|
PAX8
Paired box gene 8, also known as PAX8, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''PAX8'' gene. Function This gene is a member of the paired box ( PAX) family of transcription factors. Members of this gene family typically encode proteins which contain a paired box domain, an octapeptide, and a paired-type homeodomain. The PAX gene family has an important role in the formation of tissues and organs during embryonic development and maintaining the normal function of some cells after birth. The PAX genes give instructions for making proteins that attach themselves to certain areas of DNA. This nuclear protein is involved in thyroid follicular cell development and expression of thyroid-specific genes. PAX8 releases the hormones important for regulating growth, brain development, and metabolism. Also functions in very early stages of kidney organogenesis, the Müllerian system, and the thymus. Additionally, PAX8 is expressed in the renal excretory system, epithelial cells of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Follicular thyroid cancer accounts for 15% of thyroid cancer and occurs more commonly in women over 50 years of age. Thyroglobulin (Tg) can be used as a tumor marker for well-differentiated follicular thyroid cancer. Thyroid follicular cells are the thyroid cells responsible for the production and secretion of thyroid hormones. Cause Associated mutations Approximately one-half of follicular thyroid carcinomas have mutations in the Ras subfamily of oncogenes, most notably HRAS, NRAS, and KRAS. Mutations in MINPP1 have likewise been observed, as well as germline PTEN gene mutations responsible for Cowden syndrome of which follicular thyroid cancer is a feature. Also, a chromosomal translocation specific for follicular thyroid carcinomas is one between paired box gene 8 (PAX-8), a gene important in thyroid development, and the gene encoding peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ 1 (PPARγ1), a nuclear hormone receptor contributing to terminal differentiation of cells. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Dysgenesis
Thyroid dysgenesis is a cause of congenital hypothyroidism where the thyroid is missing (thyroid agenesis), ectopic, or severely underdeveloped. It should not be confused with iodine deficiency, or with other forms of congenital hypothyroidism, such as thyroid dyshormonogenesis, where the thyroid is present but not functioning correctly. Congenital hypothyroidism caused by thyroid dysgenesis can be associated with PAX8. __TOC__ Ectopic thyroid An ''ectopic thyroid'', also called ''accessory thyroid gland'', is a form of thyroid dysgenesis in which an entire or parts of the thyroid located in another part of the body than what is the usual case. A completely ectopic thyroid gland may be located anywhere along the path of the descent of the thyroid during its embryological development, although it is most commonly located at the base of the tongue, just posterior to the foramen cecum of the tongue. In this location, an aberrant or ectopic thyroid gland is known as a ''lingual t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pax Genes
In evolutionary developmental biology, Paired box (Pax) genes are a family of genes coding for tissue specific transcription factors containing an N-terminal paired domain and usually a partial, or in the case of four family members (PAX3, PAX4, PAX6 and PAX7), a complete homeodomain to the C-terminus. An octapeptide as well as a Pro-Ser-Thr-rich C terminus may also be present. Pax proteins are important in early animal development for the specification of specific tissues, as well as during epimorphic limb regeneration in animals capable of such. The paired domain was initially described in 1987 as the "paired box" in the ''Drosophila'' protein paired (prd; ). Groups Within the mammalian family, there are four well defined groups of Pax genes. *Pax group 1 (Pax 1 and 9), *Pax group 2 (Pax 2, 5 and 8), *Pax group 3 (Pax 3 and 7) and *Pax group 4 (Pax 4 and 6). Two more families, Pox-neuro and Pax-α/β, exist in basal bilaterian species. Orthologous genes exist throughout the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeodomain Fold
A homeobox is a DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, that regulates large-scale anatomical features in the early stages of embryonic development. Mutations in a homeobox may change large-scale anatomical features of the full-grown organism. Homeoboxes are found within genes that are involved in the regulation of patterns of anatomical development (morphogenesis) in animals, fungi, plants, and numerous single cell eukaryotes. Homeobox genes encode homeodomain protein products that are transcription factors sharing a characteristic protein fold structure that binds DNA to regulate expression of target genes. Homeodomain proteins regulate gene expression and cell differentiation during early embryonic development, thus mutations in homeobox genes can cause developmental disorders. Homeosis is a term coined by William Bateson to describe the outright replacement of a discrete body part with another body part, e.g. antennapedia—replacement of the antenna on the head of a fru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NK2 Homeobox 1
NK2 homeobox 1 (NKX2-1), also known as thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''NKX2-1'' gene. Function Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) is a protein that regulates transcription of genes specific for the thyroid, lung, and diencephalon. It is also known as thyroid specific enhancer binding protein. It is used in anatomic pathology as a marker to determine if a tumor arises from the lung or thyroid. NKX2.1 can be induced by activin A via SMAD2 signaling in a human embryonic stem cell differentiation model. NKX2.1 is key to the fetal development of lung structures. The dorsal-ventral pattern of NKX2.1 expression forms the ventral boundary in the anterior foregut. NKX2.1 is expressed only in select cells in the ventral wall of the anterior foregut, and is not expressed in the dorsal wall, where the esophagus will emerge from. Knockout mice NKX2.1 knockout in mice results in the development of a shortened trachea whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pax Genes
In evolutionary developmental biology, Paired box (Pax) genes are a family of genes coding for tissue specific transcription factors containing an N-terminal paired domain and usually a partial, or in the case of four family members (PAX3, PAX4, PAX6 and PAX7), a complete homeodomain to the C-terminus. An octapeptide as well as a Pro-Ser-Thr-rich C terminus may also be present. Pax proteins are important in early animal development for the specification of specific tissues, as well as during epimorphic limb regeneration in animals capable of such. The paired domain was initially described in 1987 as the "paired box" in the ''Drosophila'' protein paired (prd; ). Groups Within the mammalian family, there are four well defined groups of Pax genes. *Pax group 1 (Pax 1 and 9), *Pax group 2 (Pax 2, 5 and 8), *Pax group 3 (Pax 3 and 7) and *Pax group 4 (Pax 4 and 6). Two more families, Pox-neuro and Pax-α/β, exist in basal bilaterian species. Orthologous genes exist throughout the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are Gene expression, expressed in the desired Cell (biology), cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
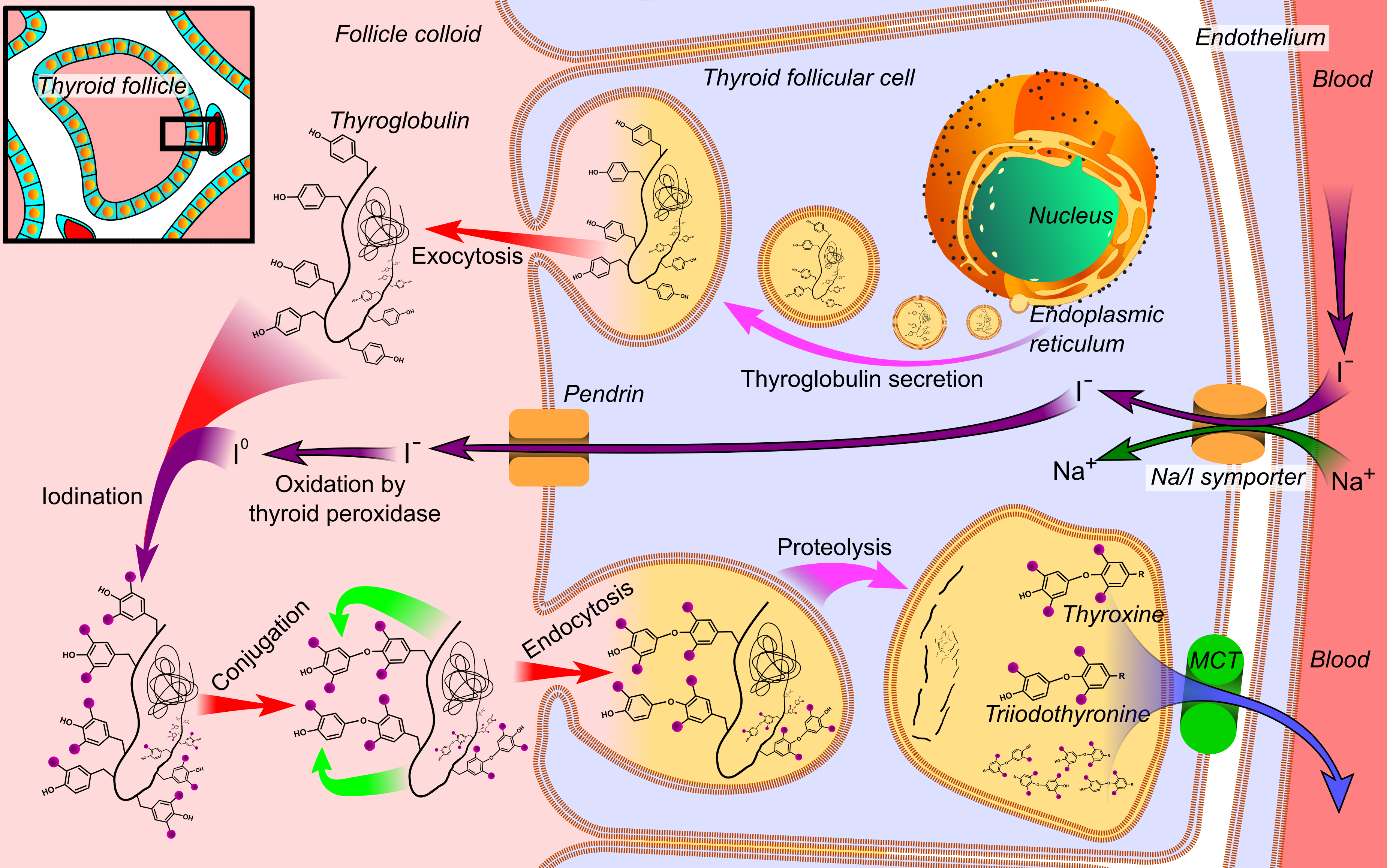
Thyroid Epithelial Cell
Thyroid follicular cells (also called thyroid epithelial cells or thyrocytes) are the major cell type in the thyroid gland, and are responsible for the production and secretion of the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). They form the single layer of cuboidal epithelium that makes up the outer structure of the almost spherical thyroid follicle. Structure Location Thyroid follicular cells form a simple cuboidal epithelium and are arranged in spherical thyroid follicles surrounding a fluid filled space known as the colloid. The interior space formed by the follicular cells is known as the follicular lumen. The basolateral membrane of follicular cells contains thyrotropin receptors which bind to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) found circulating in the blood. Calcitonin-producing parafollicular cells are also found along the basement membrane of the thyroid follicle, interspersed between follicular cells; and in spaces between the spherical follicles. Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |