|
NZR DF Class (English Electric)
The New Zealand DF class locomotive of 1954 was the first class of mainline diesel-electric locomotives built for New Zealand's national railway network, built by English Electric. It should not be confused with General Motors Electro-Motive Division DF class of 1979. Introduction They had a wheel arrangement of under the UIC classification system, generated 1120 kW (1500 hp) of power, and could achieve a maximum speed of 97 km/h. They started the process of displacing steam motive power from main lines in New Zealand, but were soon displaced themselves by the DA class of 1955. Initially, 31 DF locomotives were ordered, but this order was amended to ten DFs and 42 DG class locomotives, which in appearance was essentially half a DF but with a similar bulldog nose cab design. The DF locomotives were heavier than the later and slightly less powerful DAs and were used to haul freight trains on the North Auckland and East Coast Main Trunk lines in Northl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Traction Group
The Diesel Traction Group (DTG) is the Christchurch-based operator of a fleet of ex-New Zealand Railways Department diesel-electric locomotives. The fleet represents a full collection of New Zealand locomotive classes built by the English Electric Company and is a historically significant collection of early New Zealand diesel traction. All of the DTG's locomotives are owned by individual members through the sale of shareholdings. History The DTG was formed in September 1983 to preserve one of the DG class locomotives that were being withdrawn from service at the time. DG 772 (TMS DG 2255) was purchased from NZR and moved to Ferrymead on 17 October 1983. During 1984, the DTG investigated purchasing a second DG, this time one of the ten that were fitted with a new cab during their last major overhaul in the early 1980s, but the proposal did not proceed. In 1988, DG 772 was upgraded to mainline mechanical certification condition, repainted in its original colour scheme and used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand DA Class Locomotive
The New Zealand DA class locomotive were a class of diesel-electric mainline locomotives operated on the New Zealand railway system between 1955 and 1989. Consisting of 146 locomotives, it was the most numerous class to ever operate in New Zealand, with five more than the AB class steam locomotive. The class were A1A-A1A versions of the Electro-Motive Diesel G12 model, with the design altered slightly to run on New Zealand's rail system, and fit the small loading gauge. They were introduced between 1955 and 1967 in three phases and were the first class of diesel locomotives to seriously displace steam traction. Between 1978 and 1983, 85 locomotives were rebuilt as the DC class, of which some are still in use. All but one of the remainder were withdrawn by 1989, with six preserved. The last locomotive was refitted for shunting duties and was rebuilt as DAR 517. Introduction The DA class have their origins in the post World War II period. Like most nations New Zealand's domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Railway And Locomotive Society
The New Zealand Railway and Locomotive Society Inc is a society of railway enthusiasts, based in Wellington. It was incorporated in 1958. The society archives are in the ''Thomas McGavin Building'' on Ava railway station's former goods yard in the Hutt Valley. At one time an old railway carriage held at the Ngaio railway station was used. Publications The society publishes a magazine, the ''New Zealand Railway Observer'' (), that was first published by the New Zealand Railway Correspondence Society on a Gestetner The Gestetner is a type of duplicating machine named after its inventor, David Gestetner (18541939). During the 20th century, the term ''Gestetner'' was used as a verb—as in ''Gestetnering''. The Gestetner company established its base in Londo ... in 1944, and a newsletter ''Turntable''. The society publishes books on railway subjects. There are currently about 25 books available, as listed on the website. Most are about New Zealand railways, but there is a book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand DI Class Locomotive
The New Zealand DI class locomotive was a class of diesel-electric locomotive in New Zealand. They were built by English Electric at their plant in Rocklea, Queensland in Australia. The class is very similar to the Queensland Railways 1620 class locomotives.The 1620 Class Diesel-electric Locomotives '' Sunshine Express'' issue 588 September 2019 page 92 At the time of their introduction, the class was seen as an alternative to the DB class for use on lightly laid secondary and branch lines, more so in the South Island. The World Bank financed introduction of the Japanese built DJ class in 1968, which ensured that no further DI class locomotives were purchased by New Zealand Railways. History The DI class were an evolution of the Queensland Railways 1600 class built by English Electric at their Rocklea, Queensland plant. The DI class featured an American-style high front hood. Queensland Railways (QR) took an interest in the NZR design and were impressed by the characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Traction Group (NZ)
The Diesel Traction Group (DTG) is the Christchurch-based operator of a fleet of ex-New Zealand Railways Department diesel-electric locomotives. The fleet represents a full collection of New Zealand locomotive classes built by the English Electric Company and is a historically significant collection of early New Zealand diesel traction. All of the DTG's locomotives are owned by individual members through the sale of shareholdings. History The DTG was formed in September 1983 to preserve one of the DG class locomotives that were being withdrawn from service at the time. DG 772 (TMS DG 2255) was purchased from NZR and moved to Ferrymead on 17 October 1983. During 1984, the DTG investigated purchasing a second DG, this time one of the ten that were fitted with a new cab during their last major overhaul in the early 1980s, but the proposal did not proceed. In 1988, DG 772 was upgraded to mainline mechanical certification condition, repainted in its original colour scheme and us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR K Class (1932)
The NZR K class of 1932 was a class of mixed traffic 4-8-4 steam locomotives built by the New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) that operated on New Zealand's railway network. The locomotives were developed following the failure of the G class Garratts. The class should not be confused with the much earlier K class of 1877-78, the first American-built engines to arrive in New Zealand. History The three G class locomotives were introduced by NZR in response to increased tonnages, especially on the mountainous, demanding North Island Main Trunk Railway. However, various faults led to their swift withdrawal from service and NZR still needed a large and powerful type of locomotive. It decided to develop a conventional rather than articulated locomotive, to avoid a repeat of the G class failure. Initially conceived as a 4-8-2 locomotive, the K class was to be at least 50% more powerful than the AB class, and due to New Zealand's narrow gauge track and limited loading gauge, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federation Of Rail Organisations Of New Zealand
The Federation of Rail Organisations of New Zealand Incorporated (known by its acronym FRONZ) represents the interests of the heritage and tourist rail industry in New Zealand. Membership Our 70 members, range from commercial full-time operators such as Dunedin Railways and Christchurch Tramway to small, volunteer only, organisations such as those preserving individual railway stations or historic sites. History The group was founded as the National Federation of Rail Societies Incorporated on 30 June 1977. The group changed its name in 2002 to the Federation of Rail Organisations of New Zealand, and is known by its acronym FRONZ. In 2007, FRONZ purchased the last remaining English Electric DF class locomotive, 1501, and concluded an agreement with the Diesel Traction Group to have the locomotive moved to their premises for restoration. Activities FRONZ makes regular submissions to the Parliament on rail-related legislation and regulations, and is a regular commentator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillside Workshops
Hillside Engineering Group is a trading division of the rail operator KiwiRail in Dunedin, New Zealand. Most of its work is related to KiwiRail, but it also does work for the marine industry in Dunedin. On 19 April 2012 KiwiRail announced it was putting Hillside on the market for sale. In November 2012 KiwiRail announced it had sold part of the business to Australian firm Bradken, and the rest would be closed. The workshops continued to be used for some maintenance work by Kiwirail with a skeleton staff. In October 2019, the New Zealand Government announced that it would be investing NZ$20 million into revitalising Hillside Engineering as a major mechanical hub and engineering facility to service Kiwi Rail's locomotives and rollingstock. History Hillside was founded as the Hillside Workshops of the New Zealand Railways Department in 1901, though workshops had existed close to the current site in South Dunedin since 1875. The workshops were extensively enlarged in the late 1920s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunedin
Dunedin ( ; mi, Ōtepoti) is the second-largest city in the South Island of New Zealand (after Christchurch), and the principal city of the Otago region. Its name comes from , the Scottish Gaelic name for Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. The city has a rich Scottish, Chinese and Māori heritage. With an estimated population of as of , Dunedin is both New Zealand's seventh-most populous metro and urban area. For historic, cultural and geographic reasons the city has long been considered one of New Zealand's four main centres. The urban area of Dunedin lies on the central-eastern coast of Otago, surrounding the head of Otago Harbour, and the harbour and hills around Dunedin are the remnants of an extinct volcano. The city suburbs extend out into the surrounding valleys and hills, onto the isthmus of the Otago Peninsula, and along the shores of the Otago Harbour and the Pacific Ocean. Archaeological evidence points to lengthy occupation of the area by Māori prior to the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Plenty
The Bay of Plenty ( mi, Te Moana-a-Toi) is a region of New Zealand, situated around a bight of the same name in the northern coast of the North Island. The bight stretches 260 km from the Coromandel Peninsula in the west to Cape Runaway in the east. The Bay of Plenty Region, governed by the Bay of Plenty Regional Council, incorporates several large islands in the bay, in addition to the mainland area. Called ''Te Moana-a-Toi'' (the Sea of Toi) in the Māori language after Toi, an early ancestor, the name 'Bay of Plenty' was bestowed by James Cook in 1769 when he noticed the abundant food supplies at several Māori villages there, in stark contrast to observations he had made earlier in Poverty Bay. History According to local Māori traditions, the Bay of Plenty was the landing point of several migration canoes that brought Māori settlers to New Zealand. These include the '' Mātaatua'', '' Nukutere'', '' Tākitimu'', '' Arawa'' and '' Tainui'' canoes. Many of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northland Peninsula
The Northland Peninsula, called the North Auckland Peninsula in earlier times, is in the far north of the North Island of New Zealand. It is joined to the rest of the island by the Auckland isthmus, a narrow piece of land between the Waitematā Harbour and the Manukau Harbour in the middle of the Auckland metropolitan area. The peninsula is not conterminous with the local government area of Northland Region, which occupies the northern 80% of the peninsula. The southern section of the peninsula is administratively part of the Auckland Region. Geology The peninsula formed as an island 22 million years ago, when the area was uplifted due to interactions between the Pacific Plate and Australian Plate. Between 25 and 22 million years ago, Northland and the East Cape were adjacent, with the East Cape moving south-east due to tectonic forces. Much of the land of Northland is an allochthon, a large block of land formed elsewhere and moved into its current position. When Northland was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
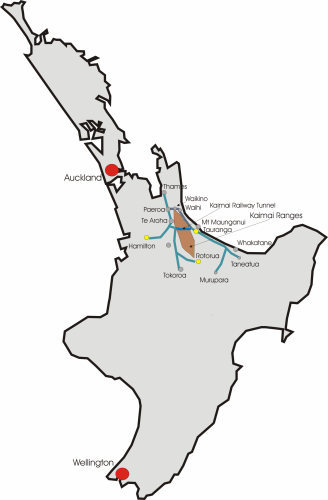
East Coast Main Trunk
The East Coast Main Trunk (ECMT) is a railway line in the North Island of New Zealand, originally running between Hamilton and Taneatua via Tauranga, connecting the Waikato with the Bay of Plenty. The ECMT now runs between Hamilton and Kawerau, with a branch line to Taneatua from the junction at Hawkens. The line is built to narrow gauge of , the uniform gauge in New Zealand. It was known as the East Coast Main Trunk Railway until 2011, when the word "Railway" was dropped. History Construction In 1880, the North Island Main Trunk railway had reached Frankton, Hamilton, from Auckland. From there, it was delayed by construction of the original Waikato River bridge (now carrying road traffic as part of Claudelands Road), before the line made its way to Morrinsville in October 1884, Te Aroha in March 1886 and Paeroa in 1898. There were also minor delays, such as in the delivery of totara sleepers. The route to Waihi through the Karangahake Gorge was surveyed in the next few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |