|
Nylon-eating Bacteria
''Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens'' KI72, popularly known as nylon-eating bacteria, is a strain of '' Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens'' that can digest certain by-products of nylon 6 manufacture. It uses a set of enzymes to digest nylon, popularly known as nylonase. Discovery and nomenclature In 1975, a team of Japanese scientists discovered a strain of bacterium, living in ponds containing waste water from a nylon factory, that could digest certain byproducts of nylon 6 manufacture, such as the linear dimer of 6-aminohexanoate. These substances are not known to have existed before the invention of nylon in 1935. It was initially named as '' Achromobacter guttatus''. Studies in 1977 revealed that the three enzymes that the bacteria were using to digest the byproducts were significantly different from any other enzymes produced by any other bacteria, and not effective on any material other than the manmade nylon byproducts. The bacterium was reassigned to ''Flavobacterium'' in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Taxonomy Database
The Genome Taxonomy Database (GTDB) is an online database that maintains information on a proposed nomenclature of prokaryotes, following a phylogenomic approach based on a set of conserved single-copy proteins. In addition to resolving paraphyletic groups, this method also reassigns taxonomic ranks algorithmically, updating names in both cases. Information for archaea was added in 2020, along with a species classification based on average nucleotide identity. Each update incorporates new genomes as well as automated and manual curation of the taxonomy. An open-source tool called GTDB-Tk is available to classify draft genomes into the GTDB hierarchy. The GTDB system, via GTDB-Tk, has been used to catalogue not-yet-named bacteria in the human gut microbiome and other metagenomic sources. The GTDB is incorporated into the '' Bergey's Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria'' in 2019 as its phylogenomic resource. Methodology The genomes used to construct the phyloge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
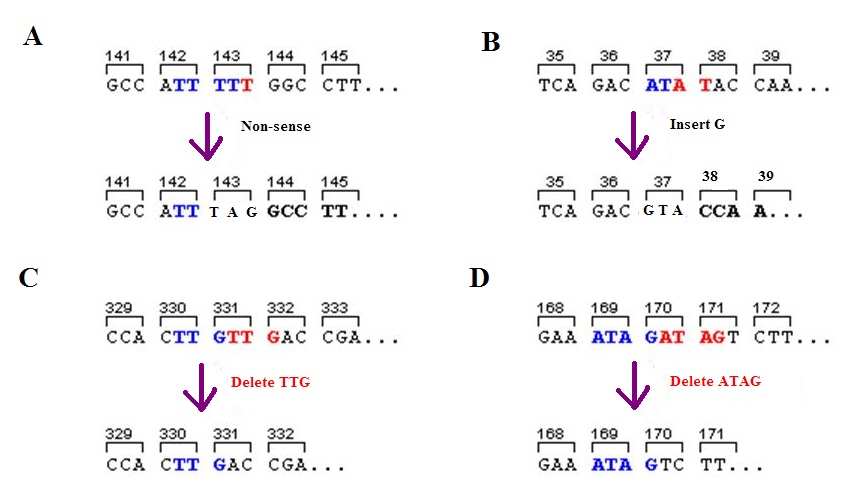
Frame-shift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymidine
Thymidine (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol dT or dThd), also known as deoxythymidine, deoxyribosylthymine, or thymine deoxyriboside, is a pyrimidine nucleoside, deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine (A) in double-stranded DNA. In cell biology it is used to cell synchronization, synchronize the cells in G1/early S phase. The prefix deoxy- is often left out since there are no precursors of thymine nucleotides involved in RNA synthesis. Before the boom in thymidine use caused by the need for thymidine in the production of the antiretroviral drug Zidovudine, azidothymidine (AZT), much of the world's thymidine production came from herring sperm. Thymidine occurs almost exclusively in DNA but it also occurs in the T arm, T-loop of tRNA. Structure and properties In its composition, deoxythymidine is a nucleoside composed of deoxyribose (a pentose sugar) joined to the pyrimidine base thymine. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Duplication
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. Gene duplications can arise as products of several types of errors in DNA replication and repair machinery as well as through fortuitous capture by selfish genetic elements. Common sources of gene duplications include ectopic recombination, retrotransposition event, aneuploidy, polyploidy, and replication slippage. Mechanisms of duplication Ectopic recombination Duplications arise from an event termed unequal crossing-over that occurs during meiosis between misaligned homologous chromosomes. The chance of it happening is a function of the degree of sharing of repetitive elements between two chromosomes. The products of this recombination are a duplication at the site of the exchange and a reciprocal deletion. Ectopic recombina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susumu Ohno
was a Japanese-American geneticist and evolutionary biologist, and seminal researcher in the field of molecular evolution. Biography Susumu Ohno was born to Japanese parents in Keijō, Chōsen (present-day Seoul, South Korea), Empire of Japan on February 1, 1928. The second of five children, he was the son of the minister of education of the Japanese Protectorate of Korea. The family returned to mainland Japan after the war in 1945. He later became a citizen of the United States. Susumu Ohno married musician Midori Aoyama in 1951. They had two sons and one daughter. His passion for science derived from his lifelong love of horses. He earned a Ph.D. in veterinary science at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology in 1949, and later a Ph.D. and D.Sc. from Hokkaido University. He went to the United States in 1951, as a visiting scholar to UCLA, and in 1952 joined the new research department at City of Hope Medical Center, where he remained in active research until 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kocuria
''Kocuria'' is a genus of gram-positive bacteria. ''Kocuria'' is named after Miloslav Kocur, a Czech microbiologist. It has been found in the milk of water deer and reindeer. Cells are coccoid, resembling ''Staphylococcus'' and ''Micrococcus'', and can group in pairs, chains, tetrads, cubical arrangements of eight, or irregular clusters. They have rigid cell walls and are either aerobic or facultative anaerobic. ''Kocuria'' can usually survive in mesophilic A mesophile is an organism that grows best in moderate temperature, neither too hot nor too cold, with an optimum growth range from . The optimum growth temperature for these organisms is 37 °C (about 99 °F). The term is mainly applied ... temperatures. Clinical significance ''Kocuria'' has been found to live on human skin and oral cavity. It is generally considered non-pathogenic but can be found in some infections. Specific infection associated with ''Kocuria'' are urinary tract infections, cholecystitis, cath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agromyces
''Agromyces'' is a genus in the phylum Actinomycetota (Bacteria). Etymology The name ''Agromyces'' derives from:Ancient Greek language, Greek noun ''agros'', field or soil; Neo-Latin grammatical gender, masculine gender noun ''myces'' (from Ancient Greek language, Greek grammatical gender, masculine gender noun ''mukēs'' -''etis''), fungus; Neo-Latin grammatical gender, masculine gender noun ''Agromyces'', soil fungus. Species The genus contains 31 species, namely * ''Agromyces albus, A. albus'' ( Dorofeeva ''et al''. 2003, ; Latin grammatical gender, masculine gender adjective ''albus'', white, referring to the white colour of colonies.) * ''Agromyces allii, A. allii'' ( Jung ''et al''. 2007, ;: Neo-Latin Latin declension, genitive case noun ''allii'', of ''Allium'', referring to the source of isolation of the micro-organisms, the rhizosphere of ''Allium'' ''victorialis'' var. ''platyphyllum''.) * ''Agromyces atrinae, A. atrinae'' ( Park ''et al''. 2010, ; Neo-Latin noun ''Atri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEROPS
MEROPS is an online database for peptidases (also known as proteases, proteinases and proteolytic enzymes) and their inhibitors. The classification scheme for peptidases was published by Rawlings & Barrett in 1993, and that for protein inhibitors by Rawlings ''et al.'' in 2004.Rawlings, N.D., Tolle, D.P. & Barrett, A.J. (2004) "Evolutionary families of peptidase inhibitors." ''Biochem J'' 378, 705-716. The most recent version, MEROPS 12.5, was released in September 2023. Overview The classification is based on similarities at the tertiary and primary structural levels. Comparisons are restricted to that part of the sequence directly involved in the reaction, which in the case of a peptidase must include the active site, and for a protein inhibitor the reactive site. The classification is hierarchical: sequences are assembled into families, and families are assembled into clans. Each peptidase, family, and clan has a unique identifier. Classification Family The families of pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seiji Negoro
Seiji (written: , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , or in hiragana) is a masculine Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include: *, Japanese ski jumper *, Japanese racing driver *, Japanese politician *, Japanese film director and producer *, Japanese golfer *, Japanese basketball player *, Japanese actor *, Japanese politician *, Japanese rugby union player *, Japanese film director *, Japanese footballer * Seiji Inagaki (born 1973), Japanese hurdler *, Japanese musician and record producer * Seiji Kameyama (亀山 晴児, born 1979), Japanese rapper better known as WISE *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese aviator *, Japanese politician *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese anime director *, Japanese professional baseball player *, Japanese footballer *Seiji Kubo (born 1973), Japanese footballer *, Japanese cross-country skier *, Japanese voice actor *, Japanese photographer *, Japanese politician *, Japanese politician *, Japanese sport wrestler *, Japanese manga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a '' Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold () resembles that of a DD-transpeptidase, from which the enzyme is thought to have evolved. β-lactam antibio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |