|
Monopoly Profit
Monopoly profit is an inflated level of profit due to the monopolistic practices of an enterprise.Bradley R. Chiller, "Essentials of Economics", New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc., 1991. Basic classical and neoclassical theory Traditional economics state that in a competitive market, no firm can command elevated premiums for the price of goods and services as a result of sufficient competition. In contrast, insufficient competition can provide a producer with disproportionate pricing power. Withholding production to drive prices higher produces additional profit, which is called ''monopoly profits''.Roger LeRoy Miller, ''Intermediate Microeconomics: Theory Issues Applications'', Third Edition, New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc, 1982. According to classical and neoclassical economic thought, firms in a perfectly competitive market are price takers because no firm can charge a price that is different from the equilibrium price set within the entire industry's perfectly competitive market.Tiro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Economics
Classical economics, classical political economy, or Smithian economics is a school of thought in political economy that flourished, primarily in Britain, in the late 18th and early-to-mid 19th century. Its main thinkers are held to be Adam Smith, Jean-Baptiste Say, David Ricardo, Thomas Robert Malthus, and John Stuart Mill. These economists produced a theory of market economies as largely self-regulating systems, governed by natural laws of production and exchange (famously captured by Adam Smith's metaphor of the invisible hand). Adam Smith's '' The Wealth of Nations'' in 1776 is usually considered to mark the beginning of classical economics.Smith, Adam (1776) An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of The Wealth of Nations. (accessible by table of contents chapter titles) AdamSmith.org The fundamental message in Smith's book was that the wealth of any nation was determined not by the gold in the monarch's coffers, but by its national income. This income was in turn bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrier To Entry
In theories of competition in economics, a barrier to entry, or an economic barrier to entry, is a fixed cost that must be incurred by a new entrant, regardless of production or sales activities, into a market that incumbents do not have or have not had to incur. Because barriers to entry protect incumbent firms and restrict competition in a market, they can contribute to distortionary prices and are therefore most important when discussing antitrust policy. Barriers to entry often cause or aid the existence of monopolies and oligopolies, or give companies market power. Barriers of entry also have an importance in industries. First of all it is important to identify that some exist naturally, such as brand loyalty. Governments can also create barriers to entry to meet consumer protection laws, protecting the public. In other cases it can also be due to inherent scarcity of public resources needed to enter a market. Definitions Various conflicting definitions of "barrier to entry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Share
Market share is the percentage of the total revenue or sales in a market that a company's business makes up. For example, if there are 50,000 units sold per year in a given industry, a company whose sales were 5,000 of those units would have a 10percent share in that market. "Marketers need to be able to translate and incorporate sales targets into market share because this will demonstrate whether forecasts are to be attained by growing with the market or by capturing share from competitors. The latter will almost always be more difficult to achieve. Market share is closely monitored for signs of change in the competitive landscape, and it frequently drives strategic or tactical action."Farris, Paul W.; Neil T. Bendle; Phillip E. Pfeifer; David J. Reibstein (2010). ''Marketing Metrics: The Definitive Guide to Measuring Marketing Performance.'' Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc. . The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses the definitions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item is a function of an item's perceived necessity, price, perceived quality, convenience, available alternatives, purchasers' disposable income and tastes, and many other options. Factors influencing demand Innumerable factors and circumstances affect a consumer's willingness or to buy a good. Some of the common factors are: The price of the commodity: The basic demand relationship is between potential prices of a good and the quantities that would be purchased at those prices. Generally, the relationship is negative, meaning that an increase in price will induce a decrease in the quantity demanded. This negative relationship is embodied in the downward slope of the consumer demand curve. The assumption of a negative relationship is reaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economies Of Scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control. This is just a partial description of the concept. Economies of scale apply to a variety of the organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a production, plant or an entire enterprise. When average costs start falling as output increases, then economies of scale occur. Some economies of scale, such as capital cost of manufacturing facilities and friction loss of transportation and industrial equipment, have a physical or engineering basis. The economic concept dates back to Adam Smith and the idea of obtaining larger production returns through the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Cost
The unit cost is the price incurred by a company A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared ... to produce, store and sell one unit of a particular product. Unit costs include all fixed costs and all variable costs involved in production. Cost unit is a form of measurement of volume of production or service. Cost unit vs unit cost Cost unit is the standard unit for buying the minimum of any product. Unit cost is the minimum cost for buying any standard unit. References {{Business-term-stub Costs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Market
In economics, the product market is the marketplace where final goods or services are sold to businesses and the public sector. Focusing on the sale of finished goods, it does not include trading in raw or other intermediate materials. Related, but contrasting, terms are ''financial market'' and '' labour market''. ''Product market regulation'' is a term for the placing of restrictions upon the operation of the product market. According to an OECD ranking in 1998, English-speaking and Nordic countries had the least-regulated product markets in the OECD.OECD (2005), "Product Market Regulation in OECD Countries: From 1998 to 2003", in OECD, Economic Policy Reforms 2005: Going for Growth, OECD Publishing. The least-regulated product markets were to be found in: #United Kingdom #Australia #United States #Canada #New Zealand #Denmark #Ireland According to the OECD, indicators for product market regulation include price controls, foreign ownership barriers, and tariffs, among other thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Cost
In accounting and economics, 'fixed costs', also known as indirect costs or overhead costs, are business expenses that are not dependent on the level of goods or services produced by the business. They tend to be recurring, such as interest or rents being paid per month. These costs also tend to be capital costs. This is in contrast to variable costs, which are volume-related (and are paid per quantity produced) and unknown at the beginning of the accounting year. Fixed costs have an effect on the nature of certain variable costs. For example, a retailer must pay rent and utility bills irrespective of sales. As another example, for a bakery the monthly rent and phone line are fixed costs, irrespective of how much bread is produced and sold; on the other hand, the wages are variable costs, as more workers would need to be hired for the production to increase. For any factory, the fix cost should be all the money paid on capitals and land. Such fixed costs as buying machines and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
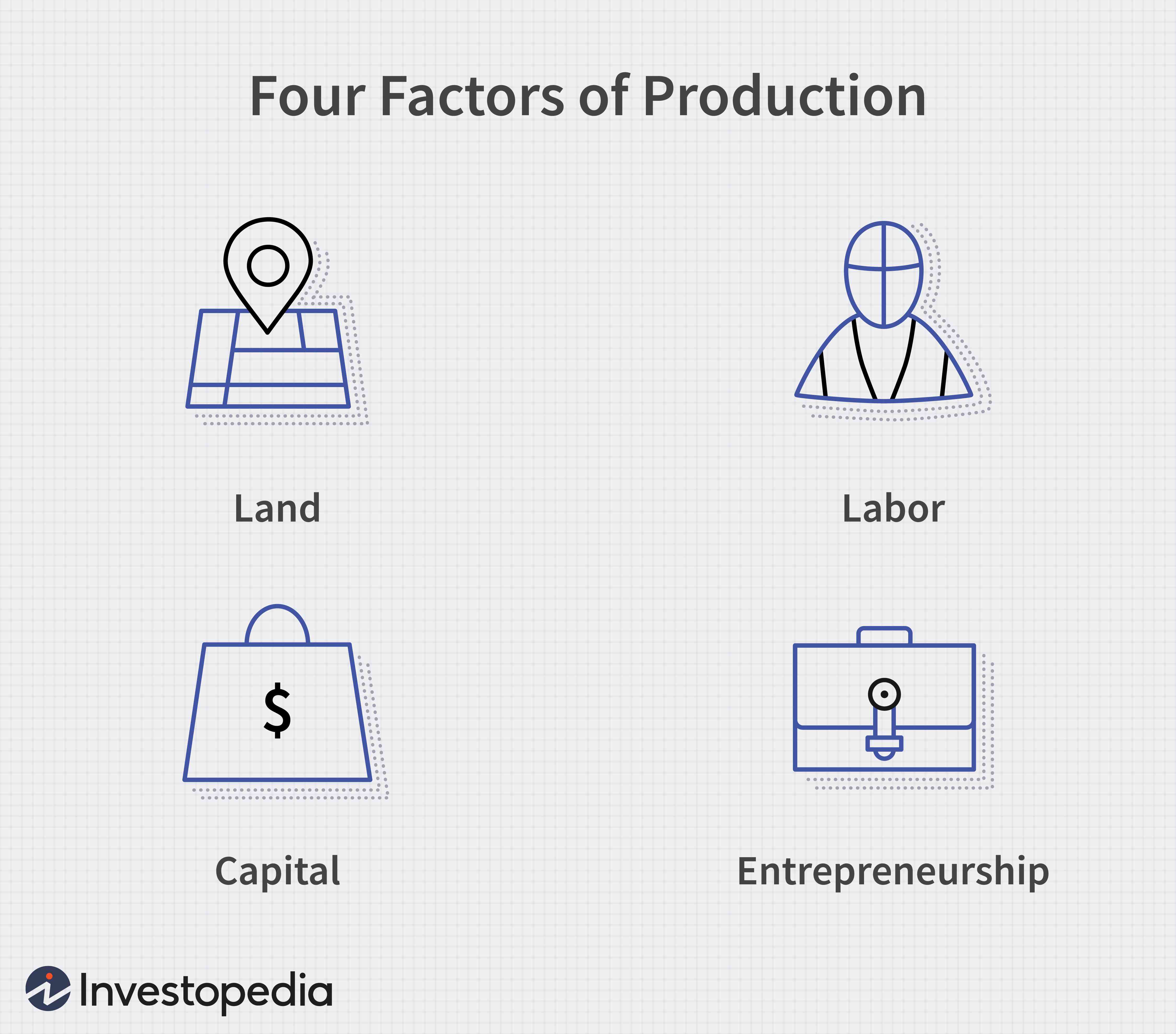
Production (economics)
Production is the process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output will be a good or service which has value and contributes to the utility of individuals. The area of economics that focuses on production is called production theory, and it is closely related to the consumption (or consumer) theory of economics. The production process and output directly result from productively utilising the original inputs (or factors of production). Known as primary producer goods or services, land, labour, and capital are deemed the three fundamental production factors. These primary inputs are not significantly altered in the output process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors as they are byproducts of land, labour and capital. Delving further, primary facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(OH)), mixed with the two iron oxides goethite (FeO(OH)) and haematite (Fe2O3), the aluminium clay mineral kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) and small amounts of anatase (TiO2) and ilmenite (FeTiO3 or FeO.TiO2). Bauxite appears dull in luster and is reddish-brown, white, or tan. In 1821, the French geologist Pierre Berthier discovered bauxite near the village of Les Baux in Provence, southern France. Formation Numerous classification schemes have been proposed for bauxite but, , there was no consensus. Vadász (1951) distinguished lateritic bauxites (silicate bauxites) from karst bauxite ores (carbonate bauxites): * The carbonate bauxites occur predominantly in Europe, Guyana, Suriname, and Jamaica above carbonate rocks (limesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoa
Alcoa Corporation (an acronym for Aluminum Company of America) is a Pittsburgh-based industrial corporation. It is the world's eighth-largest producer of aluminum. Alcoa conducts operations in 10 countries. Alcoa is a major producer of primary aluminum, fabricated aluminum, and alumina combined, through its active and growing participation in all major aspects of the industry: technology, mining, refining, smelting, fabricating, and recycling. In May 2007, Alcoa Inc. made a US$27 billion hostile takeover bid for Alcan in an attempt to form the world's largest aluminum producer. The bid was withdrawn when Alcan announced a friendly takeover by Rio Tinto in July 2007. On November 1, 2016, Alcoa Inc. split into two entities: a new one called Alcoa Corporation, which is engaged in the mining and manufacture of raw aluminum, and the renaming of Alcoa Inc. to Arconic Inc., which processes aluminum and other metals. After relocating its corporate operations to New York City ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Agent
In economics, an agent is an actor (more specifically, a decision maker) in a model of some aspect of the economy. Typically, every agent makes decisions by solving a well- or ill-defined optimization or choice problem. For example, ''buyers'' (consumers) and ''sellers'' ( producers) are two common types of agents in partial equilibrium models of a single market. Macroeconomic models, especially dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models that are explicitly based on microfoundations, often distinguish households, firms, and governments or central banks as the main types of agents in the economy. Each of these agents may play multiple roles in the economy; households, for example, might act as consumers, as workers, and as voters in the model. Some macroeconomic models distinguish even more types of agents, such as workers and shoppers or commercial banks. The term ''agent'' is also used in relation to principal–agent models; in this case, it refers specifically to someone de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |