|
Moyasta Junction Railway Station
The West Clare Railway (WCR) originally operated in County Clare, Ireland, between 1887 and 1961. This narrow-gauge railway ran from the county town of Ennis, via numerous stopping-points along the West Clare coast to two termini, at Kilrush and Kilkee, with the routes diverging at Moyasta Junction. The system was the last operating narrow gauge passenger system in Ireland and connected with the mainline rail system at Ennis, where a station still stands today for bus and train services to Limerick and Galway. Intermediate stops included Ennistymon, Lahinch and Milltown Malbay. A preservation society maintains a railway museum at Moyasta Junction station, and successfully re-opened a section of the railway as a passenger-carrying heritage line with diesel traction in the 1990s, and with steam motive power from 2009. The Railway was notorious for poor timekeeping, resulting in litigation and a celebrated comic song. Construction The Famine was over and there was a new gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
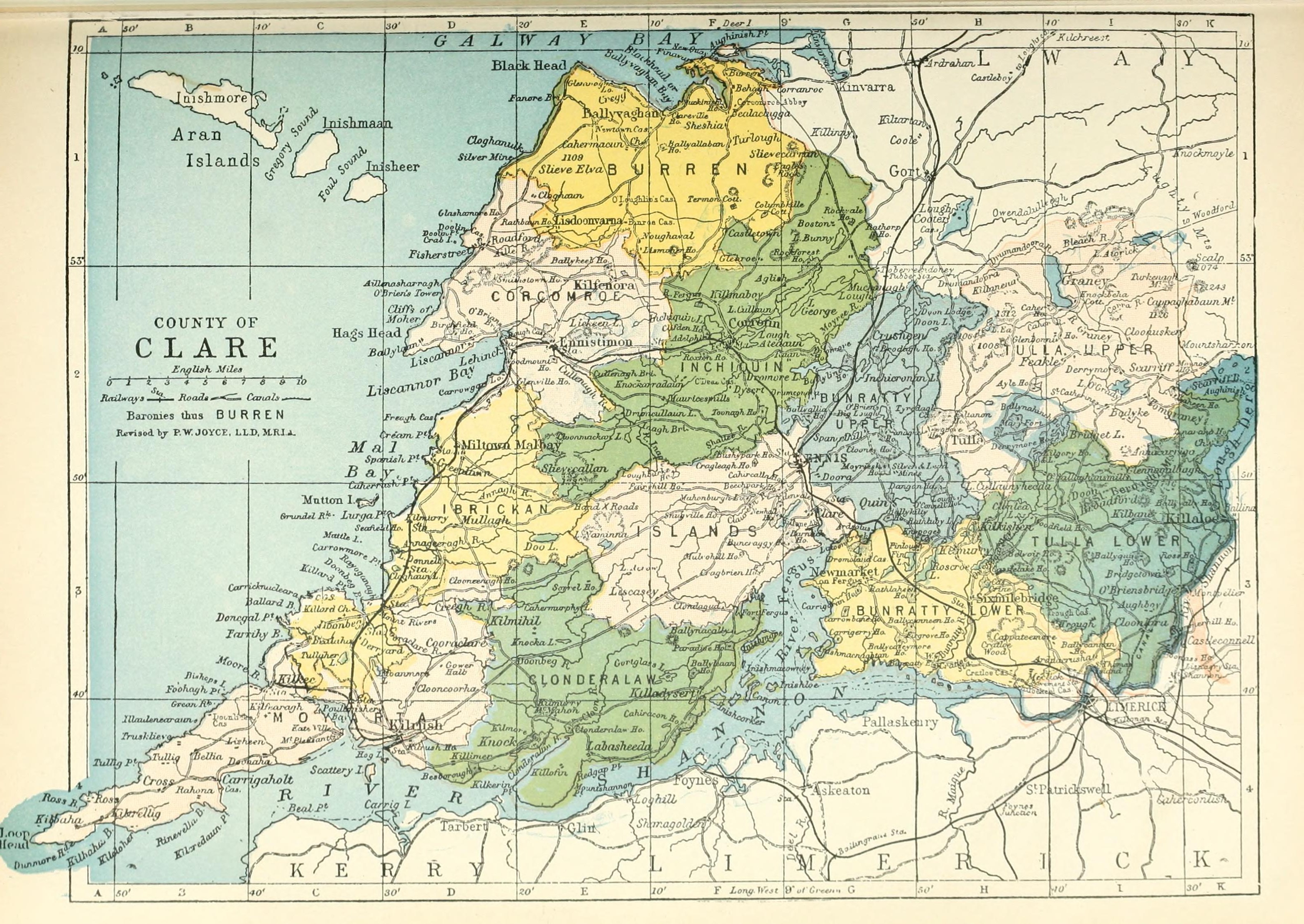
County Clare
County Clare ( ga, Contae an Chláir) is a county in Ireland, in the Southern Region and the province of Munster, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the local authority. The county had a population of 118,817 at the 2016 census. The county town and largest settlement is Ennis. Geography and subdivisions Clare is north-west of the River Shannon covering a total area of . Clare is the seventh largest of Ireland's 32 traditional counties in area and the 19th largest in terms of population. It is bordered by two counties in Munster and one county in Connacht: County Limerick to the south, County Tipperary to the east and County Galway to the north. Clare's nickname is ''the Banner County''. Baronies, parishes and townlands The county is divided into the baronies of Bunratty Lower, Bunratty Upper, Burren, Clonderalaw, Corcomroe, Ibrickan, Inchiquin, Islands, Moyarta, Tulla Lower and Tulla Upper. These in turn are divided into civil pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterford, Limerick And Western Railway
The Waterford, Limerick and Western Railway (WL&WR), formerly the Waterford and Limerick Railway up to 1896, was at the time it was amalgamated with the Great Southern and Western Railway in 1901 the fourth largest railway in Ireland, with a main line stretching from Limerick to Waterford and branches to Sligo and Tralee. Inception The Limerick & Waterford Railway Act was passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom on 31 May 1826 and had the distinction of being the first act authorising an Irish railway. No construction followed and it was 1845 before the Waterford & Limerick Railway was authorised, the first section of the line being opened from Limerick to Tipperary on 9 May 1848, the remainder of the main line being opened in stages, finally reaching Waterford in 1854. Secondary lines The company eventually operated two long branch lines which extended from Limerick, north west to Sligo and south west to Tralee. Branch lines By 1900, there were a number of branch lines: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dübs And Company
Dübs & Co. was a locomotive manufacturer in Glasgow, Scotland, founded by Henry Dübs in 1863 and based at the Queens Park Works in Polmadie. In 1903 it amalgamated with two other Glasgow locomotive manufacturers to create the North British Locomotive Company. Preserved locomotives Eleven locomotives built for the New Zealand Railways Department, numerous others in South Africa and the Isle of Man. Preserved locomotives in New Zealand Four members of the 0-4-0 A class built in 1873 have been preserved. A 64 and A 67 are in full operational condition on vintage railways; A 64 resides at The Plains Vintage Railway & Historical Museum in Ashburton. A 67 is owned and operated by the Ocean Beach Railway / Otago Railway & Locomotive Society Inc, while A 62 is in private ownership and it is understood that the smokebox has been snapped from the boiler. A 66 (also owned by the Ocean Beach Railway) was damaged by fire when the building in which it was kept on static display wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The type is sometimes known as a Webb or a Branchliner. Overview While some locomotives with this wheel arrangement had tenders, the majority were tank locomotives which carried their coal and water onboard. Usage Finland Finland used two classes of 0-6-2T locomotive, the Vr2 and the Vr5. The Vr2 class was numbered in the range from 950 to 965. Five of them are preserved in Finland, no. 950 at Joensuu, no. 951 at Tuuri, no. 953 at Haapamäki, no. 961 at Jyväskylä and no. 964 at the Veturimuseo at Toijala. The Vr5 class was numbered in the range from 1400 to 1423. No. 1422 is preserved at Haapamäki. Philippines There were 30 ''Dagupan''-type locomotives built between 1889 and 1890. All were tank locomotives, weighed and were run a maximum speed of . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrangement used on both tender and tank locomotives in versions with both inside and outside cylinders. In the United Kingdom, the Whyte notation of wheel arrangement was also often used for the classification of electric and diesel-electric locomotives with side-rod coupled driving wheels. Under the UIC classification, popular in Europe, this wheel arrangement is written as C if the wheels are coupled with rods or gears, or Co if they are independently driven, the latter usually being electric and diesel-electric locomotives. Overview History The 0-6-0 configuration was the most widely used wheel arrangement for both tender and tank steam locomotives. The type was also widely used for diesel switchers (shunters). Because they lack lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Gauge
Railways with a track gauge of fall within the category of broad gauge railways. , they were extant in Australia, Brazil and Ireland. History 600 BC :The Diolkos (Δίολκος) across the Isthmus of Corinth in Greece – a grooved paved trackway – was constructed with an average gauge of . 1840 : The Grand Duchy of Baden State Railway was constructed in 1840-1851 to gauge before being converted to in 1854–1855. 1843 : The Board of Trade of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, after investigating a dispute caused by diverse gauges, recommended the use of in Ireland. 1846 : The Regulating the Gauge of Railways Act 1846 made mandatory throughout all of Ireland. 1847 : The Swiss Northern Railway was opened as a line and converted to in 1854. 1854 : The first Australian railway to operate steam-powered freight and passenger services, Melbourne and Hobson's Bay Railway Company, was built as a line. 1858 : The first Brazilian railway was opened: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Southern Railways
The Great Southern Railways Company (often Great Southern Railways, or GSR) was an Irish company that from 1925 until 1945 owned and operated all railways that lay wholly within the Irish Free State (the present-day Republic of Ireland). The period was difficult with rising operating costs and static to failing income. The early part of the period was soon after infrastructure losses of the Irish Civil War. The Emergency or Second World War at the end of the period saw shortages of coal and raw materials with increased freight traffic and restricted passenger traffic. History Context Civil unrest in Ireland had led to the assumption of governmental control of all railways operating in Island of Ireland on 22 December 1916 through the Irish Railways Executive Committee, later succeeded by the Ministry of Transport. Control was returned to the management of the companies on 15 August 1921. The Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921 establishing the Irish Free State and subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donkey
The domestic donkey is a hoofed mammal in the family Equidae, the same family as the horse. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domesticated in Africa some years ago, and has been used mainly as a working animal since that time. There are more than 40 million donkeys in the world, mostly in underdeveloped countries, where they are used principally as draught or pack animals. While working donkeys are often associated with those living at or below subsistence, small numbers of donkeys or asses are kept for breeding or as pets in developed countries. A male donkey is known as a ''jack'' or ''jackass'', a female is a ''jenny'' or ''jennet'', and an immature donkey of either sex is a ''foal''. Jacks are often mated with female horses (mares) to produce '' mules''; the less common hybrid of a male horse (stallion) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Palles
Christopher Palles (25 December 1831 – 14 February 1920) was an Irish barrister, Solicitor-General, Attorney-General and a judge for over 40 years. His biographer, Vincent Thomas Hyginus Delany, described him as "the greatest of the Irish judges". He served as the last Lord Chief Baron of the Exchequer from 1874 until his retirement from the bench in 1916. Early life Palles was born on Christmas Day 1831 in County Dublin. He was the third son of Andrew Christopher Palles (1801-1880), a solicitor, and his wife Eleanor Mary Palles (née Plunkett) (1801-1877). Another son was Andrew Christopher Palles, who became an architect. Palles's ancestors (the earliest known version of the surname is de Palatio) were of Italian origin, and came to Ireland in the late fifteenth century in the entourage of their relative Ottaviano Spinelli de Palatio, who was Papal Legate, and Archbishop of Armagh from 1478 to 1513. Palles was educated at Clongowes Wood College and Trinity College Dubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ennis Courthouse
Ennis Courthouse ( ga, Teach Cúirte na hInse) is a judicial facility in Gort Road, Ennis, County Clare, Ireland. History The courthouse, which was designed by John Keane and Henry Whitestone in the neoclassical style and built in ashlar stone, was completed in 1852. The design involved a symmetrical main frontage facing the junction of Gort Road and New Road; there was a flight of steps leading up to a large hexastyle portico with Ionic order columns supporting an entablature and a modillioned pediment. A Russian artillery piece, which had been used in the Crimean War, was brought back to Ireland and placed on the lawn outside the building. A statue of Michael O'Loghlen, former Master of Rolls in Ireland, by the sculptor Joseph Robinson Kirk was installed in the courthouse in the mid-19th century. The building was originally used as a facility for dispensing justice but, following the implementation of the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898, which established county co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Are Ye Right There Michael
Are Ye Right There Michael is a song by the 19th-century and early 20th-century Irish composer and musician Percy French, parodying the state of the West Clare Railway system in rural County Clare. It was inspired by an actual train journey in 1896. Because of a slow train and the decision of the driver to stop for no apparent reason, French, though having left Sligo in the early morning, arrived so late for an 8pm recital that the audience had left. The ballad caused considerable embarrassment for the railway company, which was mocked in music halls throughout Ireland and Britain because of the song. It led to an unsuccessful libel action against French. It is said that when French arrived late for the libel hearing, the judge chided him on his lateness. French reportedly responded "Your honour, I travelled by the West Clare Railway", resulting in the case being thrown out. Lyrics :Are Ye Right There Michael :by Percy French (1902) :You may talk of Columbus's sailing :Across the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

