|
Nexus (web Browser)
WorldWideWeb (later renamed Nexus to avoid confusion between the software and the World Wide Web) is the first web browser and web page editor. It was discontinued in 1994. It was the first WYSIWYG HTML editor. The source code was released into the public domain on 30 April 1993. Some of the code still resides on Tim Berners-Lee's NeXT Computer in the CERN museum and has not been recovered due to the computer's status as a historical artifact. To coincide with the 20th anniversary of the research center giving the web to the world, a project began in 2013 at CERN to preserve this original hardware and software associated with the birth of the Web. History Tim Berners-Lee wrote what would become known as WorldWideWeb on a NeXT Computer during the second half of 1990, while working for CERN, a European nuclear research agency. The first edition was completed "some time before" 25 December 1990, according to Berners-Lee, after two months of development. The browser was announc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people used a browser. The most used browser is Google Chrome, with a 65% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%. A web browser is not the same thing as a search engine, though the two are often confused. A search engine is a website that provides links to other websites. However, to connect to a website's server and display its web pages, a user must have a web browser installed. In some technical contexts, browsers are referred to as user agents. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content from the World Wide Web or from local storage and display it on a user's device. This process b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NeXT Computer
NeXT Computer (also called the NeXT Computer System) is a workstation computer that was developed, marketed, and sold by NeXT Inc. It was introduced in October 1988 as the company's first and flagship product, at a price of , aimed at the higher-education market. It was designed around the Motorola 68030 CPU and 68882 floating-point coprocessor, with a clock speed of . Its NeXTSTEP operating system is based on the Mach microkernel and BSD-derived Unix, with a proprietary GUI using a Display PostScript-based back end. The enclosure consists of a 1-foot () die-cast magnesium cube-shaped black case, which led to the machine being informally referred to as "The Cube". The NeXT Computer was renamed NeXTcube in a later upgrade. The NeXTstation, a more affordable version of the NeXTcube, was released in 1990. Launch The NeXT Computer was launched in October 1988 at a lavish invitation-only event, " NeXT Introduction – the Introduction to the NeXT Generation of Computers for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libwww
Libwww was an early World Wide Web software library providing core functions for web browser, browsers, implementing HTML, HTTP, and other technologies. Tim Berners-Lee, at CERN, released libwww (then also called the "Common Library") in late 1992, comprising reusable code from the first browsers (WorldWideWeb and Line Mode Browser). Libwww was relied upon by the popular browser Mosaic (web browser), Mosaic. By 1997, however, interest in libwww declined, and the World Wide Web Consortium, W3C (which took over from CERN) reduced its commitment to the project. Later, the purpose of libwww was redefined to be "a testbed for protocol experiments", and in that vein it was maintained for the benefit of the W3C's web standards, standards-promoting browser Amaya (web editor), Amaya. Active development of libwww stopped in 2000. CURL, libcurl is considered to be a modern replacement for libwww. History In 1991 and 1992, Tim Berners-Lee and a student at CERN named Jean-François Groff rewr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced like the letter c'') is a General-purpose language, general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the measuring programming language popularity, most widely used programming languages, with C compilers avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Window System
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems. X provides the basic framework for a GUI environment: drawing and moving windows on the display device and interacting with a mouse and keyboard. X does not mandate the user interfacethis is handled by individual programs. As such, the visual styling of X-based environments varies greatly; different programs may present radically different interfaces. X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at version 11 (hence "X11") since September 1987. The X.Org Foundation leads the X project, with the current reference implementation, X.Org Server, available as free and open-source software under the MIT License and similar permissive licenses. Purpose and abilities X is an architecture-independent system for remote graphical user interfaces and input device capabilities. Each person u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porting
In software engineering, porting is the process of adapting software for the purpose of achieving some form of execution in a computing environment that is different from the one that a given program (meant for such execution) was originally designed for (e.g., different CPU, operating system, or third party library). The term is also used when software/hardware is changed to make them usable in different environments. Software is ''portable'' when the cost of porting it to a new platform is significantly less than the cost of writing it from scratch. The lower the cost of porting software relative to its implementation cost, the more portable it is said to be. Etymology The term "port" is derived from the Latin '' portāre'', meaning "to carry". When code is not compatible with a particular operating system or architecture, the code must be "carried" to the new system. The term is not generally applied to the process of adapting software to run with less memory on the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicola Pellow
Nicola Pellow is an English mathematician and information scientist who was one of the nineteen members of the ''WWW Project'' at CERN working with Tim Berners-Lee. She joined the project in November 1990, while an undergraduate maths student enrolled on a sandwich course at Leicester Polytechnic (now De Montfort University). Pellow recalled having little experience with programming languages, "... apart from using a bit of Pascal and FORTRAN as part of my degree course." Almost immediately after Berners-Lee completed the WorldWideWeb web browser for the NeXT platform Pellow was tasked with creating a browser using her recently acquired skills in the C programming language. The outcome was that she wrote the first generic Line Mode Browser that could run on non-NeXT systems. The WWW team began to improve on her work, creating several experimental versions. Pellow was involved in porting the browser to different types of computers. She left CERN at the end of August 1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-François Groff
Jean-François Groff is a telecommunication engineer, and one of the key figures in the early development of the World Wide Web at CERN. He worked in close collaboration with Tim Berners-Lee, and helped define the HTTP protocol and HTML language. Groff is also the CTO and founder of Studio KOH, and CEO of Mobino, a mobile payments company headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. Background Groff was first introduced to computers as a young boy, around 7 or 8 years of age, by his father, a computer engineer for Saint-Gobain. Young Groff began developing his programming skills on the personal computers that were available to him at home, including Amstrad, and later Atari computers. He graduated with a telecommunications degree from Telecom Paris. Works Groff co-authored an article titled ''The World-Wide Web: The Information Universe'' with Tim Berners-Lee, Robert Cailliau Robert Cailliau (, born 26 January 1947) is a Belgian informatics engineer, computer scientist and author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Cailliau
Robert Cailliau (, born 26 January 1947) is a Belgian informatics engineer, computer scientist and author who proposed the first (pre-www) hypertext system for CERN in 1987 and collaborated with Tim Berners-Lee on the World Wide Web (jointly winning the ACM Software System Award) from before it got its name. He designed the historical logo of the WWW, organized the first International World Wide Web Conference at CERN in 1994 and helped transfer Web development from CERN to the global Web consortium in 1995. Together with Dr. James Gillies, Cailliau wrote ''How the Web Was Born'', the first book-length account of the origins of the World Wide Web. Biography Cailliau was born in Tongeren, Belgium. In 1958 he moved with his parents to Antwerp. After secondary school he graduated from Ghent University in 1969 as civil engineer in electrical and mechanical engineering (Dutch: Burgerlijk Werktuigkundig en Elektrotechnisch ingenieur). He also has an MSc from the University of Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
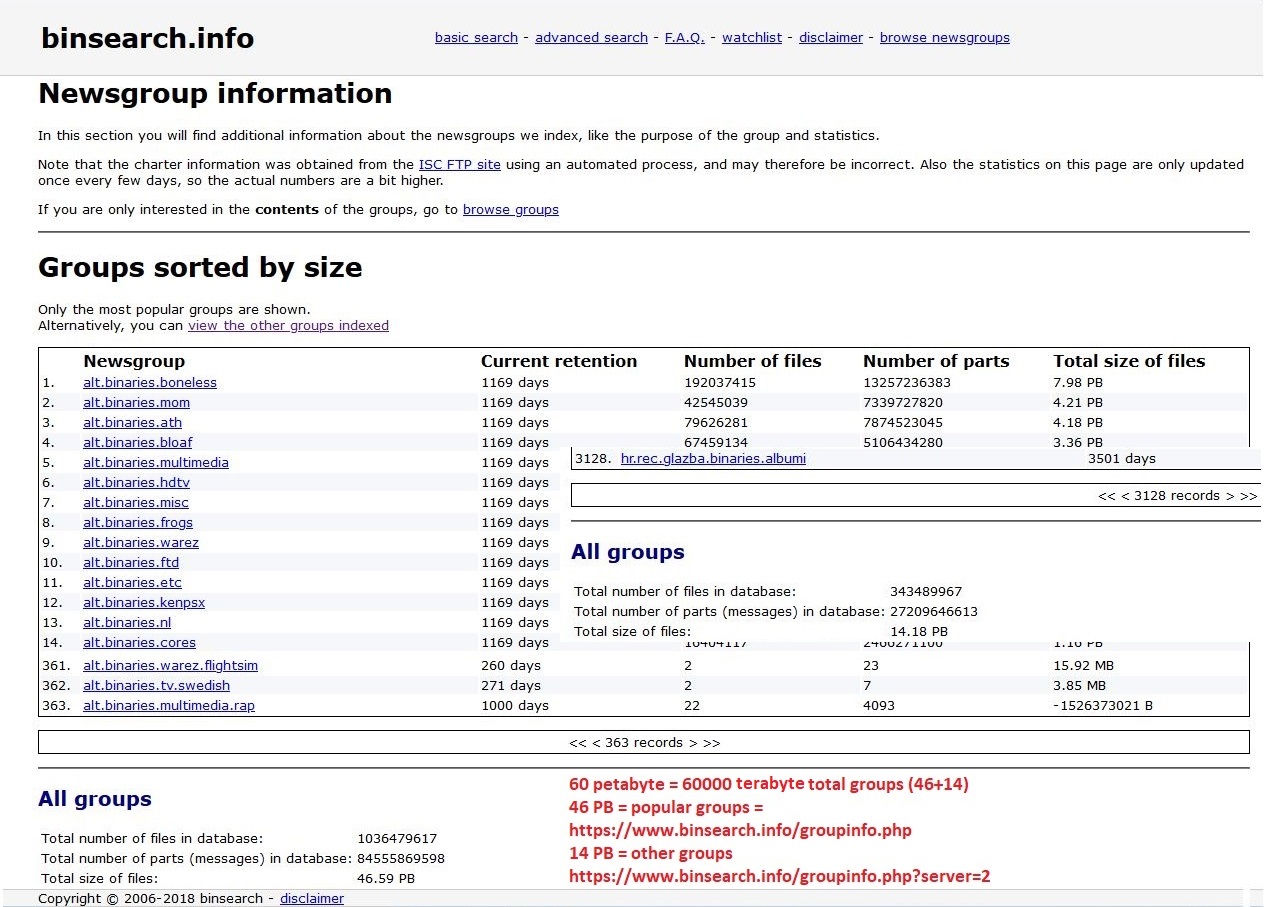
Newsgroups
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system, for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are discussion groups and are not devoted to publishing news. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption of the World Wide Web, Usenet newsgroups were among the most popular Internet services, and have retained their noncommercial nature in contrast to the increasingly ad-laden web. In recent years, this form of open discussion on the Internet has lost considerable ground to individually-operated browser-accessible forums and big media social networks such as Facebook and Twitter. Communication is facilitated by the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) which allows connection to Usenet servers and data transfer over the internet. Similar to another early (yet still used) prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |