|
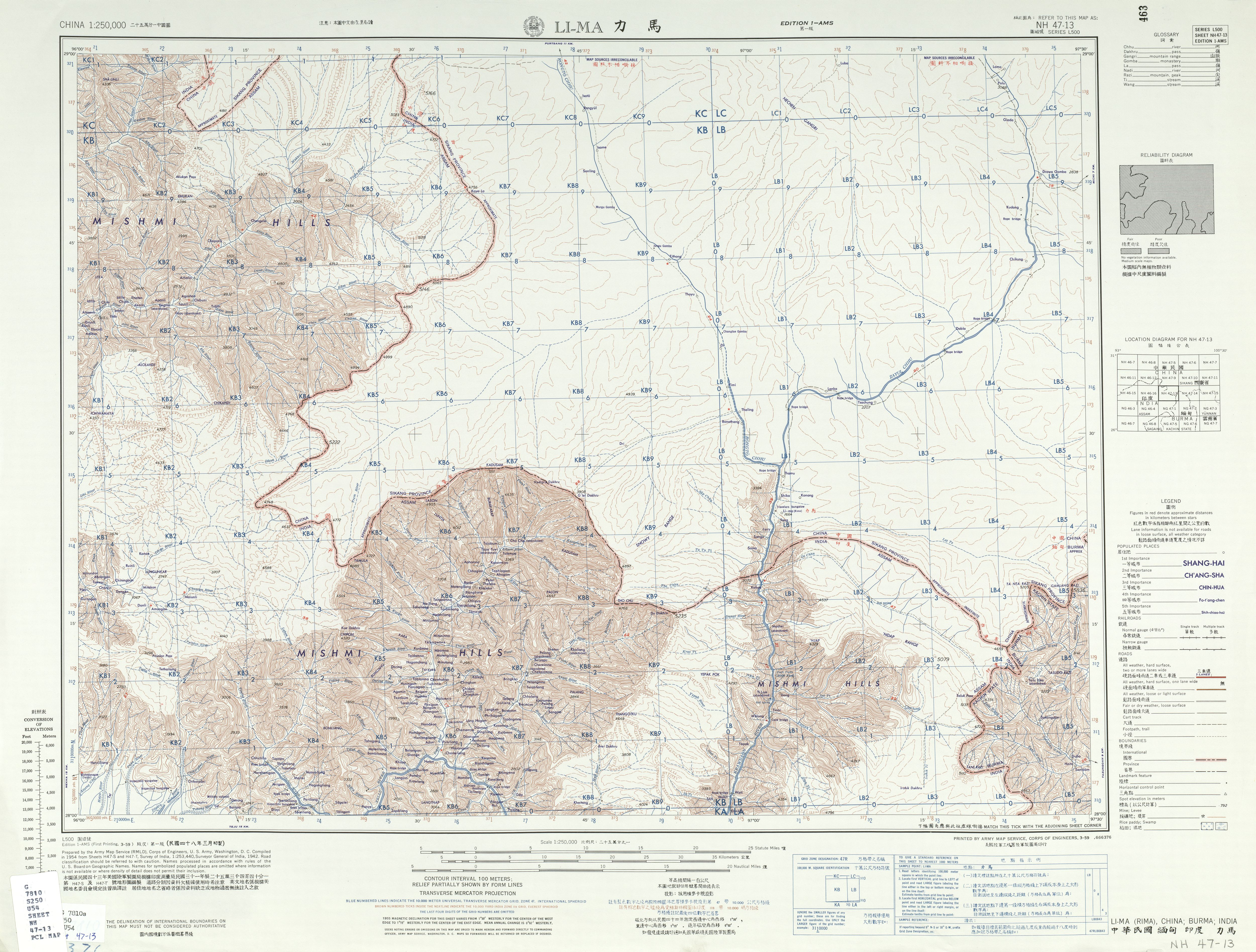
Meyor Language
Zahkring (also Eastern Mishmi or Zaiwa; known as Meyor in India and Zha (Zhahua 扎话) in China) is a language of Arunachal Pradesh and 3 villages in Tibet. Classification Zakhring has been classified as a Midzuish language. Blench and Post (2011) consider Zakhring to be an East Bodish language that has been influenced by Midzu (which they classify as a language isolate) or other divergent languages of the region. In 2015, Blench suggests that Zakhring may be a language isolate. Blench argues that Zakhring had borrowed heavily from Midzu and Tibetic, and then later borrowed from Naga languages and Jingpho as well. Scott DeLancey (2015) considers Meyor to be part of a wider Central Tibeto-Burman group. Names Li and Jiang (2001) reports that the Zakhring have no actual autonym, but are referred to by the neighboring Taraon, Kaman language, Idu, and Tibetan peoples by various names. *' (Taraon exonym) *' (Kaman exonym) *' (Tibetan exonym) *' (Idu exonym; the Idu are locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arunachal
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed border with China in the north at the McMahon Line. Itanagar is the state capital of Arunachal Pradesh. Arunachal Pradesh is the largest of the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by area. Arunachal Pradesh shares a 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region. As of the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population of 1,382,611 and an area of . It is an ethnically diverse state, with predominantly Monpa people in the west, Tani people in the centre, Mishmi and Tai people in the east, and Naga people in the southeast of the state. About 26 major tribes and 100 sub-tribes live in the state. The main tribes of the state are Adi, Nys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Tibeto-Burman Languages
Central Tibeto-Burman or Central Trans-Himalayan is a proposed branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family proposed by Scott DeLancey (2015) on the basis of shared morphological evidence. DeLancey (2018)DeLancey, Scott (2018). ''Internal and external history of the Central branch of Tibeto-Burman/Trans-Himalayan''. Paper presented at the 28th Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society, held May 17-19, 2018 in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. considers Central Tibeto-Burman to be a linkage rather than a branch with a clearly nested internal structure. DeLancey's Central Tibeto-Burman group includes many languages in Matisoff's (2015: 1123-1127)Matisoff, James A. 2015''The Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus'' Berkeley: University of California.PDF proposed Northeast Indian areal group, which includes Tani, Deng (Digaro), “ Kuki-Chin–Naga”, Meithei, Mikir, Mru, and Sal. Languages DeLancey considers there to be strong morphological evidence for the follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miju Languages
Miju (Midžu, Miju, Mijhu), Kaman–Meyor, Midžuish, Southern Mishmi, or Geman languages are a small proposed family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken by the Kaman (Miju Mishmi) people of southeastern Tibet and Arunachal Pradesh. The languages are Kaman (Midzu/Miju) and Zakhring (Meyor). Although Zakhring appears to be Sino-Tibetan, Kaman may be more divergent. Blench and Post (2011) believe that Zakhring is an East Bodish language that has been influenced by Midzu or other divergent languages of the region, whereas Kaman may be a language isolate. Blench (2015) suggests that Meyor (Zakhring) and Kman may each be language isolates.Blench, Roger. 2015The classification of Meyor (Zakhring) m.s. Blench argues that the lexical similarities between Kman and Zakhring are borrowings, and that Zakhring had borrowed heavily from Kman and Tibetic, and then later borrowed from Naga languages and Jingpho as well. Regardless, they are not closely related to the Northern Mishmi also know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anjaw District
Anjaw District (Pron:/ˈændʒɔ:/) (Burmese : အန်််ကျော) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in north-east India. It was created district in 2004, by splitting off from the Lohit district under the Arunachal Pradesh Re-organization of Districts Amendment Act. The district borders China on the north. Hawai, at an altitude of 1296 m above sea level, is the district headquarters, located on the banks of the Lohit River, a tributary of the Brahmaputra River. It is the easternmost district in India. The furthest villages towards the border with China are Dong, Walong, Kibithu and Kaho. Anjaw is the second least populous district in India (out of 640). History During the 1962 war, parts of Anjaw were briefly occupied by China. Being a disputed border region, Indian military has always been present in the Anjaw district. During the 2020 China–India skirmishes additional troops were deployed to the region. Geography Rivers T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Tamang, Qiang, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui settlers. Since 1951, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region, and other portions in the Qinghai and Sichuan provinces. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibetan Empire extended far beyond the Tibetan Plateau, from Central Asian's Tarim Basin and the Pamirs in the west to Yunnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomi County
Bomi is a county in the northwestern portion of the West African nation of Liberia. The county was established in 1984. The county's area is . Bomi is one of 15 counties that comprise the first-level of administrative division in the nation. Tubmanburg serves as the county's capital. The County has four administrive districts. Bomi is bordered on the northwest by Grand Cape Mount County, on the northeast by Gbarpolu and Bong Counties, on the southeast by Montserrado County and on the southwest by the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2008 Liberian census, Bomi had a population of 84,119, making it the nation's eleventh most populous county. History From 1822 until the Liberian Declaration of Independence from the American Colonization Society on July 26, 1847 some 3,198 freed slaves and slaves from the Lesser Antilles, who had escaped from their slaveholders or born free left the Caribbean islands and came to Liberia with the help and support from the American Colonization S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idu Language
The Idu Mishmi language () is a small language spoken by the Mishmi people in Dibang Valley district, Lower Dibang Valley district, Lohit district, East Siang district, Upper Siang district of the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh and in Zayü County of the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. There were 8569 speakers in India in 1981 and 7000 speakers in China in 1994. It is considered an endangered language. Locations In China, Idu Mishmi is spoken in Xiba village 西巴村, which has just over 40 residents and is located at the foot of Xikong Mountain 习孔山. Xiba village is located 10 kilometers from the nearest administrative center, namely Migu village 米古村 (Jiang 2005:4). The Idu live in the Danba River 丹巴江 and E River 额河 watersheds in Zayü County, Tibet. They are officially classified by the Chinese government as ethnic Lhoba people. In India, the Idu are found in Arunachal Pradesh. Script The Idu Mishmi people did not usually have a script of their ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taraon Language
Digaro, also Taraon, Tawra, or Darang, is a Digarish language of northeastern Arunachal Pradesh, India and Zayü County, Tibet, China. Names According to Jiang, et al. (2013:2), their autonym is ' or ', and alternatively ' (Deng 登, 僜) in China. The Kaman ( Miju) call them ', the Idu call them ', and the Assamese call them ''Digaro Mishmi''. Distribution India In Arunachal Pradesh, India, Digaro Mishmi is spoken in Hayuliang, Changlagam, and Goiliang circles in the Amjaw district (''Ethnologue''). It is also spoken in Dibang Valley district and Assam Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur .... China Jiang, et al. (2013:2) reports that in Zayü County, Tibet, Taraon is spoken in the following villages. *E River watershed 额河流域 **Jiyu village 吉玉村 (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott DeLancey
Scott DeLancey (born 1949) is an American linguist from the University of Oregon. His work focuses on typology and historical linguistics of Tibeto-Burman languages as well as North American indigenous languages such as the Penutian family, particularly the Klamath. His research is known for its diversity of its thematic and theoretical reach. He is well known for having developed the concept of mirative, for promoting the study of comparative Penutian and for being a vocal proponent of the idea that a system of agreement should be reconstructed in proto-Tibeto-Burman. Sino-Tibetan linguistics DeLancey is currently undertaking field research on several Tibeto-Burman languages of Northeast India. He considers Sinitic to as a typologically mainland southeast Asian language group. The Chinese mainland consensus on Sino-Tibetan theory holds that the Sino-Tibetan language family descends from a single linguistic ancestor that accounts for shared features of monosyllabism, tonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)