|
Nodena Site
The Nodena site is an archeological site east of Wilson, Arkansas, and northeast of Reverie, Tennessee, in Mississippi County, Arkansas, United States. Around 1400–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed in the Nodena area on a meander bend of the Mississippi River. The Nodena site was discovered and first documented by James K. Hampson, archaeologist and owner of the plantation on which the Nodena site is located. Artifacts from this site are on display in the Hampson Museum State Park in Wilson, Arkansas. The Nodena site is the type site for the Nodena phase, believed by many archaeologists to be the province of Pacaha visited by the Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542. In 1900, a prehistoric mastodon skeleton was discovered south of the Nodena site. In 1964, the Nodena site was declared a National Historic Landmark and in 1966 it was added to the National Register of Historic Places. Culture of the Nodena people Nodena is the type site for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson, Arkansas
Wilson is a city in Mississippi County, Arkansas, Mississippi County, Arkansas, United States. The community is located in the Arkansas Delta and is surrounded by fertile cropland historically used to produce cotton. Wilson started as a company town in 1886 by Robert E. Lee Wilson, who would build a cotton empire and run it from the city. The Wilson Company would become so successful that all of the town's buildings were rebuilt in the Tudor Revival architecture, Tudor Revival architectural style following Wilson's son's honeymoon to England in 1925. Wilson incorporated in 1959, becoming a town with public roads and municipal government. The extensive property holdings of the Lee Wilson and Company remained in the Wilson family until 2010. The community has seen a rapid decline in economic activity and population since the advent of mechanization on the farm, reducing the need for manual labor to produce cotton. The population was 766 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government's official United States National Register of Historic Places listings, list of sites, buildings, structures, Historic districts in the United States, districts, and objects deemed worthy of Historic preservation, preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". The enactment of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing property, contributing resources within historic district (United States), historic districts. For the most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the United States Department of the Interior. Its goals are to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whelk
Whelks are any of several carnivorous sea snail species with a swirling, tapered shell. Many are eaten by humans, such as the common whelk of the North Atlantic. Most whelks belong to the family Buccinidae and are known as "true whelks." Others, such as the dog whelk, belong to several sea snail families that are not closely related. True whelks (family Buccinidae) are carnivorous, and feed on annelids, crustaceans, mussels and other molluscs, drilling holes through shells to gain access to the soft tissues. Whelks use chemoreceptors to locate their prey. Many have historically been used, or are still used, by humans and other animals as food. In a reference serving of whelk, there are of food energy, 24 g of protein, 0.34 g of fat, and 8 g of carbohydrates. Dog whelk, a predatory species, was used in antiquity to make a rich red dye that improves in color as it ages. Usage The common name "whelk" is also spelled ''welk'' or even ''wilk''. The species, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mill Creek Chert
Mill Creek chert is a type of chert found in Southern Illinois and heavily exploited by members of the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE). Artifacts made from this material are found in archaeological sites throughout the American Midwest and Southeast. It is named for a village and stream near the quarries, Mill Creek, Illinois and Mill Creek, a tributary of the Cache River. The chert was used extensively for the production of utilitarian tools such as hoes and spades, and for polished ceremonial objects such as bifaces, spatulate celts and maces. History ''Chert'' is a siliceous (silica) stone, a variety of quartz similar to flint but more brittle. It naturally occurs as large, flat, elliptically shaped nodules in creek beds, and sometimes as hill-top residuum. The nodules were formed as part of the Ullin limestone formation during the Mississippian geologic period (roughly 359 to 318 million years ago). Mill Creek Chert is a tough, coarse-grained chert, usually brow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
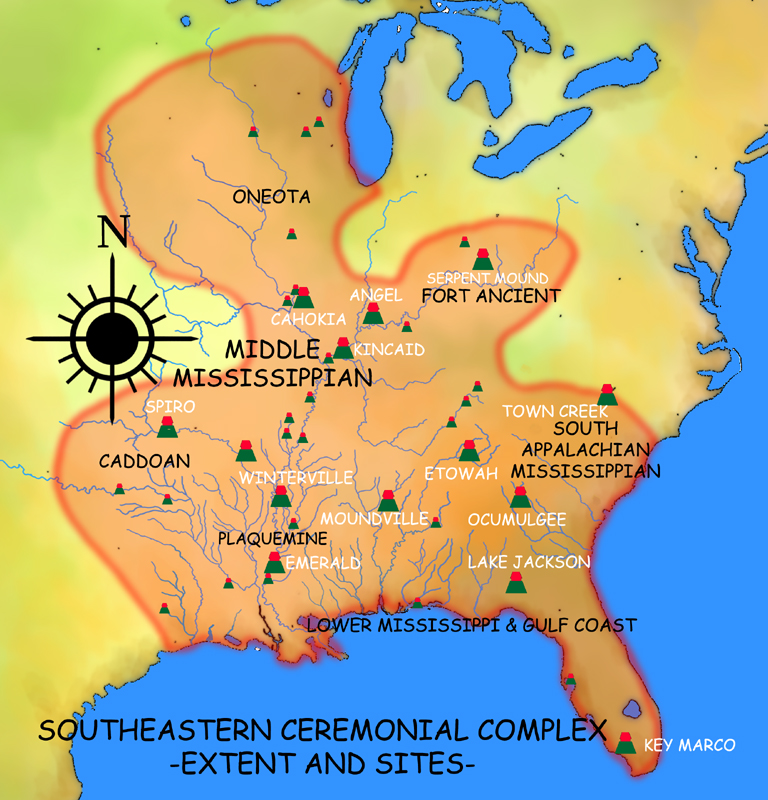
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly Southern Cult, Southern Death Cult or Buzzard Cult), abbreviated S.E.C.C., is the name given by modern scholars to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their adoption of maize agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from 1200 to 1650 CE. Due to some similarities between S.E.C.C. and contemporary Mesoamerican cultures (i.e., artwork with similar aesthetics or motifs; maize-based agriculture; and the development of sophisticated cities with large pyramidal structures), scholars from the late 1800s to mid-1900s suspected there was a connection between the two locations. One hypothesis was that Meso-Americans enslaved by conquistador Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510–1573) may have spread artistic and religious elements to North America. However, later research indicates the two cultures have no direct links and that thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
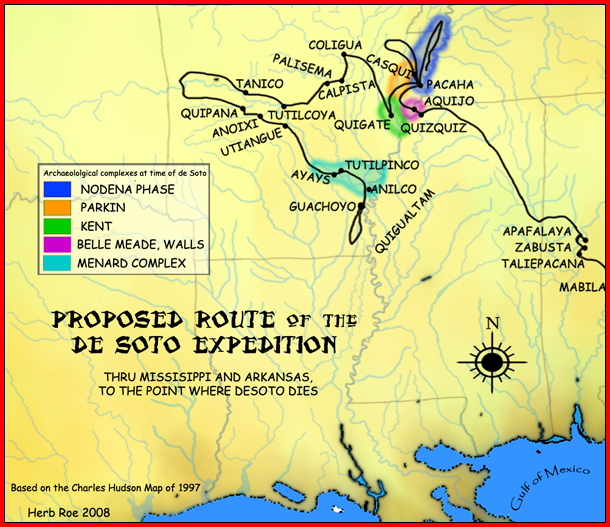
Casqui
Casqui was a Native American polity visited in 1541 by the Hernando de Soto expedition. This group inhabited fortified villages in eastern Arkansas. The tribe takes its name from the chieftain Casqui, who ruled the tribe from its primary village, thought to be located in present day Cross County, Arkansas near the town of Parkin. The suspected site is the focal point of the Parkin Archeological State Park and it has been determined that the site was continuously occupied for at least 500 years. Information about Chief Casqui and his people comes from journals made during the expedition of Hernando de Soto in 1541. Hernando de Soto Expedition When de Soto's expedition arrived in the area the Casqui walked over a mile from their village to greet the travelers and invite them to stay in the town. The travelers declined the offer and made camp outside of the village. The journals report that de Soto gave a speech to the Casqui about religion and baptized several of the villager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkin, Arkansas
Parkin is a city in Cross County, Arkansas, United States, along the St. Francis River. The population was 1,105 at the 2010 census, down from 1,602 in 2000. In the 2020 census, it dropped further to 794 people. Due to the recent population loss, a large segment of the downtown area has many abandoned and boarded-up buildings. The town has recently become known as a speed trap. Geography Parkin is located in eastern Cross County on the east bank of the St. Francis River just south of the mouth of the Tyronza River. U.S. Route 64 passes through the community, leading east to Earle and west to Wynne, the Cross County seat. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , all land. Demographics 2020 census As of the 2020 United States census, there were 794 people, 312 households, and 147 families residing in the city. 2000 census As of the census of 2000, there were 1,602 people, 603 households, and 404 families residing in the city. The po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkin Archeological State Park
Parkin Archeological State Park, also known as Parkin Indian Mound, is an archeological site and state park in Parkin, Cross County, Arkansas. Around 1350–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed at the site, at the confluence of the St. Francis and Tyronza rivers. Artifacts from this site are on display at the site museum. The Parkin site is the type site for the Parkin phase, an expression of the Mississippian culture from the Late Mississippian period. Many archeologists believe it to be part of the province of '' Casqui'', documented as visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542. Archeological artifacts from the village of the Parkin people are dated to 1400–1650 CE. The Parkin site was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1964 for its significance as a type site of the Parkin phase. In 1966, the Parkin Indian Mound was listed in the National Register of Historic Places. Parkin Archeological State Park is located at 60 Arkansas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walls Phase
The Walls phase is an archaeological phase in southwestern Tennessee and northwestern Mississippi of the Late Mississippian culture. Chucalissa is a Walls phase mound and plaza complex located on a bluff overlooking the Mississippi River. Other contemporaneous groups in the area include the Parkin phase, Tipton phase, Menard phase, and the Nodena phase. The Walls phase is the last prehistoric people to inhabit the Memphis area before the arrival of Europeans. During the early 1540s the Hernando de Soto Expedition passed through the area, stopping at many villages along the way. It is thought that the Walls phase may be the Province of Quizquiz, a Tunican people encountered by de Soto on the banks of the Mississippi River. Culture Settlement pattern The Walls phase settlements consist of one large site, located at De Soto Park in Memphis, nine single mound sites, and six smaller moundless villages scattered along the natural levees and bluffs of De Soto County, Mississipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
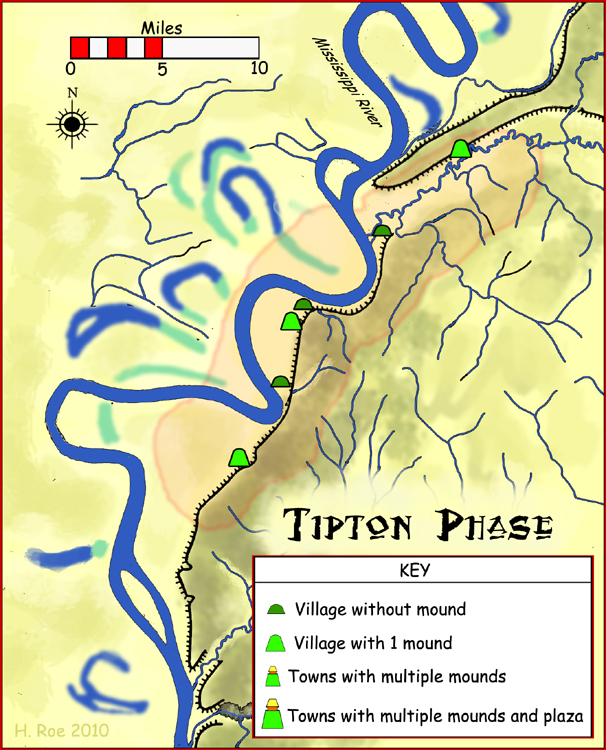
Tipton Phase
The Tipton phase is an archaeological phase in southwestern Tennessee of the Late Mississippian culture. Other contemporaneous groups in the area include the Parkin phase, Walls phase, Menard phase, and the Nodena phase. The Tipton phase is the last prehistoric people to inhabit the area before the arrival of Europeans. It is located directly across the Mississippi River from the people of the Nodena phase and directly north of the Walls phase. During the early 1540s the Hernando de Soto Expedition passed through the area, stopping at many villages in the area. The phase itself is named for Tipton County, Tennessee Tipton County is a County (United States), county located on the western end of the U.S. state of Tennessee, in the Mississippi Delta region. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 60,970. Its county seat is Covingt .... Notes Middle Mississippian culture Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands Native American hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menard–Hodges Site
The Menard–Hodges site ( 3AR4) (also known as Menard-Hodges Mounds and Osotouy), is an archaeological site in Arkansas County, Arkansas. It includes two large platform mounds as well as several house mounds. It is the type site for the Menard phase, a protohistoric Mississippian culture group. The Menard Mound was named for Frank Menard, on whose farm the mound was discovered. Description The site is considered as a possible candidate for the Province of Anilco encountered by the Hernando de Soto Entrada in 1540. It was contemporaneous with the Parkin site, believed by many archaeologists to be the location of the province of Casqui, and the Nodena site, believed by many archaeologists to be the location of the province of Pacaha. The site is also considered to be the location of the protohistoric Quapaw village of ''Osotouy'' (or ''Ossoteoue'') first encountered by French explorers in the late 17th century. The Quapaw at the time had four villages, Kappa, Ossoteoue, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wapanocca National Wildlife Refuge
The Wapanocca National Wildlife Refuge is a 5,484 acre (22 km2) wildlife refuge in Crittenden County, Arkansas, managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Wapanocca National Wildlife Refuge was established in 1961 from land acquired from the former "Wapanocca Outing Club" which was a prestigious hunting club formed in 1886. The refuge is located 3 miles (5 km) west of the Mississippi River near the city of Turrell, Arkansas. The refuge was once a bend in the Mississippi River. It is a migration stopover for warblers and other neo-tropical birds. The refuge is host to the blue heron, and the common egret as well as the bald eagle. The refuge is a major stopover on the Mississippi Flyway The Mississippi Flyway is a bird migration route that generally follows the Mississippi, Missouri, and Lower Ohio Rivers in the United States across the western Great Lakes to the Mackenzie River and Hudson Bay in Canada. The main endpoints of t .... Wapanocca consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |