|
Novikov Self-consistency Principle
The Novikov self-consistency principle, also known as the Novikov self-consistency conjecture and Larry Niven's law of conservation of history, is a principle developed by Russian physicist Igor Dmitriyevich Novikov in the mid-1980s. Novikov intended it to solve the problem of paradoxes in time travel, which is theoretically permitted in certain solutions of general relativity that contain what are known as closed timelike curves. The principle asserts that if an event exists that would cause a paradox or any "change" to the past whatsoever, then the probability of that event is zero. It would thus be impossible to create time paradoxes. History Physicists have long known that some solutions to the theory of general relativity contain closed timelike curves—for example the Gödel metric. Novikov discussed the possibility of closed timelike curves (CTCs) in books he wrote in 1975 and 1983, offering the opinion that only self-consistent trips back in time would be permitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larry Niven
Laurence van Cott Niven (; born April 30, 1938) is an American science fiction writer. His 1970 novel ''Ringworld'' won the Hugo Award for Best Novel, Hugo, Locus Award, Locus, Ditmar Award, Ditmar, and Nebula Award for Best Novel, Nebula awards. With Jerry Pournelle he wrote ''The Mote in God's Eye'' (1974) and ''Lucifer's Hammer'' (1977). The Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America gave him the 2015 Damon Knight Memorial Grand Master Award. His work is primarily hard science fiction, using big science concepts and theoretical physics. It also often includes elements of detective fiction and Adventure novel, adventure stories. His fantasy includes the series ''The Magic Goes Away'', works of rational fantasy dealing with magic as a non-renewable resource. Biography Niven was born in Los Angeles. He is a great-grandson of Edward L. Doheny, an oil tycoon who drilled the first successful well in the Los Angeles City Oil Field in 1892, and also was subsequently implicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
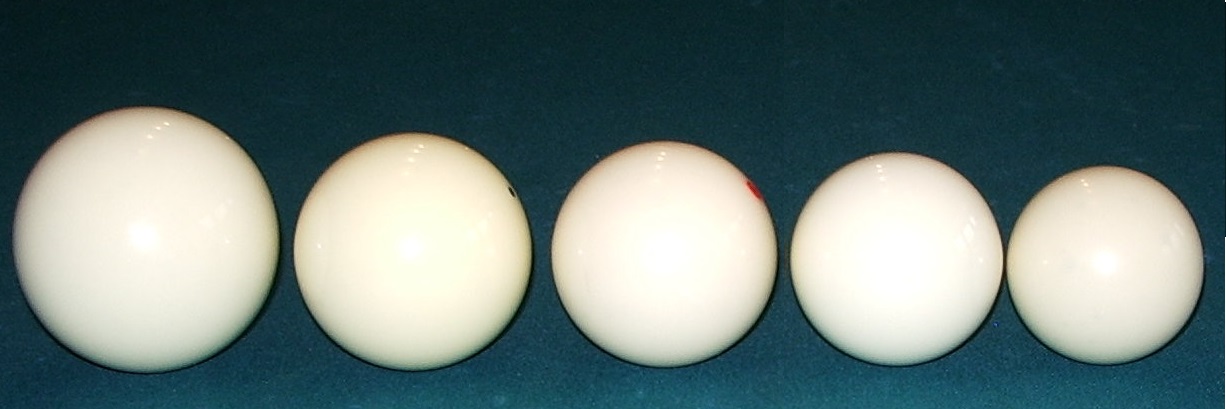
Billiard Ball
A billiard ball is a small, hard ball used in cue sports, such as carom billiards, pool, and snooker. The number, type, diameter, color, and pattern of the balls differ depending upon the specific game being played. Various particular ball properties such as hardness, friction coefficient, and resilience are important to accuracy. History Early balls were made of various materials, including wood and clay (the latter remaining in use well into the 20th century). Although affordable ox-bone balls were in common use in Europe, elephant ivory was favored since at least 1627 until the early 20th century; the earliest known written reference to ivory billiard balls is in the 1588 inventory of Thomas Howard, 4th Duke of Norfolk. This is a revised version of ''The Story of Billiards and Snooker'', 1979. Dyed and numbered balls appeared around the early 1770s. By the mid-19th century, elephants were being slaughtered for their ivory at an alarming rate, just to keep up with the dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roboticist
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots. Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer science, robotics focuses on robotic automation algorithms. Other disciplines contributing to robotics include electrical, control, software, information, electronic, telecommunication, computer, mechatronic, and materials engineering. The goal of most robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Many robots are built to do jobs that are hazardous to people, such as finding survivors in unstable ruins, and exploring space, mines and shipwrecks. Others replace people in jobs that are boring, repetitive, or unpleasant, such as cleaning, monitoring, transporting, and assembling. Today, robotics is a rapidly growing field, as technological advances continue; researching, designing, and building new robots serve various prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautology (logic)
In mathematical logic, a tautology (from ) is a formula that is true regardless of the interpretation of its component terms, with only the logical constants having a fixed meaning. For example, a formula that states, "the ball is green or the ball is not green," is always true, regardless of what a ball is and regardless of its colour. Tautology is usually, though not always, used to refer to valid formulas of propositional logic. The philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein first applied the term to redundancies of propositional logic in 1921, borrowing from rhetoric, where a tautology is a repetitive statement. In logic, a formula is satisfiable if it is true under at least one interpretation, and thus a tautology is a formula whose negation is unsatisfiable. In other words, it cannot be false. Unsatisfiable statements, both through negation and affirmation, are known formally as contradictions. A formula that is neither a tautology nor a contradiction is said to be logically c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Many-worlds Interpretation
The many-worlds interpretation (MWI) is an interpretation of quantum mechanics that asserts that the universal wavefunction is Philosophical realism, objectively real, and that there is no wave function collapse. This implies that all Possible world, possible outcomes of quantum measurements are physically realized in different "worlds". The evolution of reality as a whole in MWI is rigidly Determinism, deterministic and principle of locality, local. Many-worlds is also called the relative state formulation or the Everett interpretation, after physicist Hugh Everett III, Hugh Everett, who first proposed it in 1957.Hugh Everett]Theory of the Universal Wavefunction Thesis, Princeton University, (1956, 1973), pp. 1–140. Bryce DeWitt popularized the formulation and named it ''many-worlds'' in the 1970s. See also Cécile DeWitt-Morette, Cecile M. DeWitt, John A. Wheeler (eds,) The Everett–Wheeler Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics, ''Battelle Rencontres: 1967 Lectures in Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronology
Chronology (from Latin , from Ancient Greek , , ; and , ''wikt:-logia, -logia'') is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. It is also "the determination of the actual temporal sequence of past events".Memidex/WordNet, "chronology,memidex.com (accessed September 25, 2010). Chronology is a part of periodization. It is also a part of the discipline of history including earth history, the earth sciences, and study of the geologic time scale. Related fields Chronology is the science of locating historical events in time. It relies mostly upon chronometry, which is also known as timekeeping, and historiography, which examines the writing of history and the use of historical methods. Radiocarbon dating estimates the age of formerly living things by measuring the proportion of carbon-14 isotope in their carbon content. Dendrochronology estimates the age of trees by correlation of the var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Function
In quantum physics, a wave function (or wavefunction) is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters and (lower-case and capital psi (letter), psi, respectively). Wave functions are complex number, complex-valued. For example, a wave function might assign a complex number to each point in a region of space. The Born rule provides the means to turn these complex probability amplitudes into actual probabilities. In one common form, it says that the squared modulus of a wave function that depends upon position is the probability density function, probability density of measurement in quantum mechanics, measuring a particle as being at a given place. The integral of a wavefunction's squared modulus over all the system's degrees of freedom must be equal to 1, a condition called ''normalization''. Since the wave function is complex-valued, only its relative phase and relative magnitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path Integral Formulation
The path integral formulation is a description in quantum mechanics that generalizes the stationary action principle of classical mechanics. It replaces the classical notion of a single, unique classical trajectory for a system with a sum, or functional integral, over an infinity of quantum-mechanically possible trajectories to compute a quantum amplitude. This formulation has proven crucial to the subsequent development of theoretical physics, because manifest Lorentz covariance (time and space components of quantities enter equations in the same way) is easier to achieve than in the operator formalism of canonical quantization. Unlike previous methods, the path integral allows one to easily change coordinates between very different canonical descriptions of the same quantum system. Another advantage is that it is in practice easier to guess the correct form of the Lagrangian of a theory, which naturally enters the path integrals (for interactions of a certain type, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauchy Horizon
In physics, a Cauchy horizon is a light-like boundary of the domain of validity of a Cauchy problem (a particular boundary value problem of the theory of partial differential equations). One side of the horizon contains closed space-like geodesics and the other side contains closed time-like geodesics. The concept is named after Augustin-Louis Cauchy. Under the averaged weak energy condition (AWEC), Cauchy horizons are inherently unstable. However, cases of AWEC violation, such as the Casimir effect caused by periodic boundary conditions, do exist, and since the region of spacetime inside the Cauchy horizon has closed timelike curves it is subject to periodic boundary conditions. If the spacetime inside the Cauchy horizon violates AWEC, then the horizon becomes stable and frequency boosting effects would be canceled out by the tendency of the spacetime to act as a divergent lens. Were this conjecture to be shown empirically true, it would provide a counter-example to the stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Forward
Robert Lull Forward (August 15, 1932 – September 21, 2002) was an American physicist and science fiction writer. His literary work was noted for its scientific credibility and use of ideas developed from his career as an aerospace engineer. He also made important contributions to gravitational wave detection research. Biography Forward earned his doctorate from the University of Maryland in 1965, with a thesis entitled ''Detectors for Dynamic Gravitational Fields'', for the development of a bar antenna for the detection of gravitational radiation. Career and research He then went to work at the research labs of Hughes Aircraft, where he continued his research on gravity measurement and received 18 patents. He took early retirement in 1987, to focus on his fiction writing and consulting for such clients as NASA and the U.S. Air Force. In 1994, he co-founded the company Tethers Unlimited, Inc. with Robert P. Hoyt, where he served as chief scientist and chairman until 2002. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Institute Of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private research university in Pasadena, California, United States. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small group of institutes of technology in the United States that are devoted to the instruction of pure and applied sciences. The institution was founded as a preparatory and vocational school by Amos G. Throop in 1891 and began attracting influential scientists such as George Ellery Hale, Arthur Amos Noyes, and Robert Andrews Millikan in the early 20th century. The vocational and preparatory schools were disbanded and spun off in 1910, and the college assumed its present name in 1920. In 1934, Caltech was elected to the Association of American Universities, and the antecedents of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which Caltech continues to manage and operate, were established between 1936 and 1943 under Theodore von Kármán. Caltech has six academic divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |