|
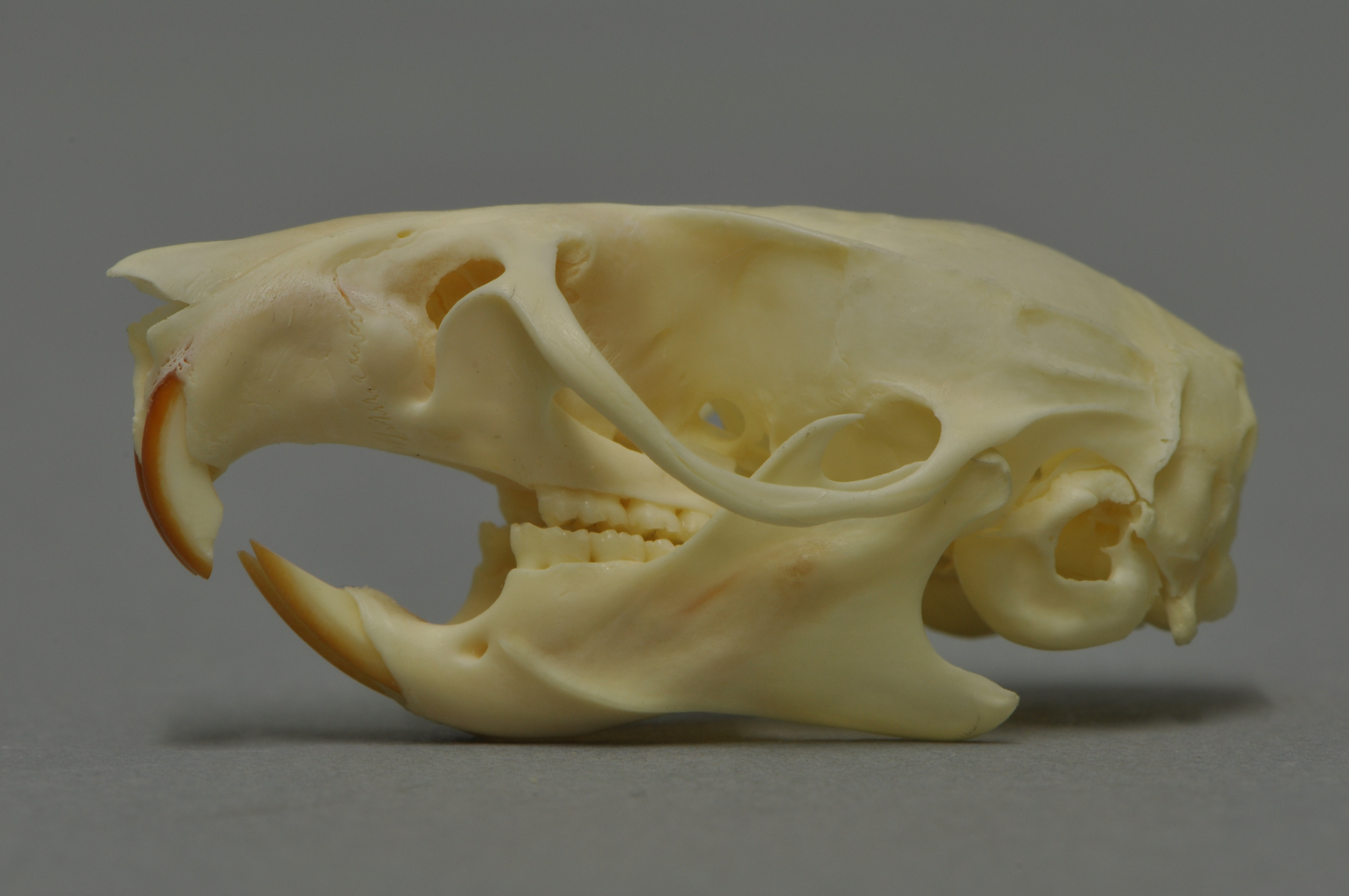
New Zealand Lesser Short-tailed Bat
The New Zealand lesser short-tailed bat (''Mystacina tuberculata'') is a small-sized omnivorous mammal endemism, endemic to the islands of New Zealand. It is one of two extant and three overall terrestrial mammal species unique to New Zealand. Its closest relative, the New Zealand greater short-tailed bat (''M. robusta''), was last seen in 1965 and is presumed extinct due to intense predation from ship rats introduced in the last few centuries. These bats are also commonly referred to as pekapeka, their Māori-language name. Lesser short-tailed bats have unique adaptations that differentiate them from bats found in other parts of the world. For example, they are fully capable of moving along the ground to search for food, and the males sing to attract partners, taking turns to do so. Lesser short-tailed bats are a vulnerable species, so extensive conservation work and research are being done to prevent extinction. Taxonomy and evolution Taxonomic classification ''Mystacina t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Edward Gray
John Edward Gray (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828). The same is used for a zoological name. Gray was keeper of zoology at the British Museum in London from 1840 until Christmas 1874, before the natural history holdings were split off to the Natural History Museum. He published several catalogues of the museum collections that included comprehensive discussions of animal groups and descriptions of new species. He improved the zoological collections to make them amongst the best in the world. Biography Gray was born in Walsall, but his family soon moved to London, where Gray studied medicine. He assisted his father in writing ''The Natural Arrangement of British Plants'' (1821). After being blackballed by the Linnean Society of London, Gray shifted his interest from botany to zoology. He began his zoological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huhu Beetle 07
The huhu beetle (''Prionoplus reticularis'') is a longhorn beetle endemic to New Zealand. It is the heaviest beetle found in New Zealand. Terminologies The Māori name ''huhu'' is ultimately Austronesian in origin from root form *''bukbuk''₃, where cognates in related languages (like Tagalog ''bukbok'') refer to weevils known to infest wood and rice across tropical Southeast Asia. In Māori, ''huhu'' has semantically evolved to refer explicitly to its larval form (also ''tunga haere'', ''tunga rākau''). As the huhu larva reaches maturity it ceases to bore in wood and casts its skin. This still edible stage is known in Māori as '. It then develops wings and legs, and while it is still white, it is known as ' or ''pepe-te-muimui''. Finally, it emerges and flies off to reproduce and is known as '. Life cycle Female adult huhu beetles oviposit their 3mm cigar-shaped eggs in clutches of 10–50, though up to 100 may be found. Eggs are laid in cryptic sites or in crack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
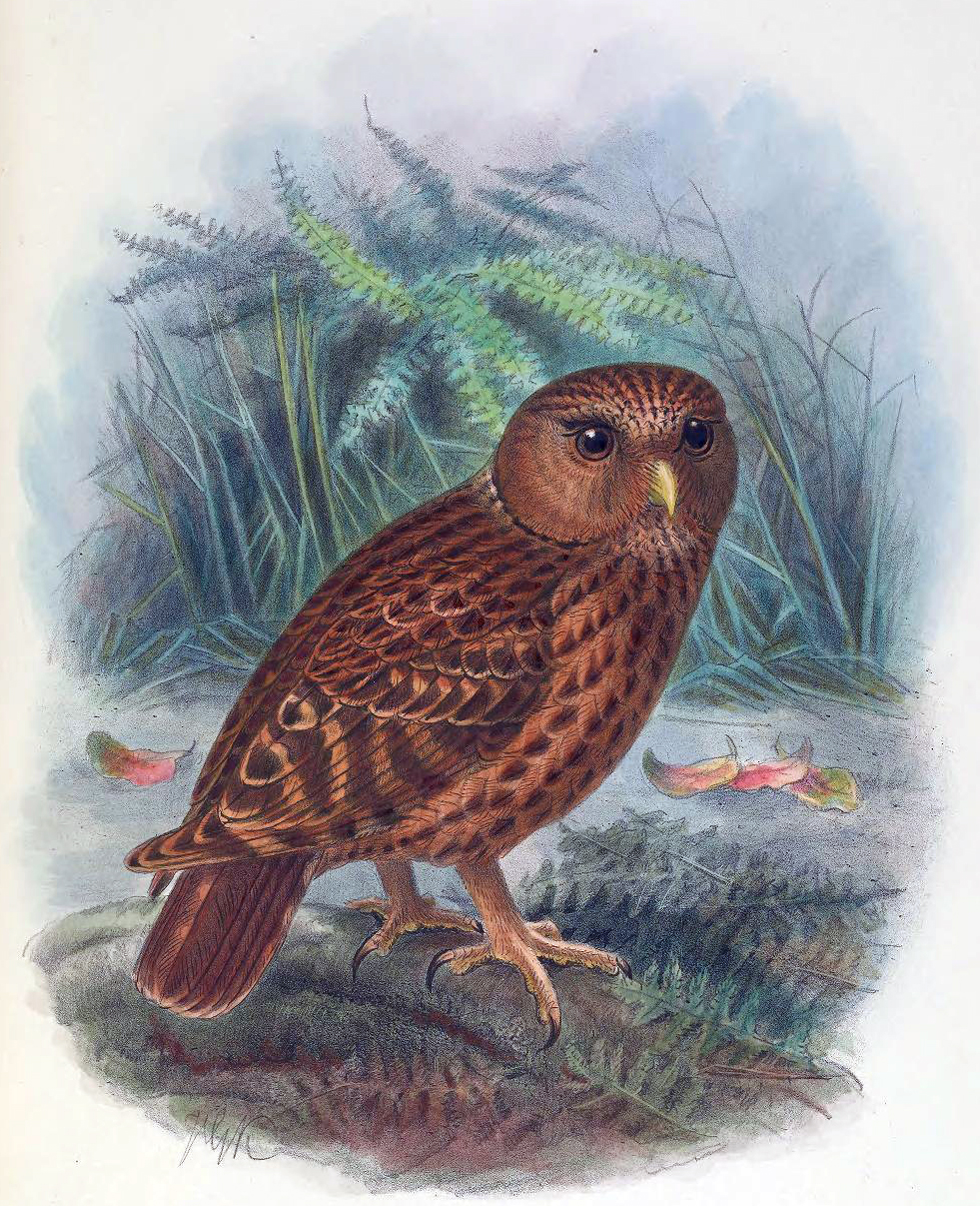
Laughing Owl
The laughing owl (''Ninox albifacies''), also known as ''whēkau'', the laughing jackass, or the white-faced owl, is an Extinction, extinct species of owl that was Endemism, endemic to New Zealand. Plentiful when European settlers arrived in New Zealand, its scientific description was published in 1845, but it was largely or completely extinct by 1914. The species was traditionally considered to belong to the monotypic genus ''Sceloglaux'' Johann Jakob Kaup, Kaup, 1848 ("scoundrel owl", probably because of the mischievous-sounding calls), although recent genetic studies indicate that it belongs with the boobook owls in the genus ''Ninox''. Taxonomy The laughing owl was originally described as ''Athene albifacies'' by George Robert Gray in 1844, based on a specimen from Waikouaiti, South Island. The type specimen is held at the British Museum (Reg. no. 1845.1.13.5). The species was later transferred by Johann Jakob Kaup to other genera, first to the Monotypic taxon, monotypic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Rat
The brown rat (''Rattus norvegicus''), also known as the common rat, street rat, sewer rat, wharf rat, Hanover rat, Norway rat and Norwegian rat, is a widespread species of common rat. One of the largest Muroidea, muroids, it is a brown or grey rodent with a body length of up to long, and a tail slightly shorter than that. It weighs between . Thought to have originated in northern China and neighbouring areas, this rodent has now spread to all continents except Antarctica, and is the dominant rat in Europe and much of North America, having become Naturalisation (biology), naturalised across the world. With rare exceptions, the brown rat lives wherever humans live, particularly in urban areas. They are omnivorous, reproduce rapidly, and can serve as a vector for several human diseases. Selective breeding of the brown rat has produced the fancy rat (rats kept as pets), as well as the laboratory rat (rats used as model organisms in biological research). Both fancy rats and laborato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious Pest (organism), pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually Morph (zoology), color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesian Rat
The Polynesian rat, Pacific rat or little rat (''Rattus exulans''), or , is the third most widespread species of rat in the world behind the brown rat and black rat. Contrary to its vernacular name, the Polynesian rat originated in Southeast Asia, and like its relatives has become widespread, migrating to most of Polynesia, including New Zealand, Easter Island, and Hawaii. It shares high adaptability with other rat species extending to many environments, from grasslands to forests. It is also closely associated with humans, who provide easy access to food. It has become a major pest in most areas of its distribution. Description The Polynesian rat is similar in appearance to other rats, such as the black rat and the brown rat. It has large, round ears, a pointed snout, black/brown hair with a lighter belly, and comparatively small feet. It has a thin, long body, reaching up to in length from the nose to the base of the tail, making it slightly smaller than other human-associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union For Conservation Of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable". Over the past decades, IUCN has widened its focus beyond conservation ecology and now incorporates issues related to sustainable development in its projects. IUCN does not itself aim to mobilize the public in support of nature conservation. It tries to influence the actions of governments, business and other stakeholders by providing information and advice and through building partners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulnerable Species
A vulnerable species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being threatened species, threatened with extinction unless the circumstances that are threatened species, threatening its survival and reproduction improve. Vulnerability is mainly caused by habitat loss or destruction of the species' home. Vulnerable habitat or species are monitored and can become increasingly threatened. Some species listed as "vulnerable" may be common in captivity (animal), captivity, an example being the military macaw. In 2012 there were 5,196 animals and 6,789 plants classified as vulnerable, compared with 2,815 and 3,222, respectively, in 1998. Practices such as cryoconservation of animal genetic resources have been enforced in efforts to conserve vulnerable breeds of livestock specifically. Criteria The International Union for Conservation of Nature uses several criteria to enter species in this category. A taxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Short-tailed Bats, Mystacina Tuberculata
Southern may refer to: Businesses * China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China * Southern Airways, defunct US airline * Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US * Southern Airways Express, Memphis-based passenger air transportation company, serving eight cities in the US * Southern Company, US electricity corporation * Southern Music (now Peermusic), US record label * Southern Railway (other), various railways * Southern Records, independent British record label * Southern Studios, recording studio in London, England * Southern Television, defunct UK television company * Southern (Govia Thameslink Railway), brand used for some train services in Southern England Media * 88.3 Southern FM, a non-commercial community radio station based in Melbourne, Australia * Heart Sussex, a radio station in Sussex, England, previously known as "Southern FM" * ''Nanfang Daily'' or ''Southern Daily'', the official Communist Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lek Mating
A lek is an aggregation of male animals gathered to engage in competitive displays and courtship rituals, known as lekking, to entice visiting females which are surveying prospective partners with which to mate. It can also refer to a space used by displaying males to defend their own share of territory for the breeding season. A lekking species is characterised by male displays, strong female mate choice, and the conferring of indirect benefits to males and reduced costs to females. Although most prevalent among birds such as black grouse, lekking is also found in a wide range of vertebrates including some bony fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and arthropods including crustaceans and insects. A classical lek consists of male territories in visual and auditory range of each other. An exploded lek, as seen in the kākāpō (the owl parrot), has more widely separated territories, but still in auditory range. Lekking is associated with an apparent paradox: strong sexual s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fission–fusion Society
In ethology, fission–fusion society is one in which the size and composition of the social group change as time passes and animals move throughout the environment; animals merge into a group (fusion)—e.g. sleeping in one place—or split (fission)—e.g. foraging in small groups during the day. For species that live in fission–fusion societies, group composition is a dynamic property. The change in composition, subgroup size, and dispersion of different groups are 3 main elements of a fission-fusion society. This social organization is found in several primates, elephants, cetaceans, ungulates, social carnivores, some birds and some fish. Species Fission-fusion societies occur among many different species of primates (e.g. chimpanzees, orangutans, and humans), elephants (e.g. forest elephants, African elephants), and bats (e.g. northern long-eared bats). The change in composition, subgroup size, and dispersion of different groups are 3 main elements of a fission-fusion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Echolocation
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological active sonar used by several animal groups, both in the air and underwater. Echolocating animals emit calls and listen to the Echo (phenomenon) , echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for animal navigation , navigation, foraging, and predation, hunting prey. Echolocation calls can be Frequency modulation, frequency modulated (FM, varying in pitch during the call) or constant frequency (CF). FM offers precise range discrimination to localize the prey, at the cost of reduced operational range. CF allows both the prey's velocity and its movements to be detected by means of the Doppler effect. FM may be best for close, cluttered environments, while CF may be better in open environments or for hunting while perched. Echolocating animals include mammals, especially odontocetes (toothed whales) and some bat species, and, using s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |