|
OMAP
The OMAP (Open Multimedia Applications Platform) family, developed by Texas Instruments, was a series of image/ video processors. They are proprietary system on chips (SoCs) for portable and mobile multimedia applications. OMAP devices generally include a general-purpose ARM architecture processor core plus one or more specialized co-processors. Earlier OMAP variants commonly featured a variant of the Texas Instruments TMS320 series digital signal processor. The platform was created after December 12, 2002, as STMicroelectronics and Texas Instruments jointly announced an initiative for ''Open Mobile Application Processor Interfaces'' (OMAPI) intended to be used with 2.5 and 3G mobile phones, that were going to be produced during 2003. (This was later merged into a larger initiative and renamed the MIPI Alliance.) The OMAP was Texas Instruments' implementation of this standard. (The STMicroelectronics implementation was named Nomadik.) OMAP did enjoy some success in the smart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerVR
PowerVR is a division of Imagination Technologies (formerly VideoLogic) that develops hardware and software for 2D and 3D rendering, and for video encoding, decoding, associated image processing and DirectX, OpenGL ES, OpenVG, and OpenCL acceleration. PowerVR also develops AI accelerators called Neural Network Accelerator (NNA). The PowerVR product line was originally introduced to compete in the desktop PC market for 3D hardware accelerators with a product with a better price–performance ratio than existing products like those from 3dfx Interactive. Rapid changes in that market, notably with the introduction of OpenGL and Direct3D, led to rapid consolidation. PowerVR introduced new versions with low-power electronics that were aimed at the laptop computer market. Over time, this developed into a series of designs that could be incorporated into system-on-a-chip architectures suitable for handheld device use. PowerVR accelerators are not manufactured by PowerVR, but i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
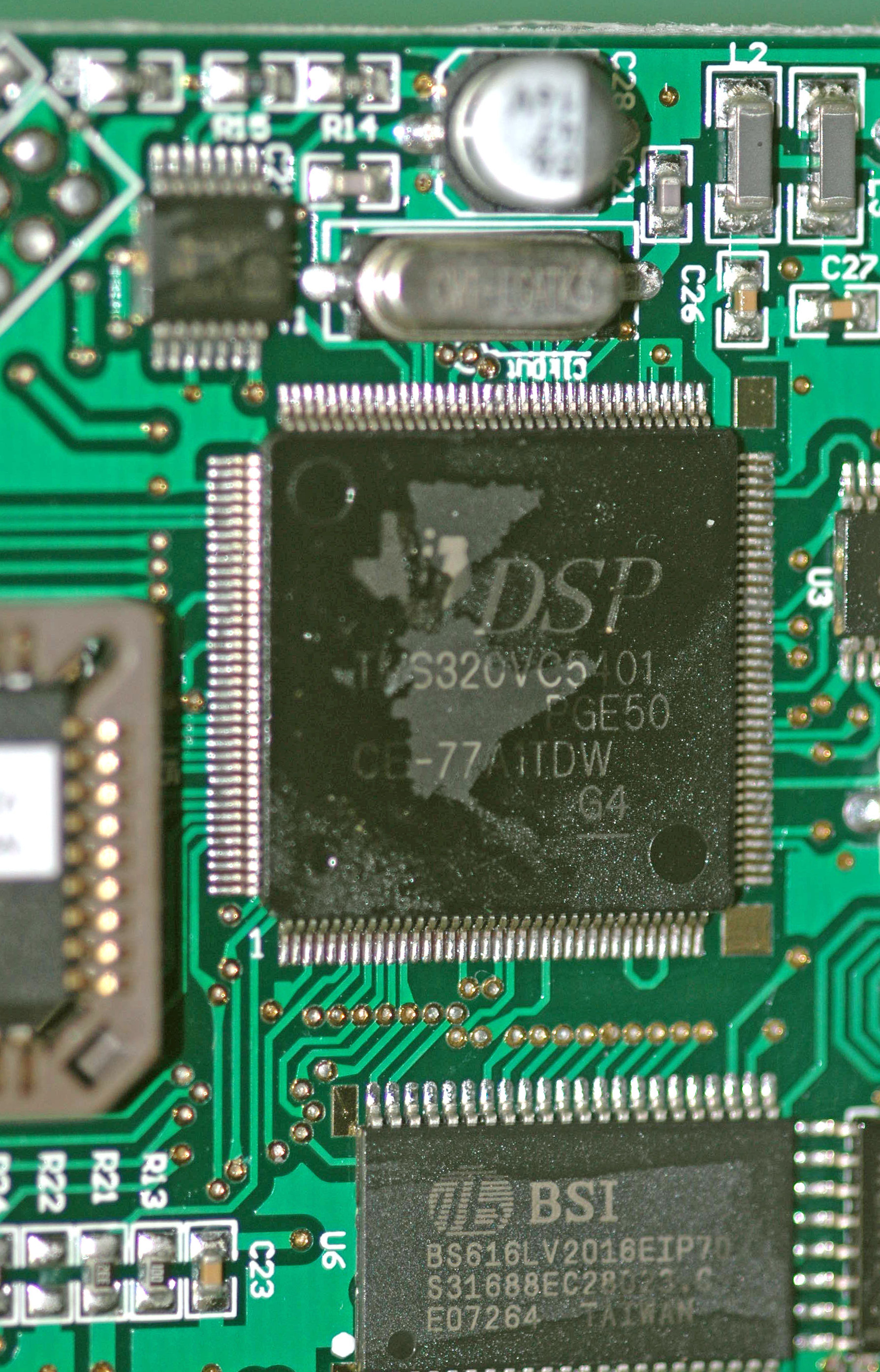
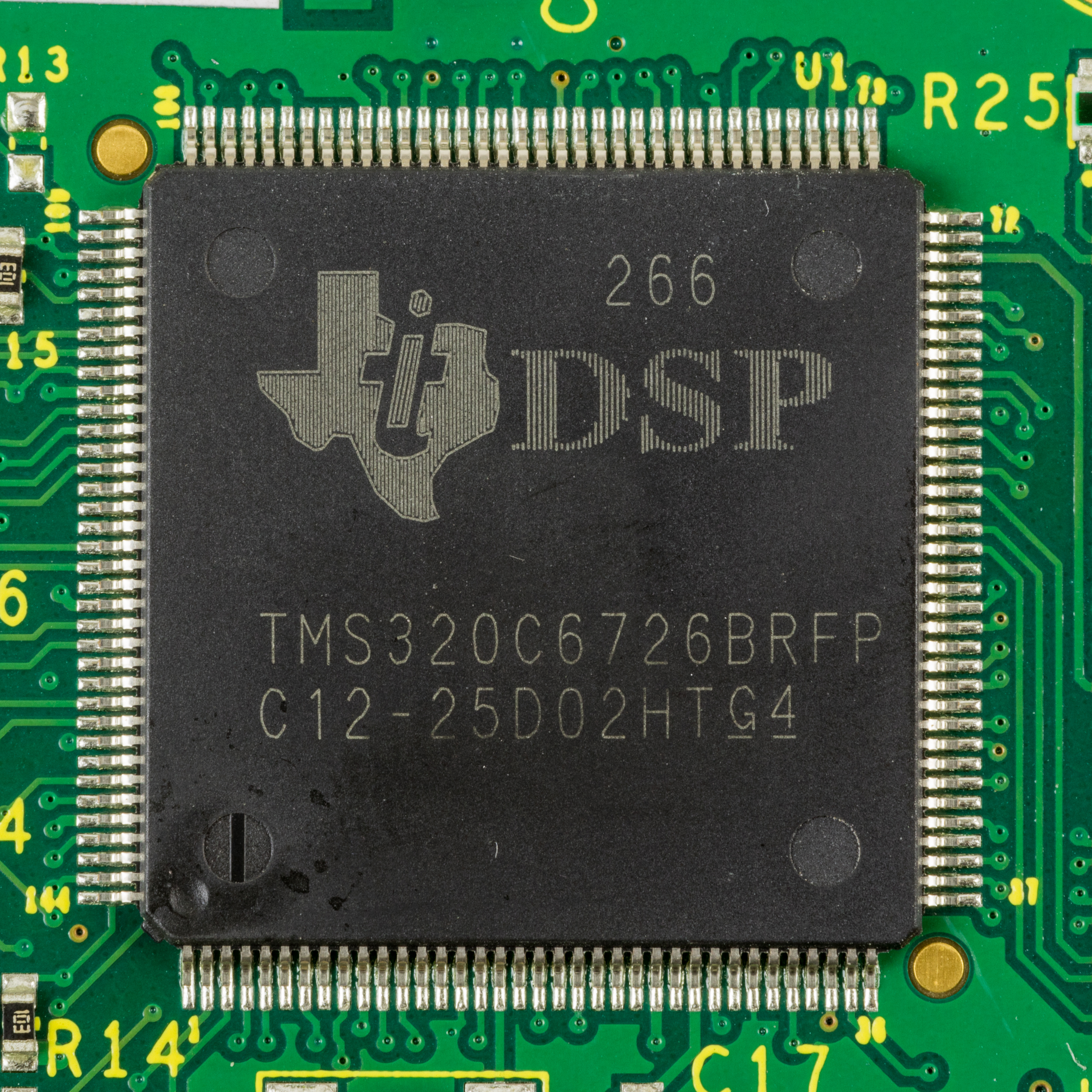
Texas Instruments TMS320
Texas Instruments TMS320 is a blanket name for a series of digital signal processors (DSPs) from Texas Instruments. It was introduced on April 8, 1983 through the TMS32010 processor, which was then the fastest DSP on the market. The processor is available in many different variants, some with fixed-point arithmetic and some with floating point arithmetic. The TMS320 processors were fabricated on MOS integrated circuit chips, including both NMOS and CMOS variants. The floating point DSP TMS320C3x, which exploits delayed branch logic, has as many as three delay slots. The flexibility of this line of processors has led to it being used not merely as a co-processor for digital signal processing but also as a main CPU. Newer implementations support standard IEEE JTAG control for boundary scan and/or in-circuit debugging. The original TMS32010 and its subsequent variants is an example of a CPU with a modified Harvard architecture, which features separate address spaces for instruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PandaBoard Described
The PandaBoard was a low-power single-board computer development platform based on the Texas Instruments OMAP4430 system on a chip (SoC). The board has been available to the public at the subsidized price of US$174 since 27 October 2010. It is a community supported development platform. The PandaBoard ES is a newer version based on the OMAP4460 SoC, with the CPU and GPU running at higher clock rates. Like its predecessor, it is a community supported development platform. Features The OMAP4430 SoC on the PandaBoard features a dual-core 1 GHz ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore CPU, a 304 MHz PowerVR SGX540 GPU, IVA3 multimedia hardware accelerator with a programmable DSP, and 1 GiB of DDR2 SDRAM. The PandaBoard ES uses a newer SoC, with a dual-core 1.2 GHz CPU and 384 MHz GPU. Primary persistent storage is via an SD Card slot allowing SDHC cards up to 32 GB to be used. The board includes wired 10/100 Ethernet as well as wireless Ethernet and Bluetooth connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BeagleBoard Described
The BeagleBoard is a low-power open-source single-board computer produced by Texas Instruments in association with Digi-Key and Newark element14. The BeagleBoard was also designed with open source software development in mind, and as a way of demonstrating the Texas Instrument's OMAP3530 system-on-a-chip. The board was developed by a small team of engineers as an educational board that could be used in colleges around the world to teach open source hardware and software capabilities. It is also sold to the public under the Creative Commons share-alike license. The board was designed using Cadence OrCAD for schematics and Cadence Allegro for PCB manufacturing; no simulation software was used. Features The BeagleBoard measures approximately 75 by 75 mm and has all the functionality of a basic computer. The OMAP3530 includes an ARM Cortex-A8 CPU (which can run Linux, Minix, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, RISC OS, or Symbian; a number of unofficial Android ports exist), a TMS320C64x+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
65 nm
The 65 nm process is an advanced lithographic node used in volume CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor fabrication. Printed linewidths (i.e. transistor gate lengths) can reach as low as 25 nm on a nominally 65 nm process, while the pitch between two lines may be greater than 130 nm. For comparison, cellular ribosomes are about 20 nm end-to-end. A crystal of bulk silicon has a lattice constant of 0.543 nm, so such transistors are on the order of 100 atoms across. Toshiba and Sony announced the 65 nm process in 2002, before Fujitsu and Toshiba began production in 2004, and then TSMC began production in 2005. By September 2007, Intel, AMD, IBM, UMC and Chartered were also producing 65 nm chips. While feature sizes may be drawn as 65 nm or less, the wavelengths of light used for lithography are 193 nm and 248 nm. Fabrication of sub-wavelength features requires special imaging technologies, such as optical proximity correction and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nokia 770
The Nokia 770 Internet Tablet is a wireless Internet appliance from Nokia, originally announced at the LinuxWorld Summit in New York City on 25 May 2005. It is designed for wireless Internet browsing and email functions and includes software such as Internet radio, an RSS news reader, ebook reader, image viewer and media players for selected types of media. The device went on sale in Europe on 3 November 2005, at a suggested retail price of €349 to €369 (£245 in the United Kingdom). In the United States, the device became available for purchase through Nokia USA's web site on 14 November 2005 for $359.99. On 8 January 2007, Nokia announced the Nokia N800, the successor to the 770. In July 2007, the price for the Nokia 770 fell to under US$150 / 150 EUR / 100 GBP. Specifications * Dimensions: 141×79×19 mm (5.5×3.1×0.7 in) * Weight: 230 g (8.1 oz) with protective cover or 185 g (6.5 oz) without. * Processor: Texas Instruments OMAP 1710 C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Signal Processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on MOS integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio signal processing, telecommunications, digital image processing, radar, sonar and speech recognition systems, and in common consumer electronic devices such as mobile phones, disk drives and high-definition television (HDTV) products. The goal of a DSP is usually to measure, filter or compress continuous real-world analog signals. Most general-purpose microprocessors can also execute digital signal processing algorithms successfully, but may not be able to keep up with such processing continuously in real-time. Also, dedicated DSPs usually have better power efficiency, thus they are more suitable in portable devices such as mobile phones because of power consumption constraints. DSPs often use special memory architectures that are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments DaVinci
The Texas Instruments DaVinci is a family of system on a chip processors that are primarily used in embedded video and vision applications. Many processors in the family combine a Digital signal processor, DSP core based on the Texas Instruments TMS320, TMS320 C6000 VLIW DSP family and an ARM architecture, ARM CPU core into a single system on chip. By using both a general-purpose processor and a DSP, the control and media portions can both be executed by processors that excel at their respective tasks. Later chips in the family included DSP only and ARM only processors. All the later chips integrate several accelerators to offload commodity application specific processing from the processor cores to dedicated accelerators. Most notable among these are HDVICP, an H.264, SVC and MPEG-4 compression and decompression engine, ISP, an accelerator engine with sophisticated methods for enhancing video, primarily input from camera sensors and an OSD engine for display acceleration. Some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Processor
An image processor, also known as an image processing engine, image processing unit (IPU), or image signal processor (ISP), is a type of media processor or specialized digital signal processor (DSP) used for image processing, in digital cameras or other devices. Image processors often employ parallel computing even with SIMD or MIMD technologies to increase speed and efficiency. The digital image processing engine can perform a range of tasks. To increase the system integration on embedded devices, often it is a system on a chip with multi-core processor architecture. Function Bayer transformation The photodiodes employed in an image sensor are color-blind by nature: they can only record shades of grey. To get color into the picture, they are covered with different color filters: red, green and blue ( RGB) according to the pattern designated by the Bayer filter - named after its inventor. As each photodiode records the color information for exactly one pixel of the image, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, which h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomadik
Nomadik is a family of microprocessors for multimedia applications from STMicroelectronics. It is based on ARM9 ARM architecture and was designed specifically for mobile devices. On December 12, 2002, STMicroelectronics and Texas Instruments jointly announced an initiative for ''Open Mobile Application Processor Interfaces'' (OMAPI) intended to be used with 2.5 and 3G mobile phones, that were going to be produced during 2003. (This was later merged into a larger initiative and renamed the MIPI alliance.) The Nomadik was STMicroelectronics' implementation of this standard. Nomadik was first presented on October 7, 2003 in the CEATEC show in Tokyo, and later that year the Nomadik won the Microprocessor Report Analysts' Choice Award for application processors. The family was aimed at 2.5G/ 3G mobile phones, personal digital assistants and other portable wireless products with multimedia capability. In addition it was suitable for automotive multimedia applications. The most known d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globally. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog chips and embedded processors, which account for more than 80% of its revenue. TI also produces TI digital light processing technology and education technology products including calculators, microcontrollers, and multi-core processors. The company holds 45,000 patents worldwide as of 2016. Texas Instruments emerged in 1951 after a reorganization of Geophysical Service Incorporated, a company founded in 1930 that manufactured equipment for use in the seismic industry, as well as defense electronics. TI produced the world's first commercial silicon transistor in 1954, and the same year designed and manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |