|
Platysace Effusa
''Platysace effusa'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a tuberous, perennial herb or shrub with linear leaves and white flowers in a compound umbel. Description ''Platysace effusa'' is a tuberous, perennial herb or shrub that typically grows to a height of and has wand-like branches. Its leaves are linear to wedge-shaped, usually long and often crowded. White flowers are borne in compound umbels with 4 to 8 rays on thin peduncles longer than the leaves, each ray with a partial umbel. Flowering occurs in most months and the fruit is flat and about long and notched at the base. Taxonomy This species was first formally described in 1849 by Nikolai Turczaninow who gave it the name ''Trachymene effusa'' in the journal ''Bulletin de la Société Impériale des Naturalistes de Moscou'' from specimens collected by James Drummond. In 1939, Cecil Norman transferred the species to '' Platysace'' as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turcz
Turcz is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Sępopol, within Bartoszyce County, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, close to the border with the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. References Villages in Bartoszyce County {{Bartoszyce-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platysace
''Platysace'' is a genus of about 22 species of woody perennial herbs, shrubs and subshrubs in the family Apiaceae, and is endemic to Australia. The flowers are borne on the ends of branches in a compound umbel and are bisexual or male with white, cream-coloured or pinkish flowers. Description Plants in the genus ''Platysace'' are woody perennial herbs, shrubs or subshrubs and have simple or lobed leaves. The flowers are borne on the ends of branches in a compound umbel with small bracts and bracteoles but that sometimes fall off as the flowers open. The flowers are bisexual or male, sometimes without sepals, and have white, cream-coloured or pinkish, elliptical to egg-shaped petals. The fruit has 2 compressed mericarps. Taxonomy The genus ''Platysace'' was first described in 1845 by Alexander von Bunge in Lehmann's ''Plantae Preissianae'', and the first species he described (the type species) was '' Platysace cirrosa''. A 2021 molecular phylogenetic study suggested that it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Flora Of Australia
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Western Australia
The flora of Western Australia comprises 10,842 published native vascular plant species and a further 1,030 unpublished species. They occur within 1,543 genus, genera from 211 Family (biology), families; there are also 1,335 naturalised alien or invasive plant species more commonly known as weeds. There are an estimated 150,000 cryptogam species or nonvascular plants which include lichens, and fungi although only 1,786 species have been published, with 948 algae and 672 lichen the majority. History Indigenous Australians have a long history with the flora of Western Australia. They have for over 50,000 years obtained detailed information on most plants. The information includes its uses as sources for food, shelter, tools and medicine. As Indigenous Australians passed the knowledge along orally or by example, most of this information has been lost, along many of the names they gave the flora. It was not until Europeans started to explore Western Australia that systematic written de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallee Bioregion
Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeography, biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie bioregions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive ''Eucalyptus'' mallee (habit), mallee vegetation. It has an area of . About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Mallee region has a complex shape with tortuous boundaries, but may be roughly approximated as the triangular area south of a line from Bruce Rock, Western Australia, Bruce Rock to Eyre, Western Australia, Eyre, but not within 40 kilometres (25 mi) of the south coast, except at its eastern limits. It has an area of about 79000 square kilometres (31000 mi2), making it about a qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarrah Forest
Jarrah Forest, also known as the Southwest Australia woodlands, is an interim Australian bioregion and ecoregion located in the south west of Western Australia.IBRA Version 6.1 data The name of the bioregion refers to the region's dominant plant community, jarrah forest – a tall, open forest in which the dominant overstory tree is jarrah ('''').Koch, J. M., & Samsa, G. P. (2007). Restoring Jarrah forest trees after bauxite mining in Western Australia. Restoration Ecology, 15(s4), S17- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geraldton Sandplains
Geraldton Sandplains is an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia, interim Australian bioregion of Western Australia. It has an area of . The Geraldton Sandplains is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion, as assessed by the World Wildlife Fund. Subregions See also * Shark Bay, Western Australia References Further reading * Thackway, R and I D Cresswell (1995) ''An interim biogeographic regionalisation for Australia : a framework for setting priorities in the National Reserves System Cooperative Program'' Version 4.0 Canberra : Australian Nature Conservation Agency, Reserve Systems Unit, 1995. Biogeography of Western Australia IBRA regions Plains of Australia Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub in Australia Southwest Australia {{WesternAustralia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperance Plains
Esperance Plains, also known as Eyre Botanical District, is a biogeography, biogeographic region in southern Western Australia on the South_coast_of_Western_Australia , south coast between the Avon Wheatbelt and Hampton bioregions, and bordered to the north by the Mallee (biogeographic region), Mallee region. It is a plain punctuated by granite and quartz outcrops and ranges, with a semi-arid Mediterranean climate and vegetation consisting mostly of mallee-heath and Proteaceae, proteaceous scrub. About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a bioregion under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Esperance Plains may be roughly approximated as the land within of the coast between Albany, Western Australia, Albany and Point Culver on the south coast of Western Australia. It has an area of about , making it about 9% of the Southwest Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
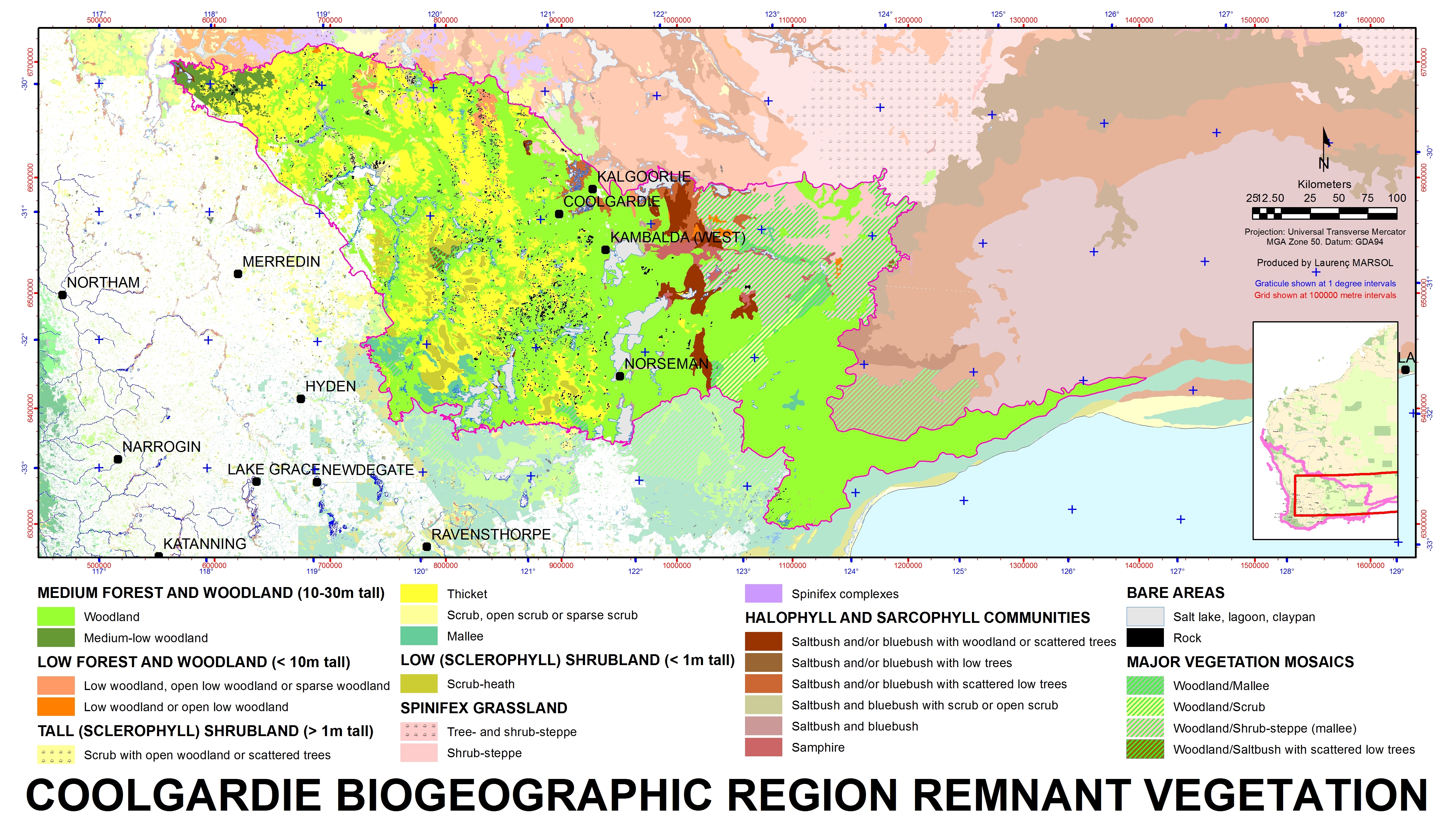
Coolgardie Bioregion
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avon Wheatbelt
The Avon Wheatbelt is a bioregion in Western Australia. It has an area of . It is considered part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion. Geography The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is mostly a gently undulating landscape with low relief. It lies on the Yilgarn craton, an ancient block of crystalline rock, which was uplifted in the Tertiary and dissected by rivers. The craton is overlain by laterite deposits, which in places have decomposed into yellow sandplains, particularly on low hills. Steep-sided erosional gullies, known as breakaways, are common. Beecham, Brett (2001). "Avon Wheatbelt 2 (AW2 - Re-juvenated Drainage subregion)" in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001. Accessed 15 May 2022/ref> In the south and west (the Katanning subregion), streams are mostly perennial, and feed rivers which drain westwards to empt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (often shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name, or a scientific name; more informally, it is also called a Latin name. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), the system is also called nomenclature, with an "n" before the "al" in "binominal", which is a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system". The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus ''Homo'' and within this genus to the species ''Hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Botany, British And Foreign
''Journal of Botany, British and Foreign'' is a monthly journal that was published from 1863 to 1942, and founded by Berthold Carl Seemann who was the editor until his death in 1871. It was initially published by Robert Hardwicke. Seemann himself took on most of the financial responsibility for the journal, which was never profitable, although he was assisted by various other botanists. He was succeeded as editor by Henry Trimen an employee of the British Museum, who also probably took on the expense of running it. Trimen resigned as editor on being appointed director of the Royal Botanical Gardens in Ceylon Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ... in 1879, and was succeeded by James Britten, another employee of the British Museum, who continued in the post for 45 yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |