|
Ngatutura Volcanic Field
The extinct Ngatutura volcanic field that was active between 1.54 and 1.83 million years ago is one of four volcanic fields in an intraplate back arc relationship with the still active Hauraki Rift and the presently dormant Auckland volcanic field. The other volcanic fields, which are part of the Auckland Volcanic Province, are the oldest, Okete to the south near Raglan in late Pliocene times (2.7-1.8 Ma). and to the north the younger South Auckland volcanic field. Geology This field is smaller than the other three and has far fewer basaltic volcanic centres. However at least 16 volcanic centres, mostly scoria cones associated with lava flows of limited hawaiite to nepheline hawaiite composition are known. Some of the basalt deposits in this region of the coast are now known to be related to the West Ngatutura volcanic field with a stratigraphic age of c. 3.5 Ma around 60 km offshore. The earlier work on the field had suggested fewer centres being: #Initial vent #*This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In New Zealand
This is a partial list of active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes in New Zealand. Kermadec Arc and Havre Trough North Island Taupō Volcanic Zone Elsewhere Mangakino Culdera South Island Other Ross Dependency New Zealand also has ''de facto'' administration over Ross Dependency in Antarctica, which contains the following volcanoes: References External links {{GeoGroupTemplateNew Zealand's Volcanoesat GNS Science New Zealand Volcanoes Volcanoes A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ... Geography of the Kermadec Islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
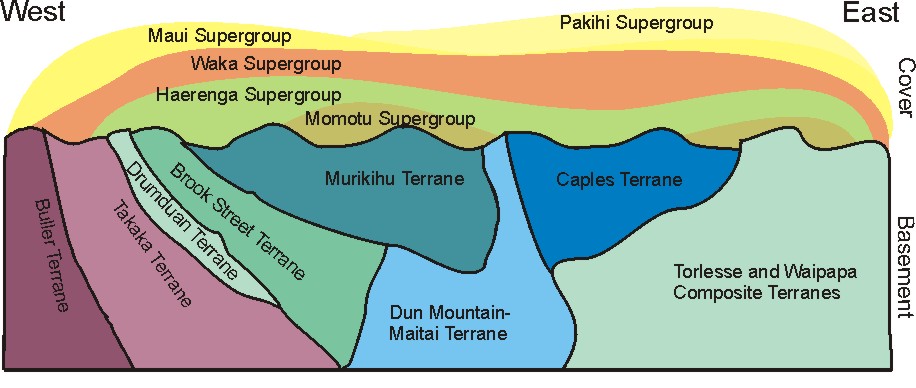
Geology Of New Zealand
The geology of New Zealand is noted for its volcanic activity, earthquakes and geothermal areas because of its position on the boundary of the Australian Plate and Pacific Plates. New Zealand is part of Zealandia, a microcontinent nearly half the size of Australia that broke away from the Gondwanan supercontinent about 83 million years ago. New Zealand's early separation from other landmasses and subsequent evolution have created a unique fossil record and modern ecology. New Zealand's geology can be simplified into three phases. First the basement rocks of New Zealand formed. These rocks were once part of the super-continent of Gondwana, along with South America, Africa, Madagascar, India, Antarctica and Australia. The rocks that now form the, mostly submerged, continent of Zealandia were then nestled between Eastern Australia and Western Antarctica. Secondly New Zealand drifted away from Gondwana and many sedimentary basins formed, which later became the sedimentary rocks cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism Of New Zealand
The volcanism of New Zealand has been responsible for many of the country's geographical features, especially in the North Island and the country's outlying islands. While the land's volcanism dates back to before the Zealandia microcontinent rifted away from Gondwana 60–130 million years ago, activity continues today with minor eruptions occurring every few years. This recent activity is primarily due to the country's position on the boundary between the Indo-Australian and Pacific Plates, a part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, and particularly the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate. New Zealand's rocks record examples of almost every kind of volcanism observed on Earth, including some of the world's largest eruptions in geologically recent times. None of the South Island's volcanoes are active. Major eruptions New Zealand has been the site of many large explosive eruptions during the last two million years, including several of supervo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Waikato
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Waikato
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogenetic Volcanic Fields
{{disambiguation ...
Monogenetic may refer to: * Monogenetic in biology, of or pertaining to monogenesis (Mendelian inheritance) * Monogenetic volcanic field in geology, a cluster of volcanoes that only erupted once * Monogenetic theory of pidgins in linguistics, a theory about the origin of creole languages See also * Monogenous (other) * Monogenic (other) Monogenic may refer to: * Monogenic signal, in the theory of analytic signals * Monogenic disorder, disease, inheritance, or trait, a single gene disorder resulting from a single mutated gene ** Monogenic diabetes, or maturity-onset diabetes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy Of New Zealand
This is a list of the units into which the rock succession of New Zealand is formally divided. As new geological relationships have been discovered new names have been proposed and others are made obsolete. Not all these changes have been universally adopted. This table is based on the 2014 New Zealand Stratigraphic Lexicon (Litho2014). However, obsolete names that are still in use and names postdating the lexicon are included if it aids in understanding. Names for particular rock units have two parts, a proper name which is almost always a geographic location where the rock is found and a hierarchical rank (e.g. Waitematā Group). This ranking system starts with individual 'beds' of rock which can be grouped into 'members', members are grouped into 'formations', formations into 'subgroups' then 'groups'. In New Zealand, groups are further combined into 'supergroups' or for basement rocks into terranes. Not all of these hierarchical layers are necessarily present within a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism In New Zealand
The volcanism of New Zealand has been responsible for many of the country's geographical features, especially in the North Island and the country's outlying islands. While the land's volcanism dates back to before the Zealandia microcontinent rifted away from Gondwana 60–130 million years ago, activity continues today with minor eruptions occurring every few years. This recent activity is primarily due to the country's position on the boundary between the Indo-Australian and Pacific Plates, a part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, and particularly the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate. New Zealand's rocks record examples of almost every kind of volcanism observed on Earth, including some of the world's largest eruptions in geologically recent times. None of the South Island's volcanoes are active. Major eruptions New Zealand has been the site of many large explosive eruptions during the last two million years, including several of supervolcano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Waikato Region
The Waikato and King Country regions of New Zealand are built upon a basement of greywacke rocks, which form many of the hills. Much of the land to the west of the Waikato River and in the King Country to the south has been covered by limestone and sandstone, forming bluffs and a karst landscape. The volcanic cones of Karioi and Pirongia dominate the landscape near Raglan and Kawhia Harbours. To the east, the land has been covered with ignimbrite deposits from the Taupo Volcanic Zone. Large amounts of pumice from the Taupo Volcanic Zone have been deposited in the Waikato Basin and Hauraki Plains. Basement rocks As with most of New Zealand, the basement rocks of the Waikato Region and King Country are composed of greywacke (indurated sandstone, siltstone and mudstone). The Waipa Fault passes north–south through the Waikato-King Country region, from Taupiri, along the Waipā River, and south to near Ohura. It represents a major dividing line between different terranes. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hauraki Rift
The Hauraki Rift is an active NeS-to NWeSE-striking rift valley system in the North Island of New Zealand that has produced the Firth of Thames and the Hauraki Plains. It is approximately wide and long. Geology The rift valley in the north appears to be delimited in the west by the line of the Firth of Thames Fault and to the east by the Hauraki Fault. The mountains of the Coromandel (which include andesitic and basaltic back arc volcanoes) and Kaimai Range to the east and the Hunua Range to the west give it the appearance of a full graben although it has also been described as a simple structure of 2 to 3 half-grabens so the term Hauraki Graben for the low lying portions would be incorrect. However the apparent line in the south of the Firth of Thames Fault no longer follows the apparent horst structure to the west and some believe the line of the Waikato River after it leaves the old Taupō Rift gives a better guide to the western line of the rift as structures have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Auckland Region
The Auckland Region of New Zealand is built on a basement of greywacke rocks that form many of the islands in the Hauraki Gulf, the Hunua Ranges, and land south of Port Waikato. The Waitākere Ranges in the west are the remains of a large andesitic volcano, and Great Barrier Island was formed by the northern end of the Coromandel Volcanic Zone. The Auckland isthmus and North Shore are composed of Waitemata sandstone and mudstone, and portions of the Northland Allochthon extend as far south as Albany. Little Barrier Island was formed by a relatively isolated andesitic volcano, active around 1 to 3 million years ago. The Manukau and South Kaipara Harbours are protected by the recent sand dune deposits of the Awhitu and South Kaipara Peninsulas. Recent basaltic volcanic activity has produced many volcanic cones throughout the Auckland Region, including the iconic Rangitoto Island. Basement rocks As with most of New Zealand, the basement rocks of the Auckland Region are composed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)