|
Paracetamol Poisoning
Paracetamol poisoning, also known as acetaminophen poisoning, is caused by excessive use of the medication paracetamol (acetaminophen). Most people have few or non-specific symptoms in the first 24 hours following overdose. These symptoms include feeling tired, abdominal pain, or nausea. This is typically followed by absence of symptoms for a couple of days, after which yellowish skin, blood clotting problems, and confusion occurs as a result of liver failure. Additional complications may include kidney failure, pancreatitis, low blood sugar, and lactic acidosis. If death does not occur, people tend to recover fully over a couple of weeks. Without treatment, death from toxicity occurs 4 to 18 days later. Paracetamol poisoning can occur accidentally or as an attempt to die by suicide. Risk factors for toxicity include alcoholism, malnutrition, and the taking of certain other hepatotoxic medications. Liver damage results not from paracetamol itself, but from one of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol. Paracetamol relieves pain in both acute mild migraine and episodic tension headache. At a standard dose, paracetamol slightly reduces fever, though it is inferior to ibuprofen in that respect and the benefits of its use for fever are unclear, particularly in the context of fever of viral origins. The aspirin/paracetamol/caffeine combination also helps with both conditions when the pain is mild and is recommended as a Therapy#Lines of therapy, first-line treatment for them. Paracetamol is effective for post-surgical pain, but is inferior to ibuprofen for this purpose. The paracetamol/ibuprofen combination increases the drugs' potency and is superior to either drug alone. The pain relief paracetamol provides in osteoarthritis is small and clinica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activated Charcoal
"Activated" is a song by English singer Cher Lloyd. It was released on 22 July 2016 through Vixen Records. The song was made available to stream exclusively on ''Rolling Stone'' a day before to release (on 21 July 2016). Background In an interview with ''Rolling Stone'', Lloyd said about the song "I think when we first started writing 'Activated' – in the very beginning stages – I had said that I wanted a song eflectingexactly how I feel. t'sthis feeling that I have of just wanting to run as fast as I possibly can and just move. I wasn't going to just record something and release shit for the sake of having a song out, I wanted to feel something when I heard t and I wanted to feel like I did when I first started, like when I used to sing in my bedroom when I was 15." Critical reception Idolator's Robbie Daw said "Activated is a slinkly, sassy little R&B number, complete with the commanding line 'when I do the damn thing, just watch me.'" Estelle Tang of ''Elle'' said t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activated Charcoal (medication)
Activated charcoal, also known as activated carbon, is a medication used to treat poisonings that occurred by mouth. To be effective it must be used within a short time of the poisoning occurring, typically an hour. It does not work for poisonings by cyanide, corrosive agents, iron, lithium, alcohols, or malathion. It may be taken by mouth or given by a nasogastric tube. Other uses include inside hemoperfusion machines. Common side effects include vomiting, black stools, diarrhea, and constipation. A more serious side effect, pneumonitis, may result if aspirated into the lungs. Gastrointestinal obstruction and ileus are less common but serious adverse effects. Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is generally safe. Activated charcoal works by adsorbing the toxin. While charcoal has been used since ancient times for poisonings, activated charcoal has been used since the 1900s. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Poison ingesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine. Biosynthesis and occurrence Glutathione biosynthesis involves two adenosine triphosphate-dependent steps: *First, γ-glutamylcysteine is synthesized from L-glutamate and L-cysteine. This conversion requires the enzyme glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL, glutamate cysteine synthase). This reaction is the rate-limiting step in glutathione synthesis. *Second, glycine is added to the C-terminal of γ-glutamylcysteine. This condensation is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
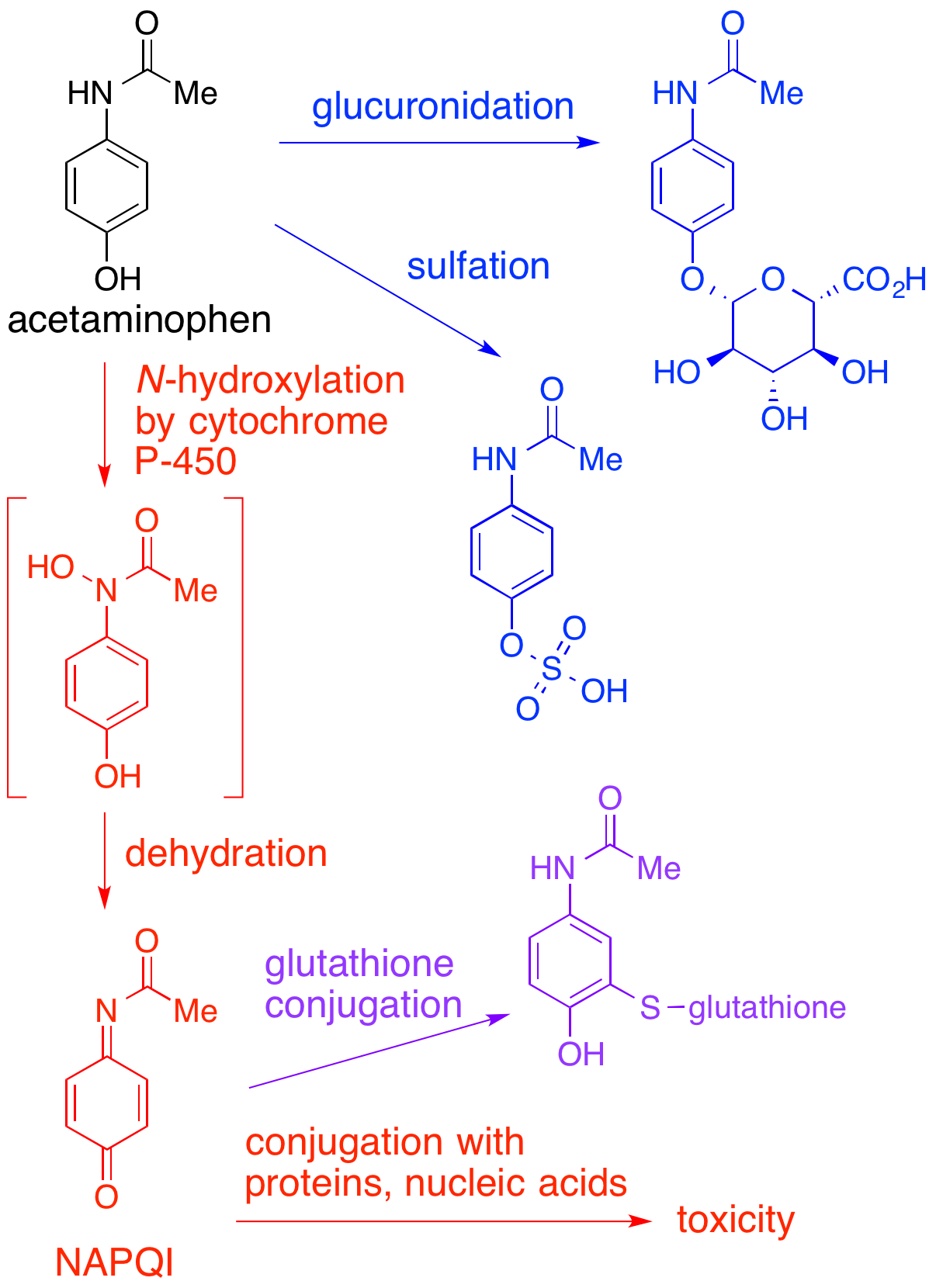
NAPQI
NAPQI, also known as NAPBQI or ''N''-acetyl-''p''-benzoquinone imine, is a toxic byproduct produced during the xenobiotic metabolism of the analgesic paracetamol (acetaminophen). It is normally produced only in small amounts, and then almost immediately detoxified in the liver. However, under some conditions in which NAPQI is not effectively detoxified (usually in the case of paracetamol overdose), it causes severe damage to the liver. This becomes apparent 3–4 days after ingestion and may result in death from fulminant liver failure several days after the overdose. Metabolism In adults, the primary metabolic pathway for paracetamol is glucuronidation. This yields a relatively non-toxic metabolite, which is excreted into bile and passed out of the body. A small amount of the drug is metabolized via the cytochrome P-450 pathway (to be specific, CYP3A4 and CYP2E1) into NAPQI, which is extremely toxic to liver tissue, as well as being a strong biochemical oxidizer. In an av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Ethylene exemplifies a primary metabolite produced large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. Some antibiotics use primary metabolites as precursors, such as actinomycin, which is created from the primary metabolite tryptophan. Some sugars are metabolites, such as fructose or glucose, which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity (from ''hepatic toxicity'') implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications and the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn from the market after approval. The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses (e.g. acetaminophen, paracetamol) and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges (e.g. halothane), may injure the organ. Other chemical agents, such as those used in laboratories and industries, natural chemicals (e.g., alpha-amanitin), and herbal remedies (two prominent examples being kava, though the causal mechanism is unknown, and comfrey, through pyrrolizidine alkaloid content) can also induce hepatotoxicity. Chemicals that cause liver injury are called hepatotoxins. More than 900 drugs have been implicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated there were 283 million people with alcohol use disorders worldwide . The term ''alcoholism'' was first coined in 1852, but ''alcoholism'' and ''alcoholic'' are considered stigmatizing and likely to discourage seeking treatment, so diagnostic terms such as ''alcohol use disorder'' and ''alcohol dependence'' are often used instead in a clinical context. Alcohol is addictive, and heavy long-term alcohol use results in many negative health and social consequences. It can damage all the organ systems, but especially affects the brain, heart, liver, pancreas, and immune system. Heavy alcohol usage can result in trouble sleeping, and severe cognitive issues like dementia, brain damage, or Wernicke–Kors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicide Method
A suicide method is any means by which a person may choose to end their life. Suicide attempts do not always result in death, and a non-fatal suicide attempt can leave the person with serious physical injuries, long-term health problems, or brain damage. Worldwide, three suicide methods predominate, with the pattern varying in different countries: these are hanging, pesticides, and firearms. Some suicides may be preventable by removing the means. Making common suicide methods less accessible leads to an overall reduction in the number of suicides. Method-specific ways to do this might include restricting access to pesticides, firearms, and commonly used drugs. Other important measures are the introduction of policies that address the misuse of alcohol and the treatment of mental disorders. Gun-control measures in a number of countries have seen a reduction in suicides and other gun-related deaths. Other preventive measures are not method-specific; these include support, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Liver Failure
Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs (such as jaundice) of liver disease, and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage (loss of function of 80–90% of liver cells). The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis (as measured by the levels of serum albumin and the prothrombin time in the blood). The 1993 classification defines ''hyperacute'' as within 1 week, ''acute'' as 8–28 days, and ''subacute'' as 4–12 weeks; both the speed with which the disease develops and the underlying cause strongly affect outcomes. Signs and symptoms The main features of acute liver failure are rapid-onset jaundice, weakness, and eventually, changes in mental status that can begin as mild confusion but progress to coma, known as hepatic encephalopathy. Encephalopathy and cerebral edema In ALF, hepatic encephalopathy leads to cerebral edema, coma, brain herniation, and eventually death. Detection of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-specific Symptoms
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body, which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernails or to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |