|
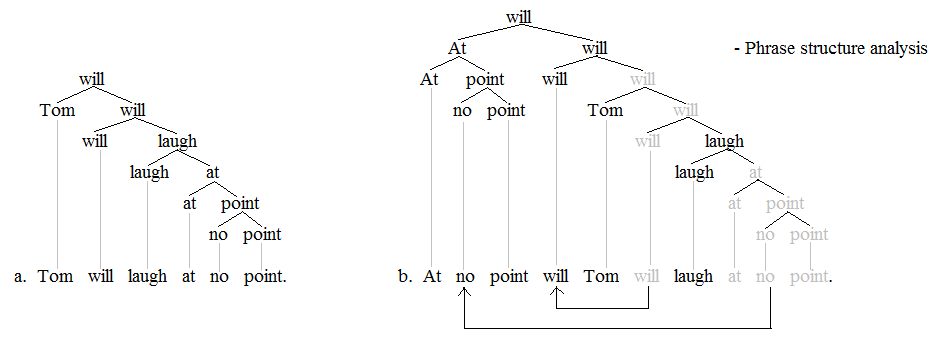
Negative Inversion
In linguistics, negative inversion is one of many types of subject–auxiliary inversion in English language, English. A negation (e.g. ''not'', ''no'', ''never'', ''nothing'', etc.) or a word that implies negation (''only'', ''hardly'', ''scarcely'') or a phrase containing one of these words precedes the finite verb, finite auxiliary verb necessitating that the subject and finite verb undergo Inversion (linguistics), inversion. Negative inversion is a phenomenon of English syntax. Other Germanic languages have a more general V2 word order, which allows inversion to occur much more often than in English, so they may not acknowledge negative inversion as a specific phenomenon. While negative inversion is a common occurrence in English, a solid understanding of just what elicits the inversion has not yet been established. It is, namely, not entirely clear why certain fronted expressions containing a negation elicit negative inversion, but others do not. As with subject-auxiliary inver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
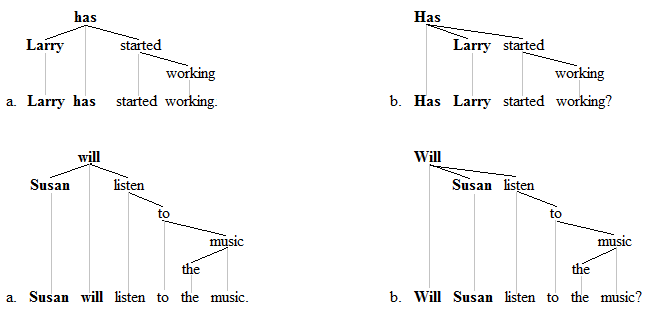
Subject–auxiliary Inversion
Subject–auxiliary inversion (SAI; also called subject–operator inversion) is a frequently occurring type of inversion (linguistics), inversion in the English language whereby a finite auxiliary verb – taken here to include finite forms of the copula (linguistics), copula ''be'' – appears to "invert" (change places) with the subject (grammar), subject. The word order is therefore Aux-S (auxiliary–subject), which is the opposite of the canonical SV (Subject–verb–object word order, subject–verb) order of declarative clauses in English. The most frequent use of subject–auxiliary inversion in English is in the formation of questions, although it also has other uses, including the formation of condition clauses, and in the syntax of sentences beginning with negative expressions (negative inversion). In certain types of English sentences, inversion is also possible with verbs other than auxiliaries; these are described in the article on the subject–verb inversion in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
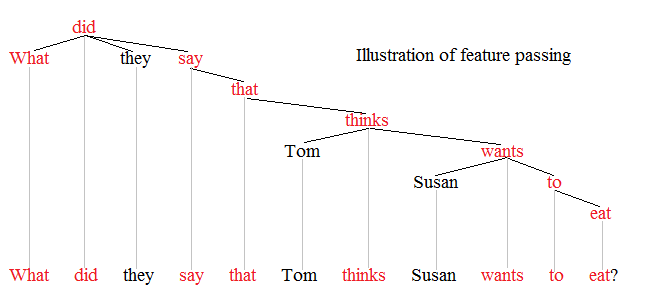
Syntactic Movement
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituents appear to have been displaced from the position in which they receive important features of interpretation. The concept of movement is controversial and is associated with so-called ''transformational'' or ''derivational'' theories of syntax (such as transformational grammar, government and binding theory, minimalist program). Representational theories (such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar, construction grammar, and most dependency grammars), in contrast, reject the notion of movement and often instead address discontinuities with other mechanisms including graph reentrancies, feature passing, and type shifters. Illustration Movement is the traditional means of explaining discontinuities such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining character of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. History In 1956, Chomsky wrote, "A phrase-structure grammar is defined by a finite vocabulary (alphabet) Vp, and a finite set Σ of initial strings in Vp, and a finite set F of rules of the form: X → Y, where X and Y are strings in Vp." Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Verb
A finite verb is a verb that contextually complements a subject, which can be either explicit (like in the English indicative) or implicit (like in null subject languages or the English imperative). A finite transitive verb or a finite intransitive verb can function as the root of an independent clause. Finite verbs are distinguished from non-finite verbs such as infinitives, participles, gerunds etc. History The term ''finite'' is derived from (past participle of "to put an end to, bound, limit") as the form "to which number and person appertain". Verbs were originally said to be ''finite'' if their form limited the possible person and number of the subject. More recently, finite verbs have been construed as any verb that independently functions as a predicate verb or one that marks a verb phrase in a predicate. Under the first of those constructions, finite verbs often denote grammatical characteristics such as gender, person, number, tense, aspect, mood, modali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discontinuity (linguistics)
In linguistics, a discontinuity occurs when a given word or phrase is separated from another word or phrase that it modifies in such a manner that a direct connection cannot be established between the two without incurring crossing lines in the Parse tree, tree structure. The terminology that is employed to denote discontinuities varies depending on the theory of syntax at hand. The terms ''discontinuous constituent'', ''displacement'', ''long distance dependency'', ''unbounded dependency'', and ''projectivity violation'' are largely synonymous with the term ''discontinuity''. There are various types of discontinuities, the most prominent and widely studied of these being topicalization, wh-fronting, scrambling (linguistics), scrambling, and extraposition. Natural languages vary with respect to the types of discontinuities that they permit. The fixed word order of English allows for relatively few discontinuities compared to, for instance, the Slavic languages, which are much more p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern Grammar, grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of Phrase structure grammar, phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a Head (linguistics), head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb, finite verb phrase constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Verb
An auxiliary verb ( abbreviated ) is a verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a participle, which respectively provide the main semantic content of the clause. An example is the verb ''have'' in the sentence ''I have finished my lunch.'' Here, the auxiliary ''have'' helps to express the perfect aspect along with the participle, ''finished''. Some sentences contain a chain of two or more auxiliary verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs, helper verbs, or (verbal) auxiliaries. Research has been conducted into split inflection in auxiliary verbs. Basic examples Below are some sentences that contain representative auxiliary verbs from English, Spanish, German and French, with the auxiliary verb marked in bold: ::a. Do you want tea? – ''do'' is an auxiliary accompanying the infinitive, ''want'', used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar
Head-driven phrase structure grammar (HPSG) is a highly lexicalized, constraint-based grammar developed by Carl Pollard and Ivan Sag. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar, and it is the immediate successor to generalized phrase structure grammar. HPSG draws from other fields such as computer science (type system, data type theory and knowledge representation) and uses Ferdinand de Saussure's notion of the sign (linguistics), sign. It uses a uniform formalism and is organized in a modular way which makes it attractive for natural language processing. An HPSG includes principles and grammar rules and lexicon entries which are normally not considered to belong to a grammar. The formalism is based on lexicalism. This means that the lexicon is more than just a list of entries; it is in itself richly structured. Individual entries are marked with types. Types form a hierarchy. Early versions of the grammar were very lexicalized with few grammatica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Functional Grammar
Lexical functional grammar (LFG) is a constraint-based grammar framework in theoretical linguistics. It posits several parallel levels of syntactic structure, including a phrase structure grammar representation of word order and constituency, and a representation of grammatical functions such as subject and object, similar to dependency grammar. The development of the theory was initiated by Joan Bresnan and Ronald Kaplan in the 1970s, in reaction to the theory of transformational grammar which was current in the late 1970s. It mainly focuses on syntax, including its relation with morphology and semantics. There has been little LFG work on phonology (although ideas from optimality theory have recently been popular in LFG research). Some recent work combines LFG with Distributed Morphology in Lexical-Realizational Functional Grammar.Ash Asudeh, Paul B. Melchin & Daniel Siddiqi (2021). ''Constraints all the way down: DM in a representational model of grammar''. In ''WCCFL 39 Proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimalist Program
In linguistics, the minimalist program is a major line of inquiry that has been developing inside generative grammar since the early 1990s, starting with a 1993 paper by Noam Chomsky. Following Imre Lakatos's distinction, Chomsky presents minimalism as a research program, program, understood as a mode of inquiry that provides a conceptual framework which guides the development of linguistic theory. As such, it is characterized by a broad and diverse range of research directions. For Chomsky, there are two basic Minimalist grammar, minimalist questions—What is language? and Why does it have the properties it has?—but the answers to these two questions can be framed in any theory.Boeckx, Cedric ''Linguistic Minimalism. Origins, Concepts, Methods and Aims'', pp. 84 and 115. Conceptual framework Goals and assumptions Minimalism is an approach developed with the goal of understanding the nature of language. It models a speaker's knowledge of language as a computational syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government And Binding Theory
Government and binding (GB, GBT) is a theory of syntax and a phrase structure grammar in the tradition of transformational grammar developed principally by Noam Chomsky in the 1980s. This theory is a radical revision of his earlier theories and was later revised in '' The Minimalist Program'' (1995) and several subsequent papers, the latest being ''Three Factors in Language Design'' (2005). Although there is a large literature on government and binding theory which is not written by Chomsky, Chomsky's papers have been foundational in setting the research agenda. The name refers to two central subtheories of the theory: ''government'', which is an abstract syntactic relation applicable, among other things, to the assignment of case; and '' binding'', which deals chiefly with the relationships between pronouns and the expressions with which they are co-referential. GB was the first theory to be based on the principles and parameters model of language, which also underlies the later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |