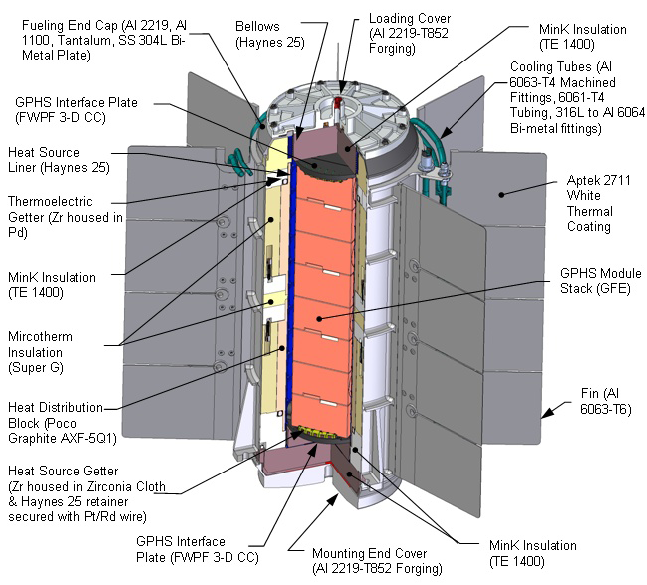
|
Multi-mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator
The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for NASA space missions such as the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Energy's Office of Space and Defense Power Systems within the Office of Nuclear Energy. The MMRTG was developed by an industry team of Aerojet Rocketdyne and Teledyne Energy Systems. Background Space exploration missions require safe, reliable, long-lived power systems to provide electricity and heat to spacecraft and their science instruments. A uniquely capable source of power is the radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – essentially a nuclear battery that reliably converts heat into electricity. Radioisotope power has been used on eight Earth orbiting missions, eight missions to the outer planets, and the Apollo missions after Apollo 11 to the Moon. The outer Solar System missions are the ''Pioneer 10'' and ''11'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MMRTG Schematic - English Labels
The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for NASA space missions such as the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Energy's Office of Space and Defense Power Systems within the Office of Nuclear Energy. The MMRTG was developed by an industry team of Aerojet Rocketdyne and Teledyne Energy Systems. Background Space exploration missions require safe, reliable, long-lived power systems to provide electricity and heat to spacecraft and their science instruments. A uniquely capable source of power is the radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – essentially a nuclear battery that reliably converts heat into electricity. Radioisotope power has been used on eight Earth orbiting missions, eight missions to the outer planets, and the Apollo missions after Apollo 11 to the Moon. The outer Solar System missions are the ''Pioneer 10'' and ''11'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, '' Voyager 1'', on a trajectory that took longer to reach gas giants Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with ice giants Uranus and Neptune. ''Voyager 2'' remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets. ''Voyager 2'' was the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System. ''Voyager 2'' successfully fulfilled its primary mission of visiting the Jovian system in 1979, the Saturnian system in 1981, Uranian system in 1986, and the Neptunian system in 1989. The spacecraft is now in its extended mission of studying interstellar space. It has been operating for as of ; , it has reached a distance of from Earth. The probe entered interstellar space on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an essential source of renewable energy, and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the Sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air. The large magnitude of solar energy available makes it a highly appealing source of electricity. In 2020 solar energy has been the cheapest source of Electricity. In Saudi Arabia a power purchase agre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially used for electricity generation and as photosensors. A photovoltaic system employs solar modules, each comprising a number of solar cells, which generate electrical power. PV installations may be ground-mounted, rooftop-mounted, wall-mounted or floating. The mount may be fixed or use a solar tracker to follow the sun across the sky. Photovoltaic technology helps to mitigate climate change because it emits much less carbon dioxide than fossil fuels. Solar PV has specific advantages as an energy source: once installed, its operation generates no pollution and no greenhouse gas emissions, it shows scalability in respect of power needs and silicon has large availability in the Earth's crust, although other materials required in PV sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Brog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Gradient
A temperature gradient is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the temperature changes the most rapidly around a particular location. The temperature gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of degrees (on a particular temperature scale) per unit length. The SI unit is kelvin per meter (K/m). Temperature gradients in the atmosphere are important in the atmospheric sciences (meteorology, climatology and related fields). Mathematical description Assuming that the temperature ''T'' is an intensive quantity, i.e., a single-valued, continuous and differentiable function of three-dimensional space (often called a scalar field), i.e., that :T=T(x,y,z) where ''x'', ''y'' and ''z'' are the coordinates of the location of interest, then the temperature gradient is the vector quantity defined as :\nabla T = \begin , , \end Physical processes Climatology On a global and annual basis, the dynamics of the atmosphere (and the oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onsager Reciprocal Relations
In thermodynamics, the Onsager reciprocal relations express the equality of certain ratios between flows and forces in thermodynamic systems out of equilibrium, but where a notion of local equilibrium exists. "Reciprocal relations" occur between different pairs of forces and flows in a variety of physical systems. For example, consider fluid systems described in terms of temperature, matter density, and pressure. In this class of systems, it is known that temperature differences lead to heat flows from the warmer to the colder parts of the system; similarly, pressure differences will lead to matter flow from high-pressure to low-pressure regions. What is remarkable is the observation that, when both pressure and temperature vary, temperature differences at constant pressure can cause matter flow (as in convection) and pressure differences at constant temperature can cause heat flow. Perhaps surprisingly, the heat flow per unit of pressure difference and the density (matter) flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seebeck Effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. At the atomic scale, an applied temperature gradient causes charge carriers in the material to diffuse from the hot side to the cold side. This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is affected by the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers. The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect, Peltier effect, and Thomson effect. The Seebeck and Peltier effects are different manifestations of the same physical process; textbooks may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium-238
Plutonium-238 (238Pu or Pu-238) is a fissile, radioactive isotope of plutonium that has a half-life of 87.7 years. Plutonium-238 is a very powerful alpha emitter; as alpha particles are easily blocked, this makes the plutonium-238 isotope suitable for usage in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) and radioisotope heater units. The density of plutonium-238 at room temperature is about 19.8 g/cc. The material will generate about 0.57 watts/gram of 238Pu. The bare sphere critical mass of metallic plutonium-238 is not precisely known, but its calculated range is between 9.04 and 10.07 kilograms. History Initial production Plutonium-238 was the first isotope of plutonium to be discovered. It was synthesized by Glenn Seaborg and associates in December 1940 by bombarding uranium-238 with deuterons, creating neptunium-238. The subsequent decay via β− decay creates Plutonium-238. + → + 2 The neptunium isotope then undergoes β− decay to plut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuclide the decay rate, and thus the half-life (''t''1/2) for tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay ( ), beta decay ( ), and gamma decay ( ), all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. A fourth type of common decay is electron capture, in which an unstable nucleus captures an inner electron from one of the electron shells. The loss of that electron from the shell results in a cascade of electrons dropping down to that lower shell resulting in emission of discrete X-rays from the transitions. A common example is iodine-125 commonly used in medical settings. Radioactive decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |