|
Nondominant Seventh Chord
In music theory, a nondominant seventh chord is both a diatonic chord and a seventh chord, but it does not possess dominant function, and thus it is ''not'' a dominant seventh chord. Since the V and vii chords are the dominant function chords, the "major minor seventh" V7 and "half-diminished seventh" vii7 are the dominant seventh chords. Since the nondominant function chords are I, i, ii, ii, iii, III, IV, iv, vi, and VI, the nondominant seventh chord qualities include the augmented major seventh chord, major seventh chord, minor major seventh chord, minor seventh chord, and major minor seventh chords that do not possess dominant function, such as, in melodic minor, IV. To analyze seventh chords indicate the quality of the triad; major: I, minor: ii, half-diminished: vii, or augmented: III+; and the quality of the seventh; same: 7, or different: or . With chord letters used to indicate the root and chord quality, and add 7, thus a seventh chord on ii in C major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmented Major Seventh Chord
In music, an augmented major seventh chord or major seventh sharp five chord is a seventh chord composed of a root, major third, augmented fifth, and major seventh (1, 3, 5, 7). It can be viewed as an augmented triad with an additional major seventh. When using popular-music symbols, it is denoted by augM7, +M7, +7, M75, M7(5), M7/5, M7+5, maj+7, +7, etc. For example, the augmented major seventh chord built on C, written as CaugM7, has pitches C–E–G–B: : The chord can be represented by the integer notation . The augmented major seventh chord is associated with the augmented scale (see jazz scale and chord-scale system). This chord also comes from the third mode of both the harmonic minor and the melodic minor scales. For example, the third mode of the A melodic minor scale outlines an augmented major seventh chord, as shown below. : As with dominant seventh chords, nondominant seventh chords including the augmented major seventh usually progress according to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
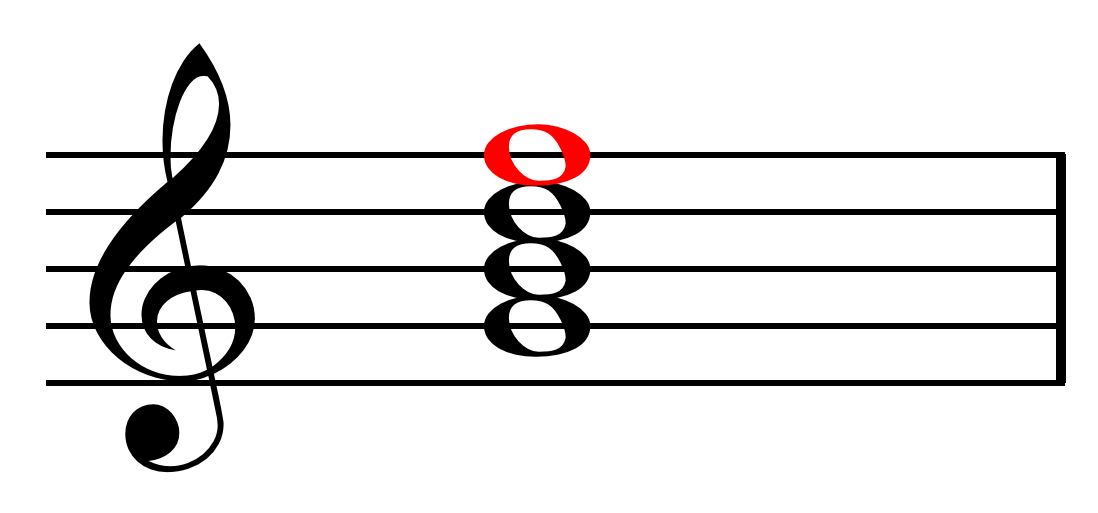
Major Seventh Chord
In music, a major seventh chord is a seventh chord in which the third is a major third above the root and the seventh is a major seventh above the root. The major seventh chord, sometimes also called a ''Delta chord'', can be written as maj7, M7, , ⑦, etc. The "7" doesn't have to be superscripted, but if it is, then any alterations, added tones, or omissions are usually also superscripted. For example, the major seventh chord built on C, commonly written as Cmaj7, has pitches C–E–G–B: : It can be represented by the integer notation . According to Forte, the major seventh chord is exemplified by IV7, which originates melodically. Forte, Allen (1979). ''Tonal Harmony in Concept & Practice'', p. 150. . : The just major seventh chord is tuned in the ratios 8:10:12:15, as a just major chord is tuned 4:5:6 and a just major seventh is tuned 15:8. The minor-minor sixth chord (minor triad with an added minor sixth) is an inversion of this chord. Examples In 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resolution (music)
Resolution in western tonal music theory is the move of a note or chord from dissonance (an unstable sound) to a consonance (a more final or stable sounding one). Dissonance, resolution, and suspense can be used to create musical interest. Where a melody or chordal pattern is expected to resolve to a certain note or chord, a different but similarly suitable note can be resolved to instead, creating an interesting and unexpected sound. For example, the deceptive cadence. Basis Resolution has a strong basis in tonal music, since atonal music generally contains a more constant level of dissonance and lacks a tonal center to which to resolve. The concept of "resolution", and the degree to which resolution is "expected", is contextual as to culture and historical period. In a classical piece of the Baroque The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Progression
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is constant. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is called the radius. Usually, the radius is required to be a positive number. A circle with r=0 (a single point) is a degenerate case. This article is about circles in Euclidean geometry, and, in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted. Specifically, a circle is a simple closed curve that divides the plane into two regions: an interior and an exterior. In everyday use, the term "circle" may be used interchangeably to refer to either the boundary of the figure, or to the whole figure including its interior; in strict technical usage, the circle is only the boundary and the whole figure is called a '' disc''. A circle may also be defined as a special k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major And Minor
In Western music, the adjectives major and minor may describe a chord, scale, or key. As such, composition, movement, section, or phrase may be referred to by its key, including whether that key is major or minor. Intervals Some intervals may be referred to as ''major'' and ''minor''. A major interval is one semitone larger than a minor interval. The words ''perfect'', ''diminished'', and ''augmented'' are also used to describe the quality of an interval. Only the intervals of a second, third, sixth, and seventh (and the compound intervals based on them) may be major or minor (or, rarely, diminished or augmented). Unisons, fourths, fifths, and octaves and their compound interval must be perfect (or, rarely, diminished or augmented). In Western music, a minor chord "sounds darker than a major chord". Kamien, Roger (2008). ''Music: An Appreciation'', 6th Brief Edition, p. 46. . Scales and chords The other uses of ''major'' and ''minor'' generally refer to scales a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root (chord)
In music theory, the concept of root is the idea that a chord can be represented and named by one of its notes. It is linked to harmonic thinking—the idea that vertical aggregates of notes can form a single unit, a chord. It is in this sense that one speaks of a "C chord" or a "chord on C"—a chord built from C and of which the note (or pitch) C is the root. When a chord is referred to in Classical music or popular music without a reference to what type of chord it is (either major or minor, in most cases), it is assumed a major triad, which for C contains the notes C, E and G. The root need not be the bass note, the lowest note of the chord: the concept of root is linked to that of the inversion of chords, which is derived from the notion of invertible counterpoint. In this concept, chords can be inverted while still retaining their root. In tertian harmonic theory, wherein chords can be considered stacks of third intervals (e.g. in common practice tonality), the root ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord Letters
Chord may refer to: * Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously ** Guitar chord a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning * Chord (geometry), a line segment joining two points on a curve * Chord (astronomy), a line crossing a foreground astronomical object during an occultation which gives an indication of the object's size and/or shape * Chord (graph theory), an edge joining two nonadjacent nodes in a cycle * Chord in truss construction – an outside member of a truss, as opposed to the inner "webbed members" * Chord (aeronautics), the distance between the front and back of a wing, measured in the direction of the normal airflow. The term chord was selected due to the curved nature of the wing's surface * Chord (peer-to-peer), a peer-to-peer protocol and algorithm for distributed hash tables (DHT) * Chord (concurrency), a concurrency construct in some object-oriented programming languages * In British railway terminology, a chor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh (chord)
In music, the seventh factor of a chord is the note or pitch seven scale degrees above the root or tonal center. When the seventh is the bass note, or lowest note, of the expressed chord, the chord is in third inversion . Conventionally, the seventh is fourth in importance to the root, fifth, and third, with third inversion being the third strongest inversion and the seventh variably minor or major. In jazz In jazz chords and theory, and classical music theory, the seventh is what defines a chord as a " seventh chord". Moreover, most triads that appear in lead sheets or fake books can have sevenths added to them, using the performer's discretion and "ear". For example, if a tune is in the key of C, if there is a G chord, the chord-playing performer will usually "voice" this chord as G7. While in a strict classical music context, the notes of a G7 chord would be "G–B–D–F", in jazz, the fifth of the chord is often omitted. The root is also often omitted if playin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmented Chord
Augment or augmentation may refer to: Language * Augment (Indo-European), a syllable added to the beginning of the word in certain Indo-European languages *Augment (Bantu languages), a morpheme that is prefixed to the noun class prefix of nouns in certain Bantu languages *Augment, a name sometimes given to the verbal ''ō-'' prefix in Nahuatl grammar Technology *Augmentation (obstetrics), the process by which the first and/or second stages of an already established labour is accelerated or potentiated by deliberate and artificial means *Augmentation (pharmacology), the combination of two or more drugs to achieve better treatment results *Augmented reality, a live view of a physical, real-world environment whose elements are ''augmented'' by computer-generated sensory input *Augmented cognition, a research field that aims at creating revolutionary human-computer interactions *Augment (Tymshare), a hypertext system derived from Douglas Engelbart's oN-Line System, renamed "Augment" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Chord
In music theory, a minor chord is a chord that has a root, a minor third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord comprises only these three notes, it is called a minor triad. For example, the minor triad built on C, called a C minor triad, has pitches C–E–G: In harmonic analysis and on lead sheets, a C minor chord can be notated as Cm, C−, Cmin, or simply the lowercase "c". A minor triad is represented by the integer notation . A minor triad can also be described by its intervals: the interval between the bottom and middle notes is a minor third, and the interval between the middle and top notes is a major third. By contrast, a major triad has a major third on the bottom and minor third on top. They both contain fifths, because a minor third (three semitones) plus a major third (four semitones) equals a perfect fifth (seven semitones). Chords that are constructed of consecutive (or "stacked") thirds are called '' tertian.'' In Western classical music from 1600 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Chord
In music theory Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the " rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (k ..., a major chord is a chord (music), chord that has a root (chord), root, a major third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord comprises only these three notes, it is called a major Triad (music), triad. For example, the major triad built on C, called a C major triad, has pitches C–E–G: In harmonic analysis and on lead sheet, lead sheets, a C major chord can be notated as C, CM, CΔ, or Cmaj. A major triad is represented by the Pitch class#Integer notation, integer notation . A major triad can also be described by its Interval (music), intervals: the interval between the bottom and middle notes is a major third, and the interval between the middle and top notes is a minor third. By contrast, a Minor triad, minor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)