|
Middle Income Trap
The middle income trap is an economic development situation in which a country that attains a certain income (due to given advantages) gets stuck at that level. The term was introduced by the World Bank in 2006 and is defined by them as the 'middle-income range' countries with gross national product per capita that has remained between $1,000 to $12,000 at constant (2011) prices. Origin of the term Economists Indermit Gill and Homi Kharas coined the term at World Bank in 2006 when they were working in the ground strategies for Eastern Asian economics. MIT is a new phenomenon and was first mentioned in 2007 in Gill and Kharas's World Bank report "An East Asian Renaissance: Ideas for Economic Growth". Dynamics According to the concept, a country in the middle-income trap has lost its competitive edge in the export of manufactured goods due to rising wages, but is unable to keep up with more developed economies in the high-value-added market. As a result, newly industrialized e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and objectives. The term has been used frequently in the 20th and 21st centuries, but the concept has existed in the West for far longer. " Modernization", " Westernization", and especially " industrialization" are other terms often used while discussing economic development. Historically, economic development policies focused on industrialization and infrastructure; since the 1960s, it has increasingly focused on poverty reduction. Whereas economic development is a policy intervention aiming to improve the well-being of people, economic growth is a phenomenon of market productivity and increases in GDP; economist Amartya Sen describes economic growth as but "one aspect of the process of economic development". Economists primarily focus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Common definitions for the middle class range from the middle fifth of individuals on a nation's income ladder, to everyone but the poorest and wealthiest 20%. Theories like "Paradox of Interest" use decile groups and wealth distribution data to determine the size and wealth share of the middle class. From a Marxist standpoint, middle class initially referred to the ' bourgeoisie,' as distinct from nobility. With the development of capitalist societies and further inclusion of the bourgeoisie into the ruling class, middle class has been more closely identified by Marxist scholars with the term 'petite bourgeoisie.' There has been significant global middle-class growth over time. In February 2009, ''The Economist'' asserted that over half of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Finance
International finance (also referred to as international monetary economics or international macroeconomics) is the branch of financial economics broadly concerned with monetary and macroeconomic interrelations between two or more countries. International finance examines the dynamics of the global financial system, international monetary systems, balance of payments, exchange rates, foreign direct investment, and how these topics relate to international trade. Sometimes referred to as multinational finance, international finance is additionally concerned with matters of international financial management. Investors and multinational corporations must assess and manage international risks such as political risk and foreign exchange risk, including transaction exposure, economic exposure, and translation exposure. Some examples of key concepts within international finance are the Mundell–Fleming model, the optimum currency area theory, purchasing power parity, interest rate parit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Curse
The resource curse, also known as the paradox of plenty or the poverty paradox, is the phenomenon of countries with an abundance of natural resources (such as fossil fuels and certain minerals) having less economic growth, less democracy, or worse development outcomes than countries with fewer natural resources. There are many theories and much academic debate about the reasons for, and exceptions to, these adverse outcomes. Most experts believe the resource curse is not universal or inevitable, but affects certain types of countries or regions under certain conditions. Thesis As far back as 1711 ''The Spectator'' wrote "It is generally observed, that in countries of the greatest plenty there is the poorest living". The idea that resources might be more of an economic curse than a blessing emerged in debates in the 1950s and 1960s about the economic problems of low and middle-income countries. In 1993 Richard Auty first used the term ''resource curse'' to describe how countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, which is used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. A country scores a higher level of HDI when the lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office. The 2010 Human Development Report introduced an Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI). While the simple HDI remains useful, it stated that "the IHDI is the actual level of human development (accounting for inequality), while the HDI can be viewed as an index of 'potential' human development (or the maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
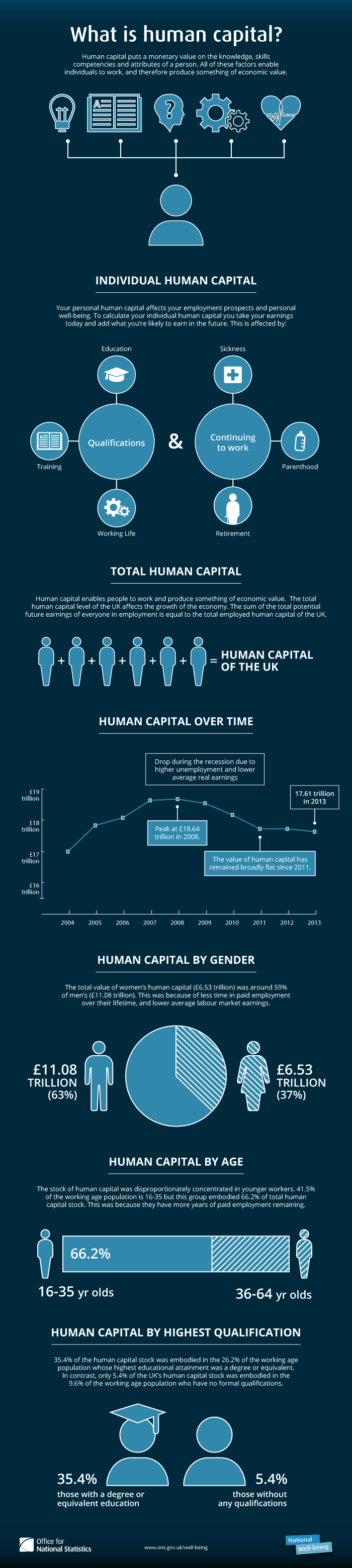
Human Capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons, an economist at MIT, and Michael Waldman, an economist at Cornell University. The concept emphasize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-sector Model
The Dual Sector model, or the Lewis model, is a model in Developmental economics that explains the growth of a developing economy in terms of a labour transition between two sectors, a traditional agricultural sector and a modern industrial sector. History Initially enumerated in an article entitled "Economic Development with Unlimited Supplies of Labor" written in 1954 by Sir Arthur Lewis, the model itself was named in Lewis's honor. First published in ''The Manchester School'' in May 1954, the article and the subsequent model were instrumental in laying the foundation for the field of Developmental economics. The article itself has been characterized by some as the most influential contribution to the establishment of the discipline. Theory The "Dual Sector Model" is a theory of development in which surplus labor from traditional agricultural sector is transferred to the modern industrial sector whose growth over time absorbs the surplus labor, promotes industrialization and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crony Capitalism
Crony capitalism, sometimes called cronyism, is an economic system in which businesses thrive not as a result of free enterprise, but rather as a return on money amassed through collusion between a business class and the political class. This is often achieved by the manipulation of relationships with state power by business interests rather than unfettered competition in obtaining permits, government grants, tax breaks, or other forms of state intervention over resources where business interests exercise undue influence over the state's deployment of public goods, for example, mining concessions for primary commodities or contracts for public works. Money is then made not merely by making a profit in the market, but through profiteering by rent seeking using this monopoly or oligopoly. Entrepreneurship and innovative practices which seek to reward risk are stifled since the value-added is little by crony businesses, as hardly anything of significant value is created by them, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity realizing or redistributing value". Others have different definitions; a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies. Innovation often takes place through the development of more-effective products, processes, services, technologies, art works or business models that innovators make available to markets, governments and society. Innovation is related to, but not the same as, invention: innovation is more apt to involve the practical implementation of an invention (i.e. new / improved ability) to make a meaningful impact in a market or society, and not all innovations require a new invention. Technical innovation often manifests itself via the engineering process when the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production process, i.e. output per unit of input, typically over a specific period of time. The most common example is the (aggregate) labour productivity measure, one example of which is GDP per worker. There are many different definitions of productivity (including those that are not defined as ratios of output to input) and the choice among them depends on the purpose of the productivity measurement and/or data availability. The key source of difference between various productivity measures is also usually related (directly or indirectly) to how the outputs and the inputs are aggregated to obtain such a ratio-type measure of productivity. Productivity is a crucial factor in the production performance of firms and nations. Increasing national producti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheap Labor
Global labor arbitrage is an economic phenomenon where, as a result of the removal of or disintegration of barriers to international trade, jobs move to nations where labor and the cost of doing business (such as environmental regulations) is inexpensive and/or impoverished labor moves to nations with higher paying jobs.The "global labor arbitrage" phenomenon has been described by economist Stephen S. Roach. See Mike Whitney"Labor arbitrage," ''Entrepreneur'', June 2006. Two common barriers to international trade are tariffs (politically imposed) and the costs of transporting goods across oceans. With the advent of the Internet, the decrease of the costs of telecommunications, and the possibility of near-instantaneous document transfer, the barriers to the trade of intellectual work product, which is essentially, any kind of work that can be performed on a computer (such as computer programming) or that makes use of a college education, have been greatly reduced. Often, a prospe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of . The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Taoyuan, Taichung, Tainan, and Kaohsiung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world. Taiwan has been settled for at least 25,000 years. Ancestors of Taiwanese indigenous peoples settled the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |