|
Nanda Dynasty
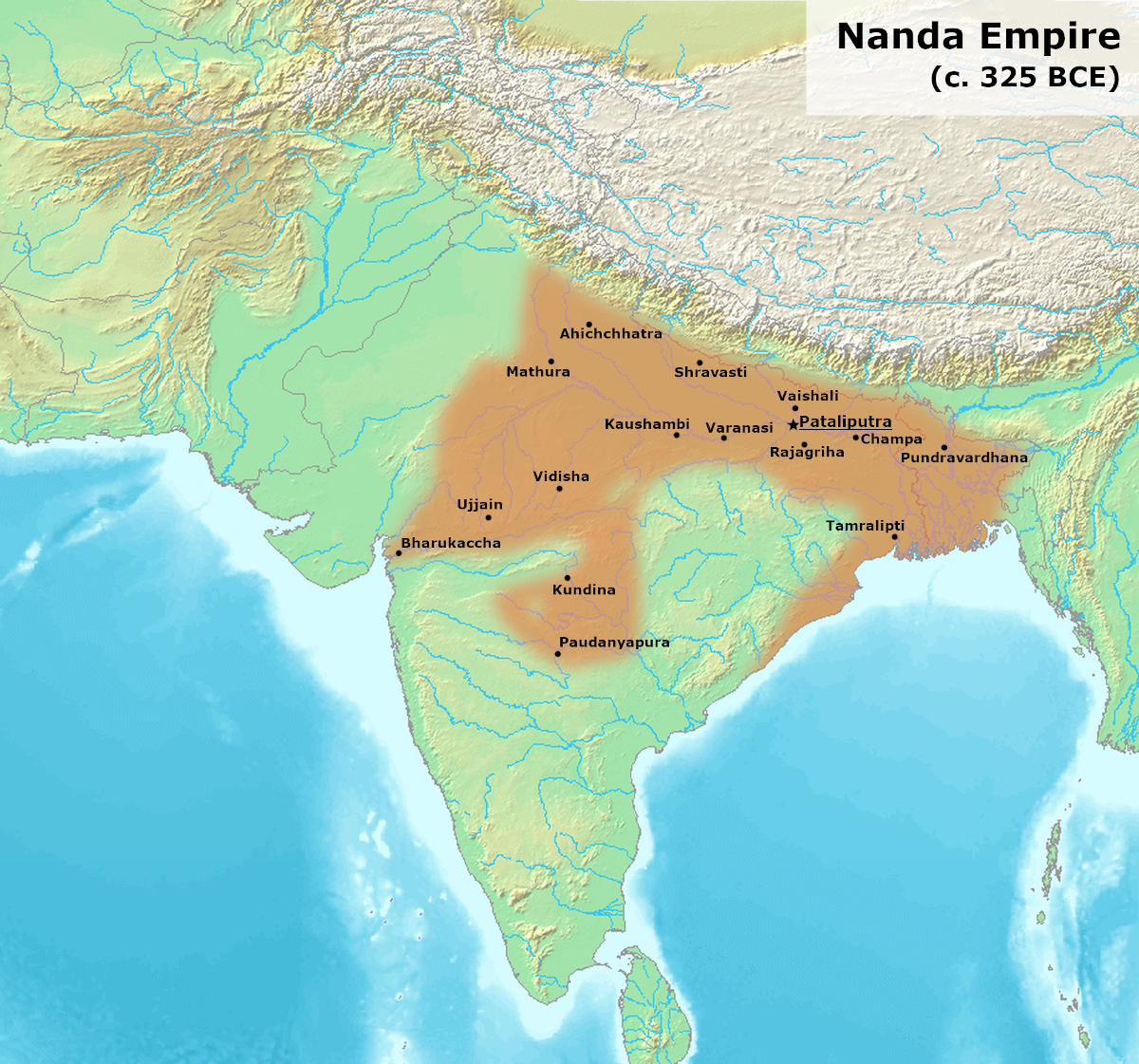
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded their empire to include a larger part of northern India. Ancient sources differ considerably regarding the names of the Nanda kings and the duration of their rule, but based on the Buddhist tradition recorded in the '' Mahavamsa'', they appear to have ruled during ''circa'' 345–322 BCE, although some theories date the start of their rule to fifth century BCE. The Nandas built on the successes of their Haryanka and Shaishunaga predecessors, and instituted a more centralised administration. Ancient sources credit them with amassing great wealth, which was probably a result of introduction of new currency and taxation system. Ancient texts also suggest that the Nandas were unpopular among their subjects because of their low status birth, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharaja
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king". A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, and Chandragupta Maurya. 'Title inflation' soon led to most being rather mediocre or even petty in real power, which led to compound titles (among other efforts) being used in an attempt to distinguish some among their ranks. The female equivalent, Maharani (or Maharanee, Mahārājñī, Maharajin), denotes either the wife of a Maharaja (or Maharana etc.) or also, in states where it was customary, a woman ruling without a husband. The widow of a Maharaja is known as a Rajmata, "queen mother". Maharajakumar generally denotes a son of a Maharaja, but more specific titulatures are often used at each court, including Yuvaraja for the heir (the crown prince). The form "Maharaj" (without "-a") indicates a separation of noble and religious o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangaridai
Gangaridai ( gr, Γανγαρίδαι; Latin: ''Gangaridae'') is a term used by the ancient Greco-Roman writers (1st century BCE-2nd century AD) to describe a people or a geographical region of the ancient Indian subcontinent. Some of these writers state that Alexander the Great withdrew from the Indian subcontinent because of the strong war elephant force of the Gangaridai. A number of modern scholars locate Gangaridai in the Ganges Delta of the Bengal region, although alternative theories also exist. Gange or Ganges, the capital of the Gangaridai (according to Ptolemy), has been identified with several sites in the region, including Chandraketugarh and Wari-Bateshwar. Names The Greek writers use the names "Gandaridae" (Diodorus), "Gandaritae", and "Gandridae" (Plutarch) to describe these people. The ancient Latin writers use the name "Gangaridae", a term that seems to have been coined by the 1st century poet Virgil. Some modern etymologies of the word Gangaridai split i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Sociological Society
Indian Sociological Society (ISS) is a professional body of sociologists in India. It publishes academic research journals, the ''Sociological Bulletin'' in English and the ''Bhartiya Samajshastra Sameeksha'' in Hindi language. History In in December 1951, the ''Indian Sociological Society'' was registered in Bombay by an initiative of its Founder-President (1951-1966), Prof. G. S. Ghurye, who was then Head of the Department of Sociology at University of Bombay. Prof. J. V. Fereira and Prof. K. M. Kapadia were the founding Secretaries. Activities Lifetime Achievement Awards From time to time, ISS grants the ''Lifetime Achievement Award'' to those who contribute to the advancement in the rigorous research knowledge and research in the field of sociology."Remembering Professor Arvind M. Shah, a Genial Doyen of Sociology", The Wire, 21 Sep 2020. Publication of academic journals From March 1952, ISS started publishing a biannual english language academic research journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalashoka
Kalashoka or Kakavarna was the son and successor of Shishunaga. He divided his kingdom between his ten sons and crowned his ninth son, Nandivardhana as the king of Magadha. Reign Shishunaga had transferred the capital of Magadha to Vaishali. Kalashoka succeeded his father Shishunaga Shishunaga (IAST: Śiśunāga, or Shusunaga) (c. 413 – 395 BCE) was the founder of the Shishunaga dynasty of the Magadha Empire in the present day northern India. Initially, he was an ''amatya'' (official) of the Magadha empire under the Har .... Kalashoka again transferred the capital to Pataliputra. According to Buddhist literature, the Second Buddhist Council, held 100 years after the Maha Parinirvana of Lord Buddha, in Vaishali, was patronised by King Kalashoka. But despite King Kalashoka's best efforts, differences among the Buddhists persisted. He divided his kingdom between his ten sons, who ruled simultaneously. References Citations Sources * * * 4th-century BC Indian monarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varna In Hinduism
''Varṇa'' ( sa, वर्ण, varṇa), in the context of Hinduism, refers to a social class within a hierarchical caste system. The ideology is epitomized in texts like ''Manusmriti'', which describes and ranks four varnas, and prescribes their occupations, requirements and duties, or ''Dharma''. *Brahmins: Vedic scholars, priests or teachers. *Kshatriyas: Rulers, administrators or warriors. *Vaishyas: Agriculturalists, farmers or merchants. *Shudras: Artisans, laborers or servants. Communities which belong to one of the four varnas or classes are called savarna Hindus. The Dalits and tribals who do not belong to any varna were called avarna. This quadruple division is a form of social stratification, quite different from the more nuanced system ''Jātis'' which correspond to the European term "caste". The varna system is discussed in Hindu texts, and understood as idealised human callings. The concept is generally traced to the '' Purusha Sukta'' verse of the Rig Veda. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class serving other three classes. The word caste comes from the Portuguese word casta. The word ''Shudra'' appears in the ''Rig Veda'' and it is found in other Hindu texts such as the ''Manusmriti'', ''Arthashastra'', '' Dharmashastras'' and '' Jyotishshastra''. In some cases, shudras participated in the coronation of kings, or were ministers and kings according to early Indian texts. History Vedas The term ''śūdra'' appears only once in the ''Rigveda''. This mention is found in the mythical story of creation embodied in the '' Purusha Sukta ("The Hymn of Man").'' It describes the formation of the four varnas from the body of a primeval man. It states that the brahmin emerged from his mouth, the kshatriya from his arms, the vaishya from his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahanandin
Mahanandin was the last king of the Shishunaga dynasty of the Indian subcontinent. The dynasty ruled parts of ancient India around the city of Pataliputra (present day Patna, Bihar). Life ''Puranas'' list Nandivardhana as the ninth Shishunaga king and his son Mahanandin as the tenth and the last Shishunaga king. Mahanandin was killed by his illegitimate son from a ''Shudra'' wife named Mahapadma Nanda Mahapadma Nanda (IAST: ''Mahāpadmānanda''; c. mid 4th century BCE), according to the Puranas, was the first Emperor of the Nanda Empire of ancient India. The Puranas describe him as a son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a Shudra .... References Citations Sources * * * 4th-century BC Indian monarchs History of Bihar Year of birth missing Year of death missing Kings of Magadha {{India-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahapadma Nanda
Mahapadma Nanda (IAST: ''Mahāpadmānanda''; c. mid 4th century BCE), according to the Puranas, was the first Emperor of the Nanda Empire of ancient India. The Puranas describe him as a son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a Shudra woman. These texts credit him with extensive conquests that expanded the Empire far beyond the Magadha region. The different Puranas variously give the length of his reign as 28 or 88 years, and state that his eight sons ruled in succession after him. The Buddhist texts don't mention him, and instead name the first Nanda ruler as robber-turned-king Ugrasena, who was succeeded by his eight brothers, the last of whom was Dhana Nanda. Reign According to the Puranas, Mahapadma or Mahapadma-pati (literally, "lord of the great lotus") was the first Nanda king. He was the son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a Shudra woman. The ''Puranas'' describe him as ''ekarat'' (sole sovereign) and ''sarva-kshatrantaka'' (destroyer of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends and other traditional lore. The Puranas are known for the intricate layers of symbolism depicted within their stories. Composed originally in Sanskrit and in other Indian languages,John Cort (1993), Purana Perennis: Reciprocity and Transformation in Hindu and Jaina Texts (Editor: Wendy Doniger), State University of New York Press, , pages 185-204 several of these texts are named after major Hindu gods such as Vishnu, Shiva, Brahma, and Adi Shakti. The Puranic genre of literature is found in both Hinduism and Jainism. The Puranic literature is encyclopedic, and it includes diverse topics such as cosmogony, cosmology, genealogies of gods, goddesses, kings, heroes, sages, and demigods, folk tales, pilgrimages, temples, medicine, astronomy, gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the context of later Vedic society wherein members were organised into four classes: ''brahmin'', kshatriya, '' vaishya'' and '' shudra''. History Early Rigvedic tribal monarchy The administrative machinery in the Vedic India was headed by a tribal king called Rajan whose position may or may not have been hereditary. The king may have been elected in a tribal assembly (called Samiti), which included women. The Rajan protected the tribe and cattle; was assisted by a priest; and did not maintain a standing army, though in the later period the rulership appears to have risen as a social class. The concept of the fourfold varna system is not yet recorded. Later Vedic period The hymn '' Purusha Sukta'' to the ''Rigveda'' describes the symbolic cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parishishtaparvan
The Parishishtaparvan () also known as the Sthaviravalicharitra () is a 12th-century Sanskrit mahakavya by Hemachandra which details the histories of the earliest Jain teachers. The poem comprises 3,460 verse couplets divided into 13 cantos of unequal length and is also notable for providing information on the political history of ancient India. The ''Trishashtishalakapurushacharitra'' (; ''The Lives of the Sixty-three Illustrious People''), an epic Sanskrit poem on the key figures in Jainism, was composed by Hemachandra at the request of the Chaulukya king, Kumarapala. The Sthaviravalicharitra (''The Lives of the Jain Elders'') is considered a self-contained sequel to this work and is consequently referred to as the Parishishtaparvan or ''The Appendix''. The period largely covered in the poem corresponds to and follows the growth of the kingdom of Magadha and the establishment of the Maurya Empire. According to Hemachandra, the sequence of rulers in the times of the Jains discu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Curtius Rufus
Quintus Curtius Rufus () was a Roman historian, probably of the 1st century, author of his only known and only surviving work, ''Historiae Alexandri Magni'', "Histories of Alexander the Great", or more fully ''Historiarum Alexandri Magni Macedonis Libri Qui Supersunt'', "All the Books That Survive of the Histories of Alexander the Great of Macedon." Much of it is missing. Apart from his name on the manuscripts, nothing else certain is known of him. This fact alone has led philologists to believe that he had another historical identity, to which, due to the accidents of time, the link has been broken. A few theories exist. They are treated with varying degrees of credibility by various authors. Meanwhile, the identity of Quintus Curtius Rufus, historian, is maintained separately. The historical ''alter ego'' Curtius' work is uniquely isolated. No other ancient work refers to it, or as far as is known, to him. Peter Pratt pointing out that the Senate and emperors frequently proscri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |