|
Neurological Examination
A neurological examination is the assessment of sensory neuron and motor responses, especially reflexes, to determine whether the nervous system is impaired. This typically includes a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history, but not deeper investigation such as neuroimaging. It can be used both as a screening tool and as an investigative tool, the former of which when examining the patient when there is no expected neurological deficit and the latter of which when examining a patient where you do expect to find abnormalities. If a problem is found either in an investigative or screening process, then further tests can be carried out to focus on a particular aspect of the nervous system (such as lumbar punctures and blood tests). In general, a neurological examination is focused on finding out whether there are lesions in the central and peripheral nervous systems or there is another diffuse process that is troubling the patient. Once the patient has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Neuron
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded receptor potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord. The sensory information travels on the afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve, to the brain via the spinal cord. Spinal nerves transmit external sensations via sensory nerves to the brain through the spinal cord. The stimulus can come from exteroreceptors outside the body, for example those that detect light and sound, or from interoreceptors inside the body, for example those that are responsive to blood pressure or the sense of body position. Types and function Sensory neurons in vertebrates are predominantly pseudounipolar or bipolar, and different types of sensory neurons have different sensory receptors that respond t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, describing a disease as acute denotation, denotes that it is of recent wikt:onset#Noun, onset; it occasionally denotes a short wikt:duration#Noun, duration. The quantification (science), quantification of how much time constitutes "short" and "recent" varies by disease and by context, but the core denotation of "acute" is always qualitative property, qualitatively in contrast with "chronic condition, chronic", which denotes long-lasting disease (for example, in acute leukaemia and chronic leukaemia). In the context of the mass noun "acute disease", it refers to the acute phase (that is, a short course) of any disease entity. For example, in an article on ulcerative enteritis in poultry, the author says, "in acute disease there may be increased mortality rate, mortality without any obvious medical sign, signs", referring to the acute form or phase of ulcerative enteritis. Meaning variations A mild stubbed toe is an acute injury. Similarly, many acute upper respirator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
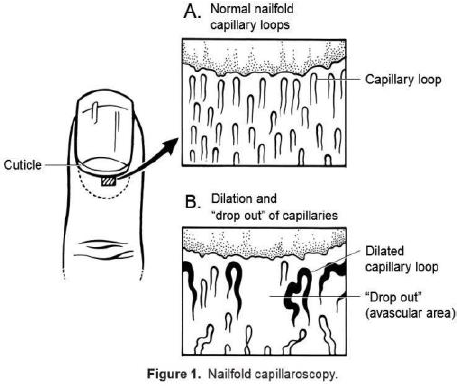
Microvascular Disease
Microangiopathy (also known as microvascular disease, small vessel disease (SVD) or microvascular dysfunction) is a disease of the microvessels, small blood vessels in the microcirculation. It can be contrasted to macroangiopathies such as atherosclerosis, where large and medium-sized arteries (e.g., aorta, carotid and coronary arteries) are primarily affected. Small vessel diseases (SVDs) affect primarily organs that receive significant portions of cardiac output such as the brain, the kidney, and the retina. Thus, SVDs are a major etiologic cause in debilitating conditions such as renal failure, blindness, lacunar infarcts, and dementia. Types Microangiopathies are involved in a variety of different diseases including: Pathophysiology The main target of small vessel diseases is the endothelium, which plays a key role in vascular homeostasis. The pathogenesis of SVDs in various organs is characterized by endothelial dysfunction, capillary rarefaction, microthrombi and mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part of a routine physical examination. It is crucial in determining the health of the retina, optic disc, and vitreous humor. The pupil is a hole through which the eye's interior can be viewed. For better viewing, the pupil can be opened wider (dilated; mydriasis) before ophthalmoscopy using medicated eye drops (dilated fundus examination). However, undilated examination is more convenient (albeit not as comprehensive), and is the most common type in primary care. An alternative or complement to ophthalmoscopy is to perform a fundus photography, where the image can be analysed later by a professional. Types There are two major types of ophthalmoscopy: * direct ophthalmoscopy, which produces an upright (unreversed) image of approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracranial Pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. This equals to 9–20 cmH2O, which is a common scale used in lumbar punctures. The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (which is induced by contraction of the diaphragm and abdominal wall muscles, the latter of which also increases intra-abdominal pressure), the valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature ( venous and arterial systems). Intracranial hypertension (IH), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mini Mental State Examination
The Mini is a very small two-door, four-seat car, produced for four decades over a single generation, with many names and variants, by the British Motor Corporation (BMC) and its successors British Leyland and the Rover Group, and finally (briefly) under BMW ownnership. Minis were built as fastbacks, estates, convertibles, and various other body styles. Minus a brief 1990s hiatus, from 1959 into 2000, an estimated 5.38 million of all variations combined were built,, and the Mini's engines also powered another 2 million Mini Metros, though the Mini eventually outlasted its successor. Initially, the Mini was marketed under the Austin and Morris names, as the Austin Seven and Morris Mini-Minor;Austin Seven – Mini, www.austinmemories.com Retrieved on 16 June 2013 the Austin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbreviated Mental Test Score
The Abbreviated Mental Test Score (AMTS) is a 10-point test designed for the rapid assessment of elderly patients for potential dementia. It is recommended as the primary screening tool in emergency and hospital settings for patients over 65. First introduced in 1972, it is now also utilized to assess mental confusion (including delirium) and other cognitive impairments. The test takes approximately 34 minutes to administer and requires no specialist training or licensing. History The AMTS was developed to address the need for a rapid, practical method of assessing cognitive impairment in geriatric patients. In 1972, Hodkinson adapted it from the 26-item Blessed Dementia Scale (BDS) by removing 16 items: 13 for repetitiveness, 2 for being too easy, and 1 for being too difficult. Validation studies revealed a near-linear correlation between AMTS and BDS scores, indicating strong convergent validity and measurement accuracy. Questionnaire and scoring The standard AMTS consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury. The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body. These three behaviours make up the three elements of the scale: eye, verbal, and motor. A person's GCS score can range from 3 (completely unresponsive) to 15 (responsive). This score is used to guide immediate medical care after a brain injury (such as a car accident) and also to monitor hospitalised patients and track their level of consciousness. Lower GCS scores are correlated with higher risk of death. However, the GCS score alone should not be used on its own to predict the outcome for an individual person with brain injury. Scoring The Glasgow Coma Scale is used for people above the age of two and is composed of three tests: eye, verbal, and motor responses. The scores for each of these tests are indicated in the table below. The Glas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is awareness of a state or object, either internal to oneself or in one's external environment. However, its nature has led to millennia of analyses, explanations, and debate among philosophers, scientists, and theologians. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of it. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination, and volition (psychology), volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling, or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, metacognition, or self-awareness, either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions, and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: ordered distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Status Examination
The mental status examination (MSE) is an important part of the clinical Psychiatric assessment, assessment process in Neurology, neurological and psychiatric practice. It is a structured way of observing and describing a patient's psychological functioning at a given point in time, under the domains of appearance, Propositional attitude, attitude, behavior, mood and affect, speech, thought process, thought content, perception, cognition, insight, and judgment. There are some minor variations in the subdivision of the MSE and the sequence and names of MSE domains. The purpose of the MSE is to obtain a comprehensive cross-sectional description of the patient's mental state, which, when combined with the biographical and historical information of the psychiatric history, allows the clinician to make an accurate medical diagnosis, diagnosis and psychiatric formulation, formulation, which are required for coherent treatment planning. The data are collected through a combination of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is a major secondary sex distinction between females and males. There is also considerable Bra size, variation in size between individuals. Permanent Breast development, breast growth during puberty is caused by estrogens in conjunction with the growth hormone. Female humans are the only mammals that permanently develop breasts at puberty; all other mammals develop their mammary tissue during the latter period of pregnancy. In females, the breast serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of lactiferous duct, ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissue (biology), tissues give the breast its distinct size and globular shape. At the ends of the ducts are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |