|
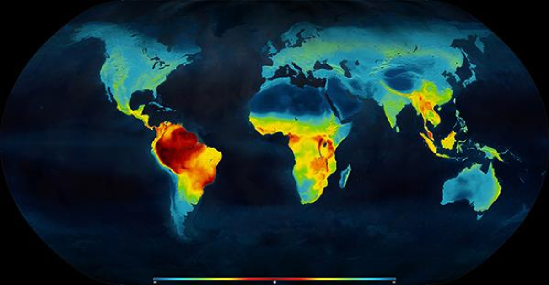
Microbial Biogeography
Microbial biogeography is a subset of biogeography, a field that concerns the distribution of organisms across space and time. Although biogeography traditionally focused on plants and larger animals, recent studies have broadened this field to include distribution patterns of microorganisms. This extension of biogeography to smaller scales—known as "microbial biogeography"—is enabled by ongoing advances in genetic technologies. The aim of microbial biogeography is to reveal where microorganisms live, at what abundance, and why. Microbial biogeography can therefore provide insight into the underlying mechanisms that generate and hinder biodiversity. Microbial biogeography also enables predictions of where certain organisms can survive and how they respond to changing environments, making it applicable to several other fields such as climate change research. History Schewiakoff (1893) theorized about the cosmopolitan habitat of free-living protozoans. In 1934, Lourens Baas Beck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the species distribution, distribution of species and ecosystems in geography, geographic space and through evolutionary history of life, geological time. Organisms and biological community (ecology), communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, allopatric speciation, isolation and habitat species-area curve, area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms. Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable Natural environment, environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, taxonomy (bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupancy–abundance Relationship
In ecology, the occupancy–abundance (O–A) relationship is the relationship between the Abundance (ecology), abundance of species and the size of their Range (biology), ranges within a region. This relationship is perhaps one of the most well-documented relationships in macroecology, and applies both intra- and interspecifically (within and among species). In most cases, the O–A relationship is a positive relationship. Although an O–A relationship would be expected, given that a species colonizing a region must pass through the origin (zero abundance, zero occupancy) and could reach some theoretical maximum abundance and distribution (that is, occupancy and abundance can be expected to co-vary), the relationship described here is somewhat more substantial, in that observed changes in range are associated with greater-than-proportional changes in abundance. Although this relationship appears to be pervasive (e.g. Gaston 1996 and references therein), and has important implicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spores
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. They were thought to have appeared as early as the mid-late Ordovician period as an adaptation of early land plants. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. In some rare cases, a diploid spore is also produced in some algae, or fungi. Under favourable conditions, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteoroids
A meteoroid ( ) is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space. Meteoroids are distinguished as objects significantly smaller than ''asteroids'', ranging in size from grains to objects up to wide. Objects smaller than meteoroids are classified as ''micrometeoroids'' or ''space dust''. Many are fragments from comets or asteroids, whereas others are impact event, collision impact space debris, debris ejected from bodies such as the Moon or Mars. The visible passage of a meteoroid, comet, or asteroid atmospheric entry, entering Earth's atmosphere is called a meteor, and a series of many meteors appearing seconds or minutes apart and appearing to originate from the same fixed point in the sky is called a meteor shower. An estimated 25 million meteoroids, micrometeoroids and other space debris enter Earth's atmosphere each day, which results in an estimated 15,000 tonnes of that material entering the atmosphere each year. A ''meteorite'' is the remains of a meteoroid that has surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroids
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). Asteroids are rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere, and are broadly classified into C-type asteroid, C-type (carbonaceous), M-type asteroid, M-type (metallic), or S-type asteroid, S-type (silicaceous). The size and shape of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from small rubble piles under a kilometer across to Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres, a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter. A body is classified as a comet, not an asteroid, if it shows a coma (tail) when warmed by solar radiation, although recent observations suggest a continuum between these types of bodies. Of the roughly one million known asteroids, the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 astronomical unit, AU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comets
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or coma surrounding the nucleus, and sometimes a tail of gas and dust gas blown out from the coma. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the outstreaming solar wind plasma acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently close and bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and can subtend an arc of up to 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religions. Comets usually have highly eccentric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panspermia
Panspermia () is the hypothesis that life exists throughout the universe, distributed by space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, and planetoids, as well as by spacecraft carrying unintended contamination by microorganisms,Forward planetary contamination like '' Tersicoccus phoenicis'', that has shown resistance to methods usually used in spacecraft assembly clean rooms: known as directed panspermia. The theory argues that life did not originate on Earth, but instead evolved somewhere else and seeded life as we know it. Panspermia comes in many forms, such as radiopanspermia, lithopanspermia, and directed panspermia. Regardless of its form, the theories generally propose that microbes able to survive in outer space (such as certain types of bacteria or plant spores) can become trapped in debris ejected into space after collisions between planets and small solar system bodies that harbor life. This debris containing the lifeforms is then transported by meteors between bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Resilience
In ecology, resilience is the capacity of an ecosystem to respond to a perturbation or Disturbance (ecology), disturbance by resisting damage and subsequently recovering. Such perturbations and disturbances can include stochastic events such as fires, flooding, windstorms, insect population explosions, and human activities such as deforestation, fracking of the ground for oil extraction, pesticide sprayed in soil, and the Introduced species, introduction of exotic plant or animal species. Disturbances of sufficient Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or duration can profoundly affect an ecosystem and may force an ecosystem to reach a Ecological threshold, threshold beyond which a different regime of processes and structures predominates. When such thresholds are associated with a critical or bifurcation theory, bifurcation point, these regime shifts may also be referred to as critical transitions. Human activities that adversely affect ecological resilience such as loss of biodiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitudinal Gradients In Species Diversity
Species richness, or biodiversity, increases from the poles to the tropics for a wide variety of terrestrial and marine organisms, often referred to as the latitudinal diversity gradient. The latitudinal diversity gradient is one of the most widely recognized patterns in ecology. It has been observed to varying degrees in Earth's past. A parallel trend has been found with elevation ( elevational diversity gradient), though this is less well-studied. Explaining the latitudinal diversity gradient has been called one of the great contemporary challenges of biogeography and macroecology (Willig et al. 2003, Pimm and Brown 2004, Cardillo et al. 2005). The question "What determines patterns of species diversity?" was among the 25 key research themes for the future identified in 125th Anniversary issue of ''Science'' (July 2005). There is a lack of consensus among ecologists about the mechanisms underlying the pattern, and many hypotheses have been proposed and debated. A recent re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere Of Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by gravity of Earth, Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar irradiance, solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between daytime, day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the atmospheric chemistry, chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolution, evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |