|
Optical Cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric oscillators and some interferometers. Light confined in the cavity reflects multiple times, producing Mode (electromagnetism), modes with certain resonance, resonance frequencies. Modes can be decomposed into longitudinal modes that differ only in frequency and transverse modes that have different intensity patterns across the cross section of the beam. Many types of optical cavities produce standing wave modes. Different resonator types are distinguished by the focal lengths of the two mirrors and the distance between them. Flat mirrors are not often used because of the difficulty of aligning them to the needed precision. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Nanoparticle Suspended In An Optical Cavity
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window panes, tableware, and optics. Some common objects made of glass are named after the material, e.g., a Tumbler (glass), "glass" for drinking, "glasses" for vision correction, and a "magnifying glass". Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the Melting, molten form. Some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring, and obsidian has been used to make arrowheads and knives since the Stone Age. Archaeological evidence suggests glassmaking dates back to at least 3600 BC in Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, Egypt, or Syria. The earliest known glass objects were beads, perhaps created accidentally during metalworking or the production of faience, which is a form of pottery using lead glazes. Due to its ease of formability int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Resonator Stability
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
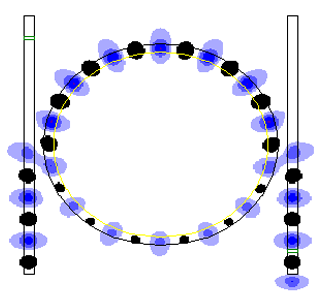
Whispering-gallery Mode
Whispering-gallery waves, or whispering-gallery modes, are a type of wave that can travel around a concave surface. Originally discovered for sound waves in the whispering gallery of St Paul's Cathedral, they can exist for light and for other waves, with important applications in nondestructive testing, lasing, cooling and sensing, as well as in astronomy. Introduction Whispering-gallery waves were first explained for the case of St Paul's Cathedral circa 1878 by Lord Rayleigh, who revised a previous misconception that whispers could be heard across the dome but not at any intermediate position. He explained the phenomenon of travelling whispers with a series of specularly reflected sound rays making up chords of the circular gallery. Clinging to the walls the sound should decay in intensity only as the inverse of the distance — rather than the inverse square as in the case of a point source of sound radiating in all directions. This accounts for the whispers being audibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Ring Resonators
An optical ring resonator is a set of waveguides in which at least one is a closed loop coupled to some sort of light input and output. (These can be, but are not limited to being, waveguides.) The concepts behind optical ring Optical cavity, resonators are the same as those behind Whispering gallery, whispering galleries except that they use light and obey the properties behind constructive interference and total internal reflection. When light of the resonant wavelength is passed through the loop from the input waveguide, the light builds up in intensity over multiple round-trips owing to constructive interference and is output to the output bus waveguide which serves as a detector waveguide. Because only a select few wavelengths will be at resonance within the loop, the optical ring resonator functions as a filter. Additionally, as implied earlier, two or more ring waveguides can be coupled to each other to form an add/drop optical filter. Background Optical ring resonators w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction-limited System
In optics, any optical instrument or systema microscope, telescope, or camerahas a principal limit to its resolution due to the physics of diffraction. An optical instrument is said to be diffraction-limited if it has reached this limit of resolution performance. Other factors may affect an optical system's performance, such as lens imperfections or aberrations, but these are caused by errors in the manufacture or calculation of a lens, whereas the diffraction limit is the maximum resolution possible for a theoretically perfect, or ideal, optical system. The diffraction-limited angular resolution, in radians, of an instrument is proportional to the wavelength of the light being observed, and inversely proportional to the diameter of its objective's entrance aperture. For telescopes with circular apertures, the size of the smallest feature in an image that is diffraction limited is the size of the Airy disk. As one decreases the size of the aperture of a telescopic lens, diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Coating
An optical coating is one or more thin-film optics, thin layers of material deposited on an optical component such as a lens (optics), lens, prism (optics), prism or mirror, which alters the way in which the optic reflection (physics), reflects and transmittance, transmits light. These coatings have become a key technology in the field of optics. One type of optical coating is an anti-reflective coating, which reduces unwanted reflections from surfaces, and is commonly used on glasses, spectacle and camera lenses. Another type is the high-reflector coating, which can be used to produce mirrors that reflect greater than 99.99% of the light that falls on them. More complex optical coatings exhibit high reflection over some range of wavelengths, and anti-reflection over another range, allowing the production of dichroism, dichroic dichroic filter, thin-film filters. Types of coating The simplest optical coatings are thin layers of metals, such as aluminium, which are deposited on g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Laser
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation is generated in the form of an emitted photon. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence, and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from the infrared (IR) to the ultraviolet (UV) spectra. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Microcavity
An optical microcavity or microresonator is a structure formed by reflecting faces on the two sides of a spacer layer or optical medium, or by wrapping a waveguide in a circular fashion to form a ring. The former type is a standing wave cavity, and the latter is a traveling wave cavity. The name ''micro''cavity stems from the fact that it is often only a few micrometers thick, the spacer layer sometimes even in the nanometer range. As with common lasers, this forms an optical cavity or ''optical resonator'', allowing a standing wave to form inside the spacer layer or a traveling wave that goes around in the ring. Applications and effects The fundamental difference between a conventional optical cavity and microcavities is the effects that arise from the small dimensions of the system, but their operational principle can often be understood in the same way as for larger optical resonators. Quantum effects of the light's electromagnetic field can be observed. For example, the spont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcseconds
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth's circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (abbreviated as arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a minute of arc, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal (base 60) subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabry–Pérot Interferometer
In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer (FPI) or etalon is an optical cavity made from two parallel reflecting surfaces (i.e.: thin mirrors). Optical waves can pass through the optical cavity only when they are in resonance with it. It is named after Charles Fabry and Alfred Perot, who developed the instrument in 1899. ''Etalon'' is from the French ''étalon'', meaning "measuring gauge" or "standard". Etalons are widely used in telecommunications, lasers and spectroscopy to control and measure the wavelengths of light. Recent advances in fabrication technique allow the creation of very precise tunable Fabry–Pérot interferometers. The device is technically an interferometer when the distance between the two surfaces (and with it the resonance length) can be changed, and an etalon when the distance is fixed (however, the two terms are often used interchangeably). Basic description The heart of the Fabry–Pérot interferometer is a pair of partially reflective glass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is an idealized beam of electromagnetic radiation whose amplitude envelope in the transverse plane is given by a Gaussian function; this also implies a Gaussian intensity (irradiance) profile. This fundamental (or TEM00) transverse Gaussian mode describes the intended output of many lasers, as such a beam diverges less and can be focused better than any other. When a Gaussian beam is refocused by an ideal lens, a new Gaussian beam is produced. The electric and magnetic field amplitude profiles along a circular Gaussian beam of a given wavelength and polarization are determined by two parameters: the waist , which is a measure of the width of the beam at its narrowest point, and the position relative to the waist.Svelto, pp. 153–5. Since the Gaussian function is infinite in extent, perfect Gaussian beams do not exist in nature, and the edges of any such beam would be cut off by any finite lens or mirror. However, the Gaussian is a useful appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |