|
Neural Plate
The neural plate is a key developmental structure that serves as the basis for the nervous system. Cranial to the primitive node of the embryonic primitive streak, ectodermal tissue thickens and flattens to become the neural plate. The region anterior to the primitive node can be generally referred to as the neural plate. Cells take on a columnar appearance in the process as they continue to lengthen and narrow. The ends of the neural plate, known as the neural folds, push the ends of the plate up and together, folding into the neural tube, a structure critical to brain and spinal cord development. This process as a whole is termed primary neurulation. Signaling proteins are also important in neural plate development, and aid in differentiating the tissue destined to become the neural plate. Examples of such proteins include bone morphogenetic proteins and cadherins. Expression of these proteins is essential to neural plate folding and subsequent neural tube formation. Involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium, non-epithelial blood cells and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follistatin
Follistatin also known as activin-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FST'' gene. Follistatin is an autocrine glycoprotein that is expressed in nearly all tissues of higher animals. Its primary function is the binding and bioneutralization of members of the TGF-β superfamily, with a particular focus on activin, a paracrine hormone. An earlier name for the same protein was FSH-suppressing protein (FSP). At the time of its initial isolation from follicular fluid, it was found to inhibit the anterior pituitary's secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Biochemistry Follistatin is part of the inhibin-activin-follistatin axis. Currently there are three reported isoforms, FS-288, FS-300, and FS-315. Two, FS-288 and FS-315, are known to be created by alternative splicing of the primary mRNA transcript. FS-300 (porcine follistatin) is thought to be the product of posttranslational modification via truncation of the C-terminal domain from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noggin (protein)
Noggin, also known as NOG, is a protein that is involved in the development of many body tissues, including nerve tissue, muscles, and bones. In humans, noggin is encoded by the ''NOG'' gene. The amino acid sequence of human noggin is highly homologous to that of rat, mouse, and '' Xenopus'' (an aquaticfrog genus). Noggin is an inhibitor of several bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs): it inhibits at least BMP2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 13, and 14. The protein's name, which is a slang English-language word for "head", was coined in reference to its ability to produce embryos with large heads when exposed at high concentrations. Function Noggin is a signaling molecule that plays an important role in promoting somite patterning in the developing embryo. It is released from the notochord and regulates bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4) during development. The absence of BMP4 will cause the patterning of the neural tube and somites from the neural plate in the developing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordin
Chordin (from Greek χορδή, string, catgut) is a protein with a prominent role in dorsal–ventral patterning during early embryonic development. In humans it is encoded for by the ''CHRD'' gene. History Chordin was originally identified in the African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'') in the laboratory of Edward M. De Robertis as a key developmental protein that dorsalizes early vertebrate embryonic tissues. It was first hypothesized that chordin plays a role in the dorsal homeobox genes in Spemann's organizer. The chordin gene was discovered through its activation following use of gsc ( goosecoid) and Xnot mRNA injections. The discoverers of chordin concluded that it is expressed in embryo regions where gsc and Xnot were also expressed, which included the prechordal plate, the notochord, and the chordoneural hinge. The expression of the gene in these regions led to the name chordin. Initial functions of chordin were thought to include recruitment of neighboring cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Symmetry
In mathematics, reflection symmetry, line symmetry, mirror symmetry, or mirror-image symmetry is symmetry with respect to a reflection. That is, a figure which does not change upon undergoing a reflection has reflectional symmetry. In 2D there is a line/axis of symmetry, in 3D a plane of symmetry. An object or figure which is indistinguishable from its transformed image is called mirror symmetric. In conclusion, a line of symmetry splits the shape in half and those halves should be identical. Symmetric function In formal terms, a mathematical object is symmetric with respect to a given operation such as reflection, rotation or translation, if, when applied to the object, this operation preserves some property of the object. The set of operations that preserve a given property of the object form a group. Two objects are symmetric to each other with respect to a given group of operations if one is obtained from the other by some of the operations (and vice versa). The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by ''BMP4'' gene. BMP4 is found on chromosome 14q22-q23. BMP4 is a member of the bone morphogenetic protein family which is part of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. The superfamily includes large families of growth and differentiation factors. BMP4 is highly conserved evolutionarily. BMP4 is found in early embryonic development in the ventral marginal zone and in the eye, heart blood and otic vesicle. Discovery Bone morphogenetic proteins were originally identified by an ability of demineralized bone extract to induce endochondral osteogenesis in vivo in an extraskeletal site. Function BMP4 is a polypeptide belonging to the TGF-β superfamily of proteins. It, like other bone morphogenetic proteins, is involved in bone and cartilage development, specifically tooth and limb development and fracture repair. This particular family member plays an important role in the onset of endochondral bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein BMP4 PDB 1reu
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins. The peripheral nervous system can be divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exception of the optic nerve (cranial nerve II), along with the retina. The second cranial nerve is not a true peripheral nerve but a tract of the diencephalon. Cranial nerve ganglia, as with all ganglia, are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response. The autonomic nervous system is regulated by integrated reflexes through the brainstem to the spinal cord and organs. Autonomic functions include control of respiration, cardiac regulation (the cardiac control center), vasomotor activity (the vasomotor center), and certain reflex actions such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting. Those are then subdivided into other areas and are also linked to autonomic subsystems and the peripheral nervous system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
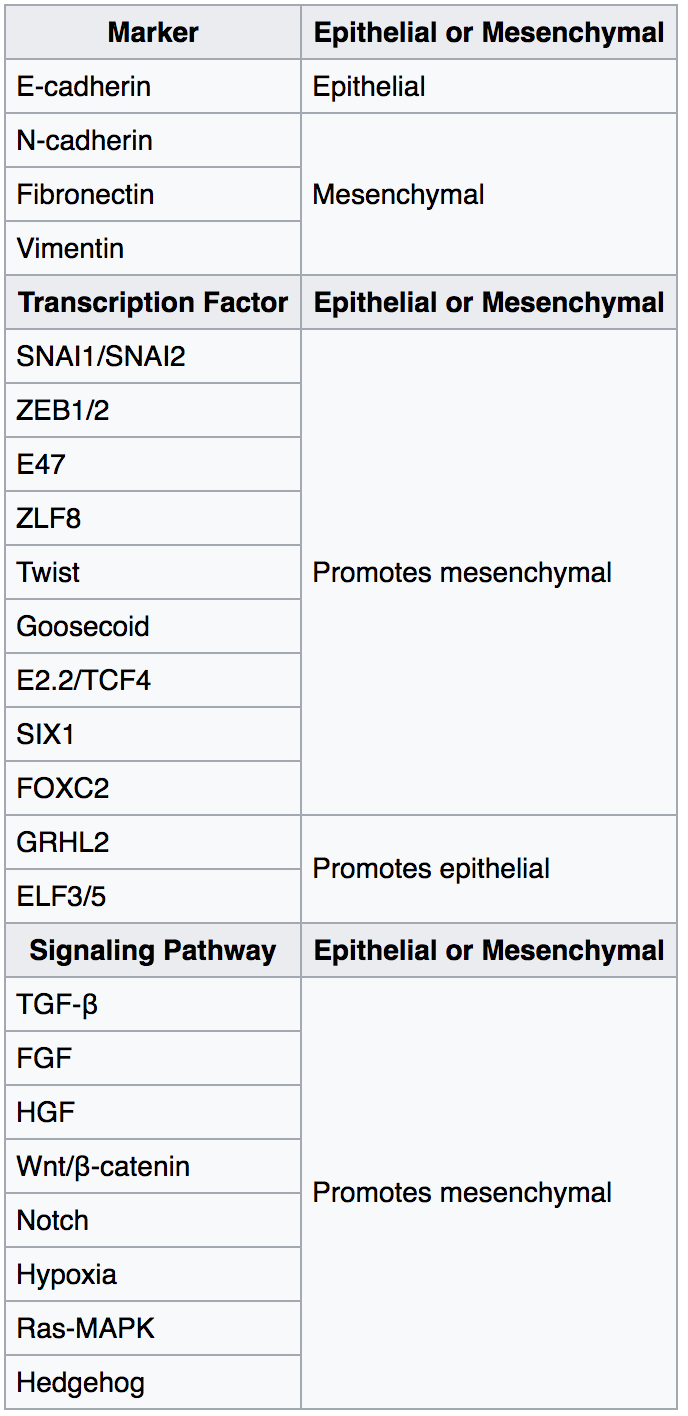
Epithelial–mesenchymal Transition
The epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process by which epithelial cells lose their cell polarity and cell–cell adhesion, and gain migratory and invasive properties to become mesenchymal stem cells; these are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types. EMT is essential for numerous developmental processes including mesoderm formation and neural tube formation. EMT has also been shown to occur in wound healing, in organ fibrosis and in the initiation of metastasis in cancer progression. Introduction Epithelial–mesenchymal transition was first recognized as a feature of embryogenesis by Betty Hay in the 1980s. EMT, and its reverse process, MET ( mesenchymal-epithelial transition) are critical for development of many tissues and organs in the developing embryo, and numerous embryonic events such as gastrulation, neural crest formation, heart valve formation, secondary palate development, and myogenesis. Epithelial and mesenchyma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |