|
Optic Axis Of A Crystal
An optic axis of a crystal is a direction in which a ray of transmitted light suffers no birefringence (double refraction). An optic axis is a direction rather than a single line: all rays that are parallel to that direction exhibit the same lack of birefringence. Crystals may have a single optic axis, in which case they are ''uniaxial'', or two different optic axes, in which case they are ''biaxial''. Non-crystalline materials generally have no birefringence and thus, no optic axis. A uniaxial crystal (e.g. calcite, quartz) is isotropic within the plane orthogonal to the optic axis of the crystal. Explanation The internal structure of crystals (the specific structure of the crystal lattice, and the specific atoms or molecules of which it is composed) causes the speed of light in the material, and therefore the material's refractive index, to depend on both the light's direction of propagation and its polarization. The dependence on polarization causes birefringence, in which two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray (optics)
In optics a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light, obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the ''wavefronts'' of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. Rays are used to model the propagation of light through an optical system, by dividing the real light field up into discrete rays that can be computationally propagated through the system by the techniques of '' ray tracing''. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. '' Ray optics'' or '' geometrical optics'' does not describe phenomena such as diffraction, which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model. Definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinary Ray
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Ellipsoid
In crystal optics, the index ellipsoid (also known as the ''optical indicatrix'' or sometimes as the ''dielectric ellipsoid'') is a geometric construction which concisely represents the refractive indices and associated polarizations of light, as functions of the orientation of the wavefront, in a doubly-refractive crystal (provided that the crystal does not exhibit optical rotation). When this ellipsoid is cut through its center by a plane parallel to the wavefront, the resulting intersection (called a ''central section'' or ''diametral section'') is an ellipse whose major and minor semiaxes have lengths equal to the two refractive indices for that orientation of the wavefront, and have the directions of the respective polarizations as expressed by the electric displacement vector . The principal semiaxes of the index ellipsoid are called the ''principal refractive indices''. It follows from the sectioning procedure that each principal semiax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Optics
Crystal optics is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''anisotropic media'', that is, media (such as crystals) in which light behaves differently depending on which direction the light is propagating. The index of refraction depends on both composition and crystal structure and can be calculated using the Gladstone–Dale relation. Crystals are often naturally anisotropic, and in some media (such as liquid crystals) it is possible to induce anisotropy by applying an external electric field. Isotropic media Typical transparent media such as glasses are ''isotropic'', which means that light behaves the same way no matter which direction it is travelling in the medium. In terms of Maxwell's equations in a dielectric, this gives a relationship between the electric displacement field D and the electric field E: : \mathbf = \varepsilon_0 \mathbf + \mathbf where ε0 is the permittivity of free space and P is the electric polarization (the vector field co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid-crystal Display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images (as in a general-purpose computer display) or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden. For instance: preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
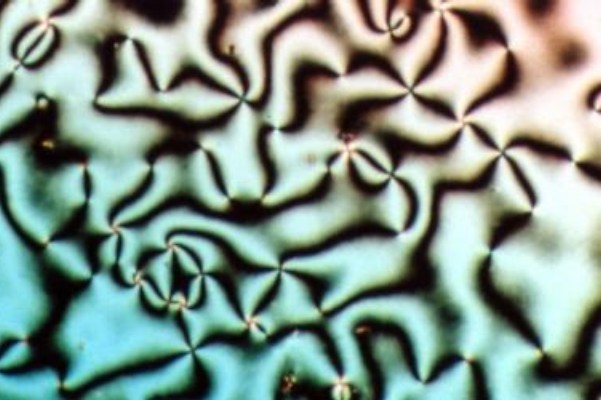
Mesophase
In chemistry and chemical physics, a mesophase is a state of matter intermediate between liquid and solid. Gelatin is a common example of a partially ordered structure in a mesophase. Further, biological structures such as the lipid bilayers of cell membranes are examples of mesophases. Georges Friedel (1922) called attention to the "mesomorphic states of matter" in his scientific assessment of observations of the so-called liquid crystals. Conventionally a crystal is solid, and crystallization converts liquid to solid. The oxymoron of the liquid crystal is resolved through the notion of mesophases. The observations noted an optic axis persisting in materials that had been melted and had begun to flow. The term ''liquid crystal'' persists as a colloquialism, but use of the term was criticized in 1993: In ''The Physics of Liquid Crystals''P.G. de Gennes & J. Prost (1993) ''The Physics of Liquid Crystals'', 2nd edition, Oxford University Press the mesophases are introduced from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, * lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Activity
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity. Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking microscopic mirror symmetry. Unlike other sources of birefringence which alter a beam's state of polarization, optical activity can be observed in fluids. This can include gases or solutions of chiral molecules such as sugars, molecules with helical secondary structure such as some proteins, and also chiral liquid crystals. It can also be observed in chiral solids such as certain crystals with a rotation between adjacent crystal planes (such as quartz) or metamaterials. When looking at the source of light, the rotation of the plane of polarization may be either to the right (dextrorota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraordinary Ray
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
Polarization ( also polarisation) is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string ''(see image)''; for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves (shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity ( Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''Π... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |