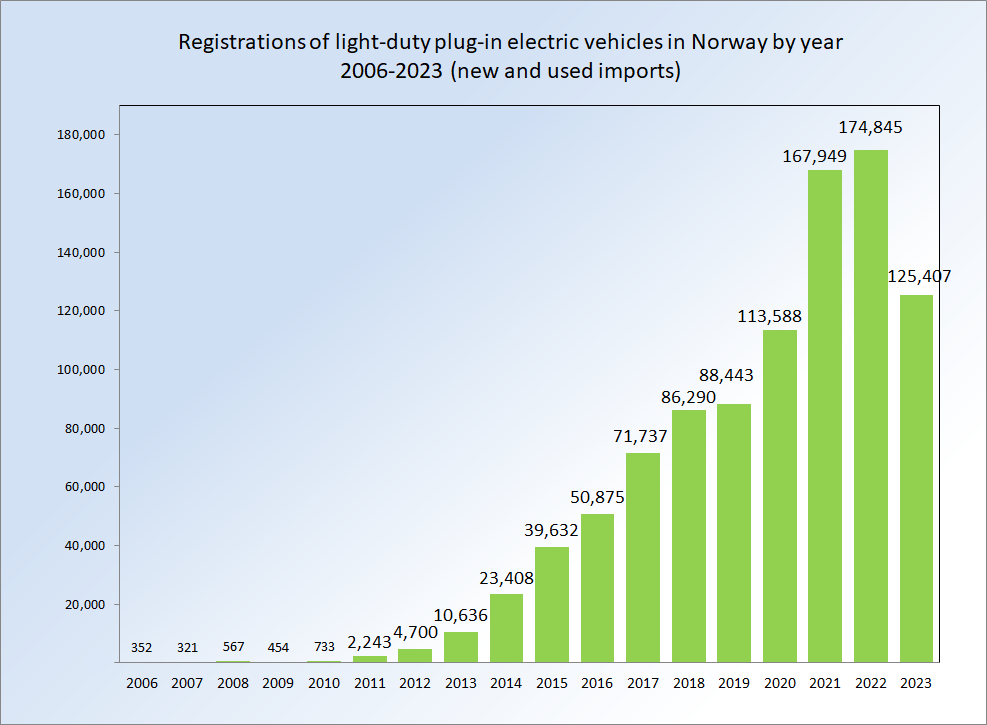
Plug-in Electric Vehicles In Norway
The Norwegian fleet of plug-in electric vehicles is the largest per capita in the world. ''See table "Elbilsalg i 2011 fordelt på måned og merke" (Electric vehicle sales in 2011, by month and brand) to see monthly sales for 2011.'' In December 2016, Norway became the first country where five in every 100 passenger cars on the road were plug-in; attained 10% in October 2018, and reached 25% in September 2022. See graph under "Personbilbestanden i Norge fordelt på drivstoff" – '', there were 18.87% all-electric cars and 6.55% plug-in hybrid cars in use on Norwegian roads. Combined plug-in electric passenger cars represented 25.42% of all passenger cars in circulation in the country''. The Norwegian plug-in car segment market share has been world's highest for several years, achieving 29.1% of new cars sold in 2016, 39.2% in 2017, 49.1% in 2018 55.9% in 2019, and 74.7% in 2020. The record uptake rate achieved in 2020 allowed Norway to become the first country in the world wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-in Electric Vehicles In Sweden
The adoption of plug-in electric vehicles in Sweden is actively supported by the Government of the Kingdom of Sweden. , a total of 355,737 light-duty plug-in electric vehicles have been registered since 2011, consisting of 226,731 plug-in hybrids, 120,343 all-electric cars, and 8,663 fully electric commercial vans. ''A total of 4,656 super clean cars and 282 all-electric vans were registered in Sweden in 2014. Super clean cars are those with carbon dioxide emissions of up to 50 g/km (two Porsche plug-in models, the Panamera S E-Hybrid and the 918 Spyder are not accounted as super clean cars, instead they are accounted with conventional hybrids). In 2011 there were 181 plug-in electric vehicles registered, 928 in 2012, 1,546 in 2013 and 4,656 super clean cars were registered during 2014. Since the introduction of the super clean car rebate in January 2012 until December 2014, a total of 7,130 super clean cars have been registered.'' Sweden has ranked among the world's top ten best- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-in Electric Vehicles In Denmark
, there were 97,121 battery electric vehicles and 97,071 plug-in hybrid vehicles registered in Denmark, together equivalent to about 7% of all vehicles in the country. , 19.1% of all new cars sold in Denmark were fully electric, and 18.0% were plug-in hybrid. In 2022, Denmark was ranked by Forbes as the third most EV-friendly country in the world. History In the late 1980s to early 1990s, a few thousand of the small, one-person and locally produced '' Ellert'' were sold in Denmark, but relatively few remain today. In the following decade, very few electric cars were sold in Denmark, but a clear increase began around 2010. Up to and including 2015, electric cars had been exempt from vehicle registration tax, but it was decided that this would be gradually outphased: In 2016, the vehicle registration tax for electric cars was placed at 20% of the normal rate, in 2017 it was planned to increase to 40% and within five years it would become the full rate. This had a large effect on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Finland
Central Finland ( fi, Keski-Suomi; sv, Mellersta Finland) is a region ( / ) in Finland. It borders the regions of Päijät-Häme, Pirkanmaa, South Ostrobothnia, Central Ostrobothnia, North Ostrobothnia, North Savo, and South Savo. The city of Jyväskylä is the regional centre and by far the largest city in the area. The largest lake in the very water-based region is Lake Päijänne (1,080 km2). Other large lakes are Lake Keitele (490 km2), Lake Konnevesi (190 km2) and Lake Kivijärvi (150 km2). The highest point in the region is Kiiskilänmäki in the municipality of Multia, which reaches an altitude of 269 meters above sea level. Kuokanjoki, Finland's shortest river and one of the world's shortest rivers is in the region. Central Finland has been one of the slowly growing regions in terms of population, but the growth has been based on the Jyväskylä sub-region's position as a significant growth center, and most of the region's municipalities are declining in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oulu
Oulu ( , ; sv, Uleåborg ) is a city, municipality and a seaside resort of about 210,000 inhabitants in the region of North Ostrobothnia, Finland. It is the most populous city in northern Finland and the fifth most populous in the country after: Helsinki, Espoo, Tampere and Vantaa, and the fourth largest urban area in the country after Helsinki, Tampere and Turku. Oulu's neighbouring municipalities are: Hailuoto, Ii, Kempele, Liminka, Lumijoki, Muhos, Pudasjärvi, Tyrnävä and Utajärvi. Due to its large population and geopolitically economic and cultural-historical location, Oulu has been called the "capital of Northern Finland". Oulu is also considered one of Europe's "living labs", where residents experiment with new technology (such as NFC tags and ubi-screens) on a community-wide scale. Despite only ranking in the top 2% universities, the University of Oulu is regionally known in the field of information technology. Oulu has also been very successful in recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tampere
Tampere ( , , ; sv, Tammerfors, ) is a city A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be de ... in the Pirkanmaa Regions of Finland, region, located in the western part of Finland. Tampere is the most populous inland city in the Nordic countries. It has a population of 244,029; the Tampere urban area, urban area has a population of 341,696; and the metropolitan area, also known as the Tampere sub-region, has a population of 393,941 in an area of . Tampere is the List of urban areas in Finland by population, second-largest urban area and List of Finnish municipalities, third most-populous individual municipality in Finland, after the cities of Helsinki and Espoo, and the most populous Finnish city outside the Greater Helsinki area. Today, Tampere is one of the major urban, econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satakunta
Satakunta (in both Finnish and Swedish, ) is a region ( / ) of Finland, part of the former Western Finland Province. It borders the regions of Southwest Finland, Pirkanmaa, South Ostrobothnia and Ostrobothnia. The capital city of the region is Pori. The name of the region literally means Hundred. The historical province of the same name was a larger area within Finland, covering modern Satakunta as well as much of Pirkanmaa. Municipalities The region of Satakunta is made up of 16 municipalities, of which 7 have city status (marked in bold). Northern Satakunta sub-region: * Jämijärvi **Population: * Kankaanpää **Population: * Karvia **Population: * Siikainen (''Siikais'') **Population: Pori sub-region: * Harjavalta **Population: * Huittinen (''Vittis'') **Population: * Kokemäki (''Kumo'') **Population: * Merikarvia (''Sastmola'') **Population: * Nakkila **Population: * Pomarkku (''Påmark'') **Population: * Pori (''Björneborg'') **Population: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turku
Turku ( ; ; sv, Åbo, ) is a city and former capital on the southwest coast of Finland at the mouth of the Aura River, in the region of Finland Proper (''Varsinais-Suomi'') and the former Turku and Pori Province (''Turun ja Porin lääni''; 1634–1997). The region was originally called Suomi (Finland), which later became the name for the whole country. As of 31 March 2021, the population of Turku was 194,244 making it the sixth largest city in Finland after Helsinki, Espoo, Tampere, Vantaa and Oulu. There were 281,108 inhabitants living in the Turku Central Locality, ranking it as the third largest urban area in Finland after the Capital Region area and Tampere Central Locality. The city is officially bilingual as percent of its population identify Swedish as a mother-tongue. It is unknown when Turku gained city rights. The Pope Gregory IX first mentioned the town ''Aboa'' in his ''Bulla'' in 1229 and the year is now used as the foundation year of Turku. Turku is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)