|
Minety And Ashton Keynes Railway Station
Minety and Ashton Keynes railway station serving the village of Minety in Wiltshire, England, was opened in 1841 on the former Cheltenham and Great Western Union Railway line from Gloucester to Swindon; it was originally called just Minety. The Cheltenham and Great Western Union connected to the South Wales Railway in and to the Great Western Railway at . The Cheltenham and Great Western Union and the South Wales lines were both later absorbed by the Great Western Railway, which provided the train services on the line. In 1905 the station was renamed Minety & Ashton Keynes. In 1948 the Great Western Railway was nationalised and the station thereafter was owned by British Rail. Although the line remains open the station closed in November 1964 and has been demolished, except for parts of the platforms. Trains run along what is now called the Golden Valley Line from London Paddington via , Didcot Parkway and Swindon, then past the three closed stations of , Minety and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minety, Wiltshire
Minety is a village in north Wiltshire, England, between Malmesbury – to the west – and Swindon. It takes its name from the water mint plant found growing in ditches around the village, and has previously been known as Myntey. It has a primary school and a successful rugby club. Geography The village is divided into Upper Minety, with St Leonard's church, and Lower Minety (or simply Minety) which grew after the railway arrived. The civil parish includes the hamlets of Brandier, Lower Moor and the former hamlet of Sawyers Hill, now part of Minety village. Swill Brook forms part of the northern boundary of the parish and joins the infant River Thames a short distance outside the parish, near Ashton Keynes. Acres Farm Meadow is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest. The Minety Battery Energy Storage Project, about west of the village, was the largest grid-connected battery in Europe when it began operation in 2021. History Fragments of an Anglo-Saxon car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didcot Parkway Railway Station
Didcot Parkway is a railway station serving the town of Didcot in Oxfordshire, England. The station was opened as Didcot on 12 June 1844 and renamed Didcot Parkway on 29 July 1985 by British Rail to reflect its role as a park and ride railhead. It is down the line from and is situated between to the east and to the west. The station is served by local services operated by Great Western Railway from to Didcot and , and by main line services from Paddington to the south-west of England and south Wales. Just to the north of the station is the Didcot Railway Centre, which is accessed through the station. The centre is a comprehensive exhibition of original Great Western Railway rolling stock, with demonstration running tracks and including a reconstructed station named Didcot Halt. History The railway has run through Didcot since 1 June 1840, when the Great Western Railway extended its main line from Reading to . During this period a stagecoach transported passengers to Oxfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1841
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Great Western Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloucester To Newport Line
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east of the border with Wales. Including suburban areas, Gloucester has a population of around 132,000. It is a port, linked via the Gloucester and Sharpness Canal to the Severn Estuary. Gloucester was founded by the Romans and became an important city and ''colony'' in AD 97 under Emperor Nerva as '' Colonia Glevum Nervensis''. It was granted its first charter in 1155 by Henry II. In 1216, Henry III, aged only nine years, was crowned with a gilded iron ring in the Chapter House of Gloucester Cathedral. Gloucester's significance in the Middle Ages is underlined by the fact that it had a number of monastic establishments, including: St Peter's Abbey founded in 679 (later Gloucester Cathedral), the nearby St Oswald's Priory, Gloucester f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Parkway Railway Station
Bristol Parkway, on the South Wales Main Line, is in the Stoke Gifford area in the northern suburbs of the Bristol conurbation. It is from London Paddington. The station was opened in 1972 by British Rail, and was the first in a new generation of park and ride/parkway stations. It is the third-most heavily used station in the West of England local authority area, after Bristol Temple Meads and . There are four platforms, and a well-equipped waiting area. The station is managed by Great Western Railway, who provide most of the trains at the station, with CrossCountry providing the rest. Electrification using 25 kV 50 Hz AC overhead system reached Bristol Parkway in late 2018, and electric trains in the Swindon and London direction commenced passenger service on 30 December 2018. This is part of the 21st-century modernisation of the Great Western Main Line. Description Bristol Parkway is located in the unitary authority of South Gloucestershire, in the Stoke Gifford area o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
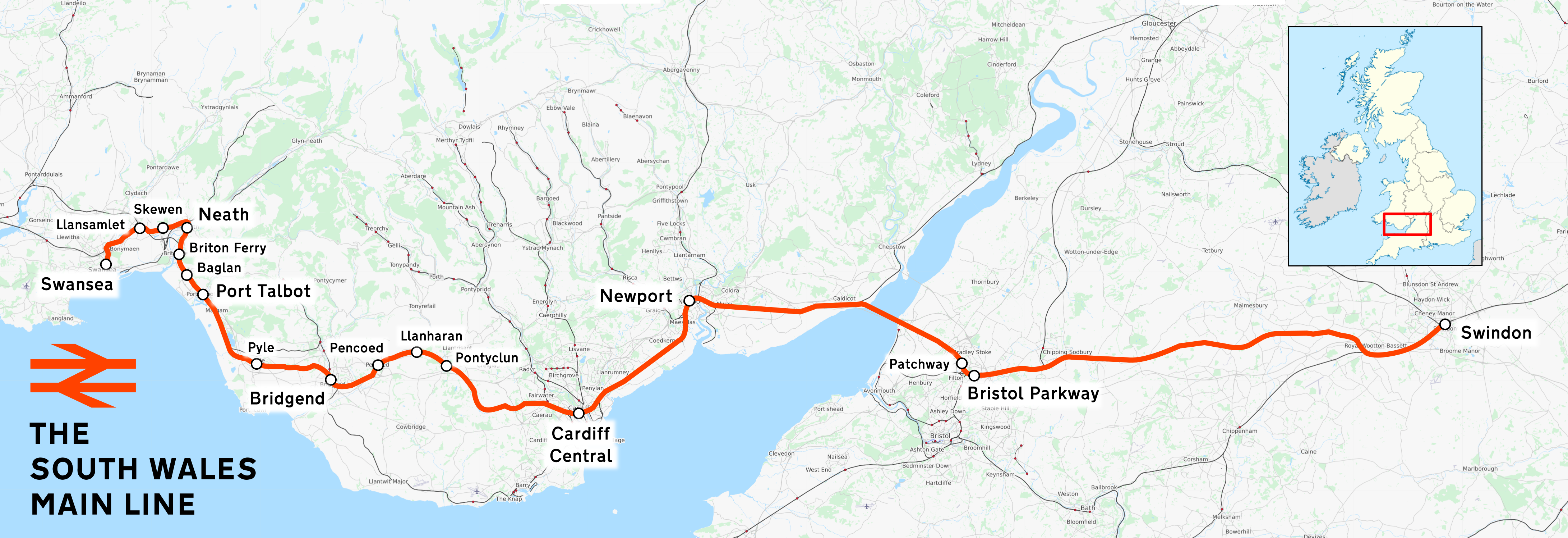
South Wales Main Line
The South Wales Main Line ( cy, Prif Linell De Cymru), originally known as the London, Bristol and South Wales Direct Railway or simply as the Bristol and South Wales Direct Railway, is a branch of the Great Western Main Line in Great Britain. It diverges from the core London-Bristol line at Royal Wootton Bassett beyond Swindon, first calling at Bristol Parkway, after which the line continues through the Severn Tunnel into South Wales. Great Western Railway operates Class 800 trains between London and South Wales, and Classes 253, 254 and 255 High Speed Trains on services between Cardiff and South West England. CrossCountry provides services from Cardiff to Nottingham via Severn Tunnel Junction and thence the Gloucester to Newport Line via Gloucester and Birmingham. Transport for Wales operates services between South Wales, and North Wales and the Midlands on the line. The line between Wootton Bassett and Cardiff Central is electrified using the 25 kV AC overhead syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Main Line
The Great Western Main Line (GWML) is a main line railway in England that runs westwards from London Paddington to . It connects to other main lines such as those from Reading to Penzance and Swindon to Swansea. Opened in 1841, it was the original route of the first Great Western Railway which was merged into the Western Region of British Railways in 1948. It is now a part of the national rail system managed by Network Rail with the majority of passenger services provided by the current Great Western Railway franchise. The line has recently been electrified along most of its length. The eastern section from Paddington to was electrified in 1998. Work to electrify the remainder of the route started in 2011 with an initial aim to complete the work all the way to Bristol by 2016, but in that year the section through Bath to Bristol Temple Meads was deferred with no date set for completion because costs had tripled. History The line was built by the Great Western Railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severn Tunnel
The Severn Tunnel ( cy, Twnnel Hafren) is a railway tunnel in the United Kingdom, linking South Gloucestershire in the west of England to Monmouthshire in south Wales under the estuary of the River Severn. It was constructed by the Great Western Railway (GWR) between 1873 and 1886 for the purpose of dramatically shortening the journey times of their trains, passenger and freight alike, between South Wales and Western England. It has often been regarded as the crowning achievement of GWR's chief engineer Sir John Hawkshaw. Prior to the tunnel's construction, lengthy detours were necessary for all traffic between South Wales and Western England, which either used ship or a lengthy diversion upriver via . Recognising the value of such a tunnel, the GWR sought its development, tasking Hawkshaw with its design and later contracting the civil engineer Thomas A. Walker to undertake its construction, which commenced in March 1873. Work proceeded smoothly until October 1879, at which poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemble Railway Station
Kemble railway station is a railway station that serves the village of Kemble in Gloucestershire, England. The station is on the to "Golden Valley" line. Despite its rural location, Kemble station has a high number of passengers, due mainly to the proximity of Cirencester. History The station was opened by the Great Western Railway (GWR) as an exchange station on 12 May 1845 with the line opening from Swindon to Gloucester. Only on 1 May 1882 did it become a public station replacing the nearby . The distance between the platforms and the large clearance between the remaining running lines is a legacy from when Kemble first opened because it originally accommodated Brunel's broad gauge tracks. These were changed to standard gauge tracks in 1892. Until the 1960s the station was a junction, with services to the nearby market towns of (to the northeast) and (southwest). Both the Tetbury branch line and the Cirencester Branch Line were closed to traffic under '' The Reshap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paddington Railway Station
Paddington, also known as London Paddington, is a Central London railway terminus and London Underground station complex, located on Praed Street in the Paddington area. The site has been the London terminus of services provided by the Great Western Railway and its successors since 1838. Much of the main line station dates from 1854 and was designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel. Paddington is the London terminus of the Great Western Main Line; passenger services are primarily operated by Great Western Railway, which provides the majority of commuter and regional passenger services to west London and the Thames Valley region as well as long-distance intercity services to South West England and South Wales. The station is also the eastern terminus for Heathrow Express and the western terminus for Elizabeth line services from Shenfield. Elizabeth line services also run through Paddington westwards to Reading, Heathrow Terminal 5, and Heathrow Terminal 4, and eastwards to Abbey W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_drawn_and_engraved_under_the_direction_of_Edward_Wedlake_Brayley.jpg)