|
Nuclear Factor Of Activated T-cells
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) is a family of transcription factors shown to be important in immune response. One or more members of the NFAT family is expressed in most cells of the immune system. NFAT is also involved in the development of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and nervous systems. NFAT was first discovered as an activator for the transcription of IL-2 in T cells (as a regulator of T cell immune response) but has since been found to play an important role in regulating many more body systems. NFAT transcription factors are involved in many normal body processes as well as in development of several diseases, such as inflammatory bowel diseases and several types of cancer. NFAT is also being investigated as a drug target for several different disorders. Family members The NFAT transcription factor family consists of five members: NFATc1, NFATc2, NFATc3, NFATc4, and NFAT5. NFATc1 through NFATc4 are regulated by calcium signalling, and are known as the classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are Gene expression, expressed in the desired Cell (biology), cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Medulla
The renal medulla (Latin: ''medulla renis'' 'marrow of the kidney') is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries which then branch to form interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, and these finally reach the glomeruli. At the glomerulus the blood reaches a highly disfavourable pressure gradient and a large exchange surface area, which forces the serum portion of the blood out of the vessel and into the renal tubules. Flow continues through the renal tubules, including the proximal tubule, the loop of Henle, through the distal tubule and finally leaves the kidney by means of the collecting duct, leading to the renal pelvis, the dilated portion of the ureter. The renal medulla contains the structures of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Release Activated Channel
Calcium release-activated channels (CRAC) are specialized plasma membrane Ca2+ ion channels. When calcium ions (Ca2+) are depleted from the endoplasmic reticulum (a major store of Ca2+) of mammalian cells, the CRAC channel is activated to slowly replenish the level of calcium in the endoplasmic reticulum. The Ca2+ Release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) Channel (CRAC-C) Family (TC# 1.A.52) is a member of the Cation Diffusion Facilitator (CDF) Superfamily. These proteins typically have between 4 and 6 transmembrane α-helical spanners (TMSs). The 4 TMS CRAC channels arose by loss of 2TMSs from 6TMS CDF carriers, an example of ' reverse' evolution'. Homology There are several proteins that belong to the CRAC-C family. A list of the currently classified members of the CRAC-C family can be found in thTransporter Classification Database This classification is based on sequence similarity which also happens to coincide with functional and structural similarities between homologues. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORAI1
Calcium release-activated calcium channel protein 1 is a calcium selective ion channel that in humans is encoded by the ''ORAI1'' gene. Orai channels play an important role in the activation of T-lymphocytes. The loss of function mutation of Orai1 causes severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) in humans The mammalian orai family has two additional homologs, Orai2 and Orai3. Orai proteins share no homology with any other ion channel family of any other known proteins. They have 4 transmembrane domains and form hexamers. Structure and function ORAI channels are activated upon the depletion of internal calcium stores, which is called the "store-operated" or the "capacitative" mechanism. They are molecular constituents of the "calcium release activated calcium currents" ( ICRAC). Upon activation of phospholipase C by various cell surface receptors, inositol trisphosphate is formed that releases calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum. The decreased calcium concentration in the endop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STIM1
Stromal interaction molecule 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STIM1'' gene. STIM1 has a single transmembrane domain, and is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum, and to a lesser extent to the plasma membrane. Even though the protein has been identified earlier, its function was unknown until recently. In 2005, it was discovered that STIM1 functions as a calcium sensor in the endoplasmic reticulum. Upon activation of the IP3 receptor, the calcium concentration in the endoplasmic reticulum decreases, which is sensed by STIM1, via its EF hand domain. STIM1 activates the "store-operated" ORAI1 calcium ion channels in the plasma membrane, via intracellular STIM1 movement, clustering under plasma membrane and protein interaction with ORAI isoforms. STIM1-mediated calcium entry is required for thrombin-induced disassembly of VE-cadherin Cadherin-5, or VE-cadherin (vascular endothelial cadherin), also known as CD144 ( Cluster of Differentiation 144), is a type of cad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for "little net". It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. There are two types of ER that share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of Cell (biology), cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ip3 Receptor
Inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R) is a membrane glycoprotein complex acting as a Ca2+ channel activated by inositol trisphosphate (InsP3). InsP3R is very diverse among organisms, and is necessary for the control of cellular and physiological processes including cell division, cell proliferation, apoptosis, fertilization, development, behavior, learning and memory. Inositol triphosphate receptor represents a dominant second messenger leading to the release of Ca2+ from intracellular store sites. There is strong evidence suggesting that the InsP3R plays an important role in the conversion of external stimuli to intracellular Ca2+ signals characterized by complex patterns relative to both space and time, such as Ca2+ waves and oscillations. Discovery The InsP3 receptor was first purified from rat cerebellum by neuroscientists Surachai Supattapone and Solomon Snyder at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. The cDNA of the InsP3 receptor was first cloned in the labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
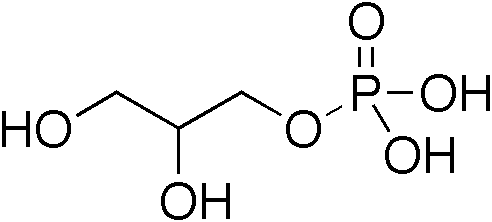
Diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate
Inositol trisphosphate or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate abbreviated InsP3 or Ins3P or IP3 is an inositol phosphate signaling molecule. It is made by hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), a phospholipid that is located in the plasma membrane, by phospholipase C (PLC). Together with diacylglycerol (DAG), IP3 is a second messenger molecule used in signal transduction in biological cells. While DAG stays inside the membrane, IP3 is soluble and diffuses through the cell, where it binds to its receptor, which is a calcium channel located in the endoplasmic reticulum. When IP3 binds its receptor, calcium is released into the cytosol, thereby activating various calcium regulated intracellular signals. Properties Chemical formula and molecular weight IP3 is an organic molecule with a molecular mass of 420.10 g/mol. Its empirical formula is C6H15O15P3. It is composed of an inositol ring with three phosphate groups bound at the 1, 4, and 5 carbon positions, and three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLCG2
1-Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PLCG2'' gene. Function From OMIM as of March 24, 2020: Enzymes of the phospholipase C family catalyze the hydrolysis of phospholipids to yield diacylglycerols and water-soluble phosphorylated derivatives of the lipid head groups. A number of these enzymes have specificity for phosphoinositides. Of the phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C enzymes, C-beta is regulated by heterotrimeric G protein-coupled receptors, while the closely related C-gamma-1 (PLCG1; MIM 172420) and C-gamma-2 enzymes are controlled by receptor tyrosine kinases. The C-gamma-1 and C-gamma-2 enzymes are composed of phospholipase domains that flank regions of homology to noncatalytic domains of the SRC oncogene product, SH2 and SH3. Interactions PLCG2 has been shown to interact with: * Bruton's tyrosine kinase, * GAB2, * LYN, * PTPN11, and * SHC1 SHC-transforming protein 1 is a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-cell Receptor
The B-cell receptor (BCR) is a transmembrane protein on the surface of a B cell. A B-cell receptor is composed of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin molecule and a signal transduction moiety. The former forms a type 1 Transmembrane protein, transmembrane receptor protein, and is typically located on the Cell membrane, outer surface of these lymphocyte cells. Through biochemical signaling and by physically acquiring antigens from the immune synapses, the BCR controls the activation of the B cell. B cells are able to gather and grab antigens by engaging biochemical modules for receptor clustering, cell spreading, generation of pulling forces, and receptor transport, which eventually culminates in endocytosis and antigen presentation. B cells' mechanical activity adheres to a pattern of negative and positive feedbacks that regulate the quantity of removed antigen by manipulating the dynamic of BCR–antigen bonds directly. Particularly, grouping and spreading increase the relation of anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |