|
Nonlinear Optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in Nonlinearity, nonlinear media, that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds. History The first nonlinear optical effect to be predicted was two-photon absorption, by Maria Goeppert Mayer for her PhD in 1931, but it remained an unexplored theoretical curiosity until 1961 and the almost simultaneous observation of two-photon absorption at Bell Labs and the discovery of second-harmonic generation by Peter Franken ''et al.'' at University of Michigan, both shortly after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. The interval of time between events is called the period. It is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times per minute (2 hertz), its period is one half of a second. Special definitions of frequency are used in certain contexts, such as the angular frequency in rotational or cyclical properties, when the rate of angular progress is measured. Spatial frequency is defined for properties that vary or cccur repeatedly in geometry or space. The unit of measurement of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) is the hertz, having the symbol Hz. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr Effect
The Kerr effect, also called the quadratic electro-optic (QEO) effect, is a change in the refractive index of a material in response to an applied electric field. The Kerr effect is distinct from the Pockels effect in that the induced index change for the Kerr effect is directly proportional to the ''square'' of the electric field instead of varying linearly with it. All materials show a Kerr effect, but certain liquids display it more strongly than others. The Kerr effect was discovered in 1875 by Scottish physicist John Kerr. Two special cases of the Kerr effect are normally considered, these being the Kerr electro-optic effect, or DC Kerr effect, and the optical Kerr effect, or AC Kerr effect. Kerr electro-optic effect The Kerr electro-optic effect, or DC Kerr effect, is the special case in which a slowly varying external electric field is applied by, for instance, a voltage on electrodes across the sample material. Under this influence, the sample becomes birefringent, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Light-matter Interaction With Free Electrons And Plasmas
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists since most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Rectification
Electro-optic rectification (EOR), also referred to as optical rectification, is a non-linear optical process that consists of the generation of a quasi-DC polarization in a non-linear medium at the passage of an intense optical beam. For typical intensities, optical rectification is a second-order phenomenon which is based on the inverse process of the electro-optic effect. It was reported for the first time in 1962, when radiation from a ruby laser was transmitted through potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and potassium dideuterium phosphate (KDdP) crystals. Explanation Optical rectification can be intuitively explained in terms of the symmetry properties of the non-linear medium: in the presence of a preferred internal direction, the polarization will not reverse its sign at the same time as the driving field. If the latter is represented by a sinusoidal wave, then an average DC polarization will be generated. Optical rectification is analogous to the electric rectif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spontaneous Parametric Down-conversion
Spontaneous parametric down-conversion (also known as SPDC, parametric fluorescence or parametric scattering) is a nonlinear instant optical process that converts one photon of higher energy (namely, a ''pump'' photon) into a pair of photons (namely, ''signal'' and ''idler'' photons) of lower energy, in accordance with the laws of law of conservation of energy, energy conservation and law of conservation of momentum, momentum conservation. It is an important process in quantum optics, for the generation of photon entanglement, entangled photon pairs and of single photons. Description A Nonlinear optics, nonlinear crystal is used to produce pairs of photons from a photon beam. In accordance with conservations of energy and momentum, the pairs need to have combined energies and momenta equal to the energy and momentum of the original photon. Because the index of refraction changes with frequency (Dispersion (optics), dispersion), only certain triplets of frequencies will be phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
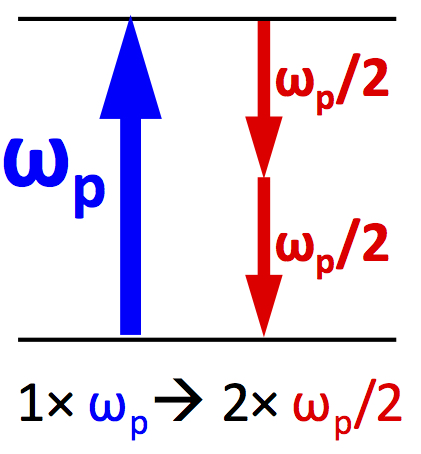
Half-harmonic Generation
Half-harmonic generation (also called wavelength doubling or frequency halving) is a nonlinear optical process in which photons "split" to generate pairs of new photons with half the energy, therefore half the frequency and twice the wavelength of the initial photons. The half-harmonic generation process is the inverse of second-harmonic generation Second-harmonic generation (SHG), also known as frequency doubling, is the lowest-order wave-wave nonlinear interaction that occurs in various systems, including optical, radio, atmospheric, and magnetohydrodynamic systems. As a prototype behav ... and can occur in optical parametric oscillators at degeneracy, and is a phase- and frequency-locked down-conversion process. In the continuous-wave regime, stable half-harmonic generation in an optical parametric oscillator was experimentally demonstrated in 1990, and in the femtosecond regime, it was experimentally demonstrated in 2012. Half-harmonic generation is used as a phase- and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Parametric Generation
An optical parametric amplifier, abbreviated OPA, is a laser light source that emits light of variable wavelengths by an optical parametric amplification process. It is essentially the same as an optical parametric oscillator, but without the optical cavity (i.e., the light beams pass through the apparatus just once or twice, rather than many many times). Optical parametric generation (OPG) Optical parametric generation (OPG) (also called "optical parametric fluorescence", or " spontaneous parametric down conversion") often precedes optical parametric amplification. In optical parametric generation, the input is one light beam of frequency ωp, and the output is two light beams of lower frequencies ωs and ωi, with the requirement ωp=ωs+ωi. These two lower-frequency beams are called the "signal" and "idler", respectively. This light emission is based on the nonlinear optical principle. The photon of an incident laser pulse (pump) is, by a nonlinear optical crystal, divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Parametric Oscillation
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is a parametric oscillator that oscillates at optical frequencies. It converts an input laser wave (called "pump") with frequency \omega_p into two output waves of lower frequency (\omega_s, \omega_i) by means of second- order nonlinear optical interaction. The sum of the output waves' frequencies is equal to the input wave frequency: \omega_s + \omega_i=\omega_p. For historical reasons, the two output waves are called "signal" and "idler", where the output wave with higher frequency is the "signal". A special case is the degenerate OPO, when the output frequency is one-half the pump frequency, \omega_s=\omega_i=\omega_p/2, which can result in half-harmonic generation when signal and idler have the same polarization. The first optical parametric oscillator was demonstrated by Joseph A. Giordmaine and Robert C. Miller in 1965, five years after the invention of the laser, at Bell Labs. Optical parametric oscillators are used as coherent light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Parametric Amplification
An optical parametric amplifier, abbreviated OPA, is a laser light source that emits light of variable wavelengths by an optical parametric amplification process. It is essentially the same as an optical parametric oscillator, but without the optical cavity (i.e., the light beams pass through the apparatus just once or twice, rather than many many times). Optical parametric generation (OPG) Optical parametric generation (OPG) (also called "optical parametric fluorescence", or " spontaneous parametric down conversion") often precedes optical parametric amplification. In optical parametric generation, the input is one light beam of frequency ωp, and the output is two light beams of lower frequencies ωs and ωi, with the requirement ωp=ωs+ωi. These two lower-frequency beams are called the "signal" and "idler", respectively. This light emission is based on the nonlinear optical principle. The photon of an incident laser pulse (pump) is, by a nonlinear optical crystal, divid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Difference-frequency Generation
Four-wave mixing (FWM) is an intermodulation phenomenon in nonlinear optics, whereby interactions between two or three wavelengths produce two or one new wavelengths. It is similar to the third-order intercept point in electrical systems. Four-wave mixing can be compared to the intermodulation distortion in standard electrical systems. It is a parametric nonlinear process, in that the energy of the incoming photons is conserved. FWM is a phase-sensitive process, in that the efficiency of the process is strongly affected by phase matching conditions. Mechanism When three frequencies (f1, f2, and f3) interact in a nonlinear medium, they give rise to a fourth frequency (f4) which is formed by the scattering of the incident photons, producing the fourth photon. Given inputs ''f1, f2,'' and ''f3'', the nonlinear system will produce : \pm f_ \pm f_ \pm f_ From calculations with the three input signals, it is found that 12 interfering frequencies are produced, three of which lie o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sum-frequency Generation
Sum-frequency generation (SFG) is a second order nonlinear optical process based on the mixing of two input photons at frequencies \omega_1 and \omega_2 to generate a third photon at frequency \omega_3. As with any \chi^ optical phenomenon in nonlinear optics, this can only occur under conditions where: the light is interacting with matter, that lacks centrosymmetry (for example, surfaces and interfaces); the light has a very high intensity (typically from a pulsed laser). Sum-frequency generation is a "parametric process", meaning that the photons satisfy energy conservation, leaving the matter unchanged: :\hbar\omega_3 = \hbar\omega_1 + \hbar\omega_2 Second-harmonic generation A special case of sum-frequency generation is second-harmonic generation, in which \omega_1=\omega_2. In fact, in experimental physics, this is the most common type of sum-frequency generation. This is because in second-harmonic generation, only one input light beam is required, but if \omega_1\neq\omega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |