|
Peranema Asperum Var. ''rectangulare
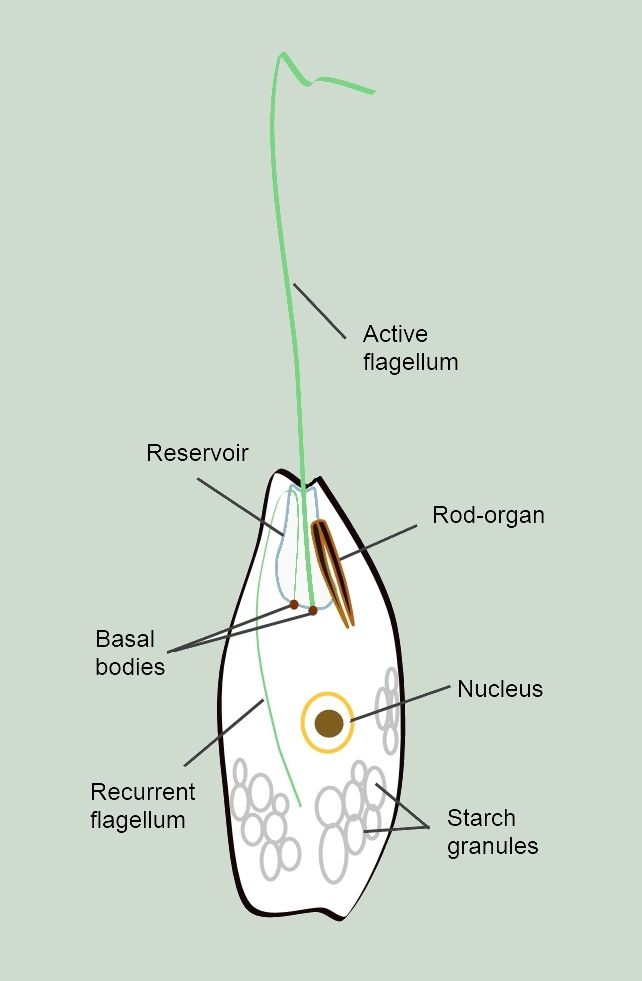
''Peranema'' is a genus of free-living phagotrophic euglenids (Euglenida; Euglenozoa; Excavata). There are more than 20 nominal species, varying in size between 8 and 200 micrometers. ''Peranema'' cells are gliding flagellates found in freshwater lakes, ponds and ditches, and are often abundant at the bottom of stagnant pools rich in decaying organic material. Although they belong to the class Euglenoidea, and are morphologically similar to the green ''Euglena'', ''Peranema'' have no chloroplasts, and do not conduct autotrophy. Instead, they capture live prey, such as yeast, bacteria and other flagellates, consuming them with the help of a rigid feeding apparatus called a "rod-organ." Unlike the green euglenids, they lack both an Eyespot apparatus, eyespot (stigma), and the Eyespot apparatus, paraflagellar body (photoreceptor) that is normally coupled with that organelle. However, while ''Peranema'' lack a localized photoreceptor, they do possess the light-sensitive protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Félix Dujardin
Félix Dujardin (5 April 1801 – 8 April 1860) was a French biologist born in Tours. He is remembered for his research on protozoans and other invertebrates. Biography In 1840 Dujardin was appointed professor of geology and mineralogy at the University of Toulouse, and during the following year was a professor of zoology and botany at Rennes. In regard to his educational background, Dujardin was largely self-taught, the son of a watchmaker. Dujardin worked with microscopic animal life, and in 1834 proposed that a new group of one-celled organisms be called Rhizopoda. He denied naturalist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg's theory that microscopic organisms were "complete organisms" similar to higher animals, specifically noting that they had specialized structures unique to single-celled organisms, which meant that the foraminiferan he was studying was not, as his contemporaries believed it to be, a mollusc. In addition to his studies of microscopic life, he did extensive rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a Protein dimer, dimer of two globular proteins, Tubulin#Eukaryotic, alpha and beta tubulin into #Structure, protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peranema In Phase Contrast
''Peranema'' is a genus of free-living phagotrophic euglenids (Euglenida; Euglenozoa; Excavata). There are more than 20 nominal species, varying in size between 8 and 200 micrometers. ''Peranema'' cells are gliding flagellates found in freshwater lakes, ponds and ditches, and are often abundant at the bottom of stagnant pools rich in decaying organic material. Although they belong to the class Euglenoidea, and are morphologically similar to the green ''Euglena'', ''Peranema'' have no chloroplasts, and do not conduct autotrophy. Instead, they capture live prey, such as yeast, bacteria and other flagellates, consuming them with the help of a rigid feeding apparatus called a "rod-organ." Unlike the green euglenids, they lack both an eyespot (stigma), and the paraflagellar body (photoreceptor) that is normally coupled with that organelle. However, while ''Peranema'' lack a localized photoreceptor, they do possess the light-sensitive protein rhodopsin, and respond to changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria: # the grouping contains its own most recent common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population), i.e. excludes non-descendants of that common ancestor # the grouping contains all the descendants of that common ancestor, without exception Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic'' grouping meets 1. but not 2., thus consisting of the descendants of a common ancestor, excepting one or more monophyletic subgroups. A '' polyphyletic'' grouping meets neither criterion, and instead serves to characterize convergent relationships of biological features rather than genetic relationships – for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, or aquatic insects. As such, these characteristic features of a polyphyletic grouping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglena Gracilis
''Euglena gracilis'' is a freshwater species of euglenid, a microscopic type of algae, in the genus ''Euglena''. It has secondary chloroplasts, and is a mixotroph able to feed by photosynthesis or phagocytosis. It has a highly flexible cell surface, allowing it to change shape from a thin cell up to 100 μm long to a sphere of approximately 20 μm. Each cell has two flagella, only one of which emerges from the flagellar pocket (reservoir) in the anterior of the cell, and can move by swimming, or by so-called "euglenoid" movement across surfaces. ''E. gracilis'' has been used extensively in the laboratory as a model organism, particularly for studying cell biology and biochemistry. Other areas of their use include studies of photosynthesis, photoreception, and the relationship of molecular structure to the biological function of subcellular particles, among others. ''Euglena gracilis'' is the most studied member of the Euglenaceae. ''E. gracilis'' was discovered as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a Multicellular organism, multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. The two main cells that do this are the Macrophages and the Neutrophils of the immune system. Where phagocytosis is used as a means of feeding and provides the organism part or all of its nourishment, it is called phagotrophy and is distinguished from osmotrophy, which is nutrition taking place by absorption. History The history of phag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Klebs
Georg Albrecht Klebs (23 October 1857 – 15 October 1918) was a German botanist from Neidenburg (Nidzica), Prussia. His brother was the historian Elimar Klebs. Life Klebs studied chemistry, philosophy, and art history at the University of Königsberg and became an assistant to Anton de Bary at the University of Strassburg. After his military service, Klebs became an assistant to Julius Sachs at the University of Würzburg and Wilhelm Pfeffer at the University of Tübingen. He became a professor at the University of Basel in 1887, the University of Halle in 1898, and the University of Heidelberg in 1907, where he founded today's botanical garden, the Botanischer Garten der Universität Heidelberg. Klebs received a Croonian Lectureship in 1910. From 1910 to 1912 he travelled through Siberia, Japan, Java, India, the Caucasus, and southern Russia. In 1913 he participated in an expedition to Egypt. He died in Heidelberg from influenza during the 1918 influenza pandemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astasia
Astasis is a lack of motor coordination marked by an inability to stand, walk or even sit without assistance due to disruption of muscle coordination. The term ''astasia'' is interchangeable with ''astasis'' and is most commonly referred to as ''astasia'' in the literature describing it. Astasis is the inability to stand or sit up without assistance in the absence of motor weakness or sensory loss (although the inclusion of 'the lack of motor weakness' has been debated by some physicians). It is categorized more as a symptom than an actual disease, as it describes a disruption of muscle coordination resulting in this deficit. The disturbance differs from cerebellar ataxia in that with astasis the gait can be relatively normal, with balance significantly impaired during transition from a seated to standing position. This balance impairment is similar to patients with vestibulocerebellar syndrome, which is a progressive neurological disease with many symptoms and effects. Astasis ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplasm
Protoplasm (; ) is the part of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is a mixture of small molecules such as ions, monosaccharides, amino acids, and macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, etc. In some definitions, it is a general term for the cytoplasm (e.g., Mohl, 1846), but for others, it also includes the nucleoplasm (e.g., Strasburger, 1882). For Sharp (1921), "According to the older usage the extra-nuclear portion of the protoplast 'the entire cell, excluding the cell wall''was called "protoplasm," but the nucleus also is composed of protoplasm, or living substance in its broader sense. The current consensus is to avoid this ambiguity by employing Strasburger's (1882) terms cytoplasm Kölliker (1863), originally as synonym for protoplasm''and nucleoplasm van Beneden (1875), or karyoplasm, used by Walther Flemming">Flemming (1878)''">karyoplasm">'term coined by Edouard Van Beneden">van Beneden (1875), or karyoplasm, used by Walther Flemming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytopharynx
A cytostome (from ''cyto-'', cell and ''stome-'', mouth) or cell mouth is a part of a cell specialized for phagocytosis, usually in the form of a microtubule-supported funnel or groove. Food is directed into the cytostome, and sealed into vacuoles. Only certain groups of protozoa, such as the Ciliophora and Excavata, have cytostomes. An example is ''Balantidium coli'', a ciliate. In other protozoa, and in cells from multicellular organisms, phagocytosis takes place at any point on the cell or feeding takes place by absorption. Structure The cytostome forms an invagination on the cell surface and is typically directed towards the nucleus of the cell.Okuda, Kendi, et al. "The cytostome of Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes is associated with the flagellar complex." Experimental parasitology 92.4 (1999): 223-231. The cytostome is often labeled as the entire invagination, but in fact the cytostome only constitutes the opening of the invagination at the surface of the cell. The rest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |