|
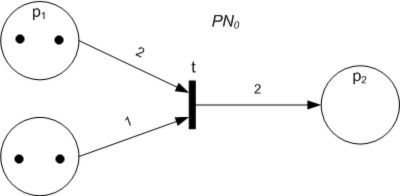
Petri Net
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition net (PT net), is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements: places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri — at the age of 13 — for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Adam Petri
Carl Adam Petri (12 July 1926 in Leipzig – 2 July 2010 in Siegburg) was a German mathematician and computer scientist. Life and work Petri created his major scientific contribution, the concept of the Petri net, in 1939 at the age of 13, for the purpose of describing chemical processes. In 1941, his father told him about Konrad Zuse's work on computing machines and Carl Adam started building his own analog computer. After earning his Abitur at Thomasschule in 1944, he was drafted into the Wehrmacht. He was taken into British captivity until 1949, when he departed England. Petri started studying mathematics at the Technische Hochschule Hannover (today, the Leibniz University Hannover) in 1950. He documented Petri nets in 1962 as part of his dissertation, (Communication with automata). From 1959 until 1962 he worked at the University of Bonn and received his PhD degree in 1962 from the Technische Universität Darmstadt. From 1963 to 1968 he established and directed the comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrency (computer Science)
Concurrency refers to the ability of a system to execute multiple tasks through simultaneous execution or time-sharing (context switching), sharing resources and managing interactions. Concurrency improves responsiveness, throughput, and scalability in modern computing, including: * Operating systems and embedded systems * Distributed systems, parallel computing, and high-performance computing * Database systems, web applications, and cloud computing Related concepts Concurrency is a broader concept that encompasses several related ideas, including: * Parallelism (simultaneous execution on multiple processing units). Parallelism executes tasks independently on multiple CPU cores. Concurrency allows for multiple ''threads of control'' at the program level, which can use parallelism or time-slicing to perform these tasks. Programs may exhibit parallelism only, concurrency only, both parallelism and concurrency, neither. * Multi-threading and multi-processing (shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Space
In computer science, a state space is a discrete space representing the set of all possible configurations of a system. It is a useful abstraction for reasoning about the behavior of a given system and is widely used in the fields of artificial intelligence and game theory. For instance, the toy problem Vacuum World has a discrete finite state space in which there are a limited set of configurations that the vacuum and dirt can be in. A "counter" system, where states are the natural numbers starting at 1 and are incremented over time has an infinite discrete state space. The angular position of an undamped pendulum is a continuous (and therefore infinite) state space. Definition State spaces are useful in computer science as a simple model of machines. Formally, a state space can be defined as a tuple [''N'', ''A'', ''S'', ''G''] where: * ''N'' is a Set (mathematics), set of states * ''A'' is a set of arcs connecting the states * ''S'' is a nonempty subset of ''N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Transitive Closure
In mathematics, a subset of a given set is closed under an operation on the larger set if performing that operation on members of the subset always produces a member of that subset. For example, the natural numbers are closed under addition, but not under subtraction: is not a natural number, although both 1 and 2 are. Similarly, a subset is said to be closed under a ''collection'' of operations if it is closed under each of the operations individually. The closure of a subset is the result of a closure operator applied to the subset. The ''closure'' of a subset under some operations is the smallest superset that is closed under these operations. It is often called the ''span'' (for example linear span) or the ''generated set''. Definitions Let be a set equipped with one or several methods for producing elements of from other elements of . Operations and (partial) multivariate function are examples of such methods. If is a topological space, the limit of a sequence of eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disjoint Sets
In set theory in mathematics and Logic#Formal logic, formal logic, two Set (mathematics), sets are said to be disjoint sets if they have no element (mathematics), element in common. Equivalently, two disjoint sets are sets whose intersection (set theory), intersection is the empty set.. For example, and are ''disjoint sets,'' while and are not disjoint. A collection of two or more sets is called disjoint if any two distinct sets of the collection are disjoint. Generalizations This definition of disjoint sets can be extended to family of sets, families of sets and to indexed family, indexed families of sets. By definition, a collection of sets is called a ''family of sets'' (such as the power set, for example). In some sources this is a set of sets, while other sources allow it to be a multiset of sets, with some sets repeated. An \left(A_i\right)_, is by definition a set-valued Function (mathematics), function (that is, it is a function that assigns a set A_i to every ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Set
In mathematics, particularly set theory, a finite set is a set that has a finite number of elements. Informally, a finite set is a set which one could in principle count and finish counting. For example, is a finite set with five elements. The number of elements of a finite set is a natural number (possibly zero) and is called the ''cardinality (or the cardinal number)'' of the set. A set that is not a finite set is called an '' infinite set''. For example, the set of all positive integers is infinite: Finite sets are particularly important in combinatorics, the mathematical study of counting. Many arguments involving finite sets rely on the pigeonhole principle, which states that there cannot exist an injective function from a larger finite set to a smaller finite set. Definition and terminology Formally, a set S is called finite if there exists a bijection for some natural number n (natural numbers are defined as sets in Zermelo-Fraenkel set theory). The number n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Computer Science (journal)
''Theoretical Computer Science'' (''TCS'') is a computer science journal published by Elsevier, started in 1975 and covering theoretical computer science. The journal publishes 52 issues a year. It is abstracted and indexed by Scopus and the Science Citation Index. According to the Journal Citation Reports, its 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... is 0.827. References Computer science journals Elsevier academic journals Academic journals established in 1975 {{comp-sci-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countable Set
In mathematics, a set is countable if either it is finite or it can be made in one to one correspondence with the set of natural numbers. Equivalently, a set is ''countable'' if there exists an injective function from it into the natural numbers; this means that each element in the set may be associated to a unique natural number, or that the elements of the set can be counted one at a time, although the counting may never finish due to an infinite number of elements. In more technical terms, assuming the axiom of countable choice, a set is ''countable'' if its cardinality (the number of elements of the set) is not greater than that of the natural numbers. A countable set that is not finite is said to be countably infinite. The concept is attributed to Georg Cantor, who proved the existence of uncountable sets, that is, sets that are not countable; for example the set of the real numbers. A note on terminology Although the terms "countable" and "countably infinite" as def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiset
In mathematics, a multiset (or bag, or mset) is a modification of the concept of a set that, unlike a set, allows for multiple instances for each of its elements. The number of instances given for each element is called the ''multiplicity'' of that element in the multiset. As a consequence, an infinite number of multisets exist that contain only elements and , but vary in the multiplicities of their elements: * The set contains only elements and , each having multiplicity 1 when is seen as a multiset. * In the multiset , the element has multiplicity 2, and has multiplicity 1. * In the multiset , and both have multiplicity 3. These objects are all different when viewed as multisets, although they are the same set, since they all consist of the same elements. As with sets, and in contrast to ''tuples'', the order in which elements are listed does not matter in discriminating multisets, so and denote the same multiset. To distinguish between sets and multisets, a notat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |