|
Namban Art
refers to Japanese art of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries influenced by contact with the or 'Southern barbarians', traders and missionaries from Europe and specifically from Portugal. It is a Sino-Japanese word, Chinese '' Nánmán'', originally referring to the peoples of South Asia and Southeast Asia. During the Nanban trade period, the word took on a new meaning when it came to designate the Portuguese, who first arrived in 1543, and later other Europeans. The term also refers to paintings which Europeans brought to Japan. History Nanban art developed after the first Portuguese ships arrived in Kyushu in 1543. While Christian icons and other objects were produced, or folding screens are particularly notable, with over 90 pairs surviving to this day. These vibrant paintings depicted foreigners of all colors arriving in Japanese ports and walking in the streets of Japanese inland towns (see figure 1). Another popular subject within Nanban art w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byōbu
are Japanese folding screens made from several joined panels, bearing decorative painting and calligraphy, used to separate interiors and enclose private spaces, among other uses. History are thought to have originated in Han dynasty China and are thought to have been imported to Japan in the 7th or 8th century (Nara period). The oldest surviving produced in Japan, the , produced in the 8th century, is kept in the Shōsōin Treasure Repository. Nara-period retained their original form of a single, free-standing, legged panel. In the 8th century, multi-paneled made their appearance, and were used as furnishings in the imperial court, mainly in important ceremonies. The six-paneled were the most common in the Nara period, and were covered in silk and connected with leather or silk cords. The painting on each panel was framed by a silk brocade, and the panel was bound with a wood frame. By the Heian period (794–1185), particularly by the 9th century, were indispens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Lacquerware
Mexican lacquerware (''laca'' or ''maque'' in Mexican Spanish) is one of the country's oldest crafts, having independent origins from Asian lacquerware. In the pre-Hispanic period, a greasy substance from the aje larvae and/or oil from the chia seed were mixed with powdered minerals to create protective coatings and decorative designs. During this period, the process was almost always applied to dried gourds, especially to make the cups that Mesoamerican nobility drank chocolate from. After the Conquest, the Spanish had indigenous craftsmen apply the technique to European style furniture and other items, changing the decorative motifs and color schemes, but the process and materials remained mostly the same. In the 19th and 20th centuries, the craft waned during armed conflicts and returned, both times with changes to the decorative styles and especially in the 20th century, to production techniques. Today, workshops creating these works are limited to Olinalá, Temalacatzingo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Lacquerware
is a Japanese craft with a wide range of fine and decorative arts, as lacquer has been used in '' urushi-e'', prints, and on a wide variety of objects from Buddha statues to ''bento'' boxes for food. The characteristic of Japanese lacquerware is the diversity of lacquerware using a decoration technique called in which metal powder is sprinkled to attach to lacquer. The invention of various techniques in Japanese history expanded artistic expression, and various tools and works of art such as are highly decorative.Masayuki Murata. ''明治工芸入門'' p.24. Me no Me, 2017 A number of terms are used in Japanese to refer to lacquerware. ''Shikki'' (漆器) means "lacquer ware" in the most literal sense, while ''nurimono'' (塗物) means "coated things", and ''urushi-nuri'' (漆塗) means "lacquer coating." The terms related to lacquer or lacquerware such as "Japanning", "Urushiol" and "''maque''" which means lacquer in Mexican Spanish, are derived from Japanese lacquer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Mexico
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to: * Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology) Architecture * American colonial architecture * French Colonial * Spanish Colonial architecture Automobiles * Colonial (1920 automobile), the first American automobile with four-wheel brakes * Colonial (Shaw automobile), a rebranded Shaw sold from 1921 until 1922 * Colonial (1921 automobile), a car from Boston which was sold from 1921 until 1922 Places * The Colonial (Indianapolis, Indiana) * The Colonial (Mansfield, Ohio), a National Register of Historic Places listing in Richland County, Ohio * Ciudad Colonial (Santo Domingo), a historic central neighborhood of Santo Domingo * Colonial Country Club (Memphis), a golf course in Tennessee * Colonial Country Club (Fort Worth), a golf course in Texas ** Fort Worth Invitational or The Colonial, a PGA golf tournament Trains * ''Colonial'' (PRR train), a Pennsylvania Railroad run between Washington, DC and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakumatsu
was the final years of the Edo period when the Tokugawa shogunate ended. Between 1853 and 1867, Japan ended its isolationist foreign policy known as and changed from a feudal Tokugawa shogunate to the modern empire of the Meiji government. The major ideological-political divide during this period was between the pro-imperial nationalists called and the shogunate forces, which included the elite swordsmen. Although these two groups were the most visible powers, many other factions attempted to use the chaos of to seize personal power.Hillsborough, ''page # needed'' Furthermore, there were two other main driving forces for dissent: first, growing resentment on the part of the (or outside lords), and second, growing anti-Western sentiment following the arrival of Matthew C. Perry. The first related to those lords whose predecessors had fought against Tokugawa forces at the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, after which they had been permanently excluded from all powerful p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japonism
''Japonisme'' is a French term that refers to the popularity and influence of Japanese art and design among a number of Western European artists in the nineteenth century following the forced reopening of foreign trade with Japan in 1858. Japonisme was first described by French art critic and collector Philippe Burty in 1872. While the effects of the trend were likely most pronounced in the visual arts, they extended to architecture, landscaping and gardening, and clothing. Even the performing arts were affected; Gilbert & Sullivan's ''The Mikado'' is perhaps the best example. From the 1860s, ''ukiyo-e,'' Japanese woodblock prints, became a source of inspiration for many Western artists. These prints were created for the commercial market in Japan. Although a percentage of prints were brought to the West through Dutch trade merchants, it was not until the 1860s that ukiyo-e prints gained popularity in Europe. Western artists were intrigued by the original use of color and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakoku
was the isolationist foreign policy of the Japanese Tokugawa shogunate under which, for a period of 265 years during the Edo period (from 1603 to 1868), relations and trade between Japan and other countries were severely limited, and nearly all foreign nationals were banned from entering Japan, while common Japanese people were kept from leaving the country. The policy was enacted by the shogunate government (or ) under Tokugawa Iemitsu through a number of edicts and policies from 1633 to 1639, and ended after 1853 when the Perry Expedition commanded by Matthew C. Perry forced the opening of Japan to American (and, by extension, Western) trade through a series of treaties, called the Convention of Kanagawa. It was preceded by a period of largely unrestricted trade and widespread piracy. Japanese mariners and merchants traveled Asia, sometimes forming communities in certain cities, while official embassies and envoys visited Asian states, New Spain (known as Mexico sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 978.Nussbaum"''Edo-jidai''"at p. 167. The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars of the Sengoku period following the collapse of the Ashikaga shogunate. Ieyasu became the ''shōgun,'' and the Tokugawa clan governed Japan from Edo Castle in the eastern city of Edo (Tokyo) along with the ''daimyō'' lords of the ''samurai'' class.Nussbaum"Tokugawa"at p. 976. The Tokugawa shogunate organized Japanese society under the strict Tokugawa class system and banned most foreigners under the isolationist policies of '' Sakoku'' to promote political stability. The Tokugawa shoguns governed Japan in a feudal system, with each ''daimyō'' administering a '' han'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persecution Of Christians In Japan
The Japanese term , from Portuguese language, Portuguese ''cristão'' (cf. Kristang language, Kristang), meaning "Christian", referred to Catholic Christians in Japanese language, Japanese and is used in Japanese texts as a historiographic term for Catholic Church in Japan, Catholics in Japan in the 16th and 17th centuries. Modern Japanese has several words for "Christian", of which the most common are the noun form :wikt:キリスト教徒, キリスト教徒, and also :wikt:クリスチャン, クリスチャン. The Japanese word :wikt:キリシタン, キリシタン is used primarily in Japanese texts for the early history of Roman Catholicism in Japan, or in relation to ''Kakure Kirishitan'', hidden Christians. However, English sources on histories of Japan generally use the term "Christian" without distinction. Christian missionaries were known as (from the Portuguese word ''padre'', "father" or "priest")#Jansen, Jansen, p. 67 or (from the Portuguese ''irmão'', "bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
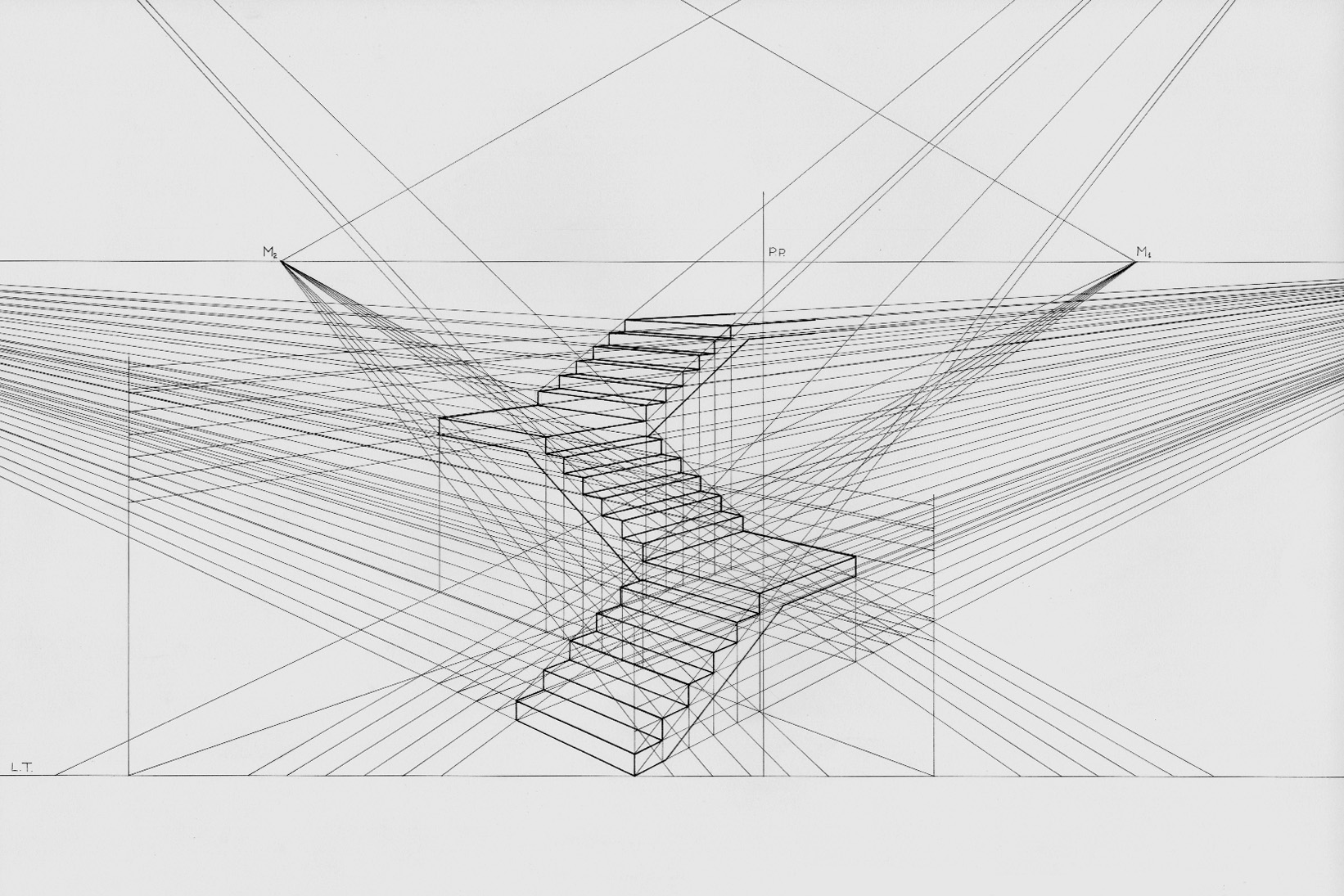
Linear Perspective
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |